
Linked lists are used to store data in discrete memory locations. Nodes containing data items are linked using pointers. Each node consists of two fields. The first field is used to store the data and the second field contains the link to the next node.
To find the middle element of the linked list, the brute force technique is to find the length of the linked list by iterating through the entire linked list until NULL is encountered, then dividing the length by 2 to get the middle element of the linked list's index. After getting the index of the intermediate element, iterate the linked list again from the beginning and stop when the required index is reached. The data item at this index gives the intermediate element.
Take a variable named "temp" to point to HEAD and initialize "len" to 0
Use temp to iterate through the linked list until NULL is reached, and increment "len" by 1 at each node.
After obtaining the length of the linked list, initialize temp to HEAD again. Iterate through the linked list until len//2.
We will use two pointers to traverse the linked list. One is called "slow pointer" and the other is called "fast pointer".
The fast pointer moves twice as fast as the slow pointer.
When the fast pointer reaches the end of the linked list, the slow pointer will be at the middle node.
Therefore, we can directly print the contents of the intermediate nodes.
Consider the following list of links. The middle element is 3.
The fast pointer has reached the last node in the linked list, and the slow pointer now points to node 3. Therefore, 3 is the middle element of the given linked list. Now, consider 6 nodes.
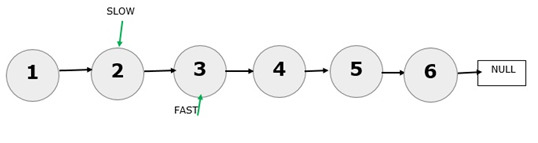
The fast pointer has reached NULL, and the slow pointer points to the 4th node. Therefore, the middle element is 4.
Make "slow" and "fast" point to the HEAD of the linked list.
Increase the fast pointer by 2 and the slow pointer by 1 until the fast pointer and fast.next are not equal to NULL
Print the value at the slow pointer.
The time complexity is O(n).
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_the_beginning(self, newVal):
newNode = Node(newVal)
newNode.next = self.head
self.head = newNode
def print_middle_element(self):
slow=self.head
fast=self.head
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
slow=slow.next #slow pointer moves one node
fast=fast.next.next #fast pointer moves two nodes
print("\n\nthe middle element is ",slow.val)
def Print_the_LL(self):
temp = self.head
if(temp != None):
print("The linked list elements are:", end=" ")
while (temp != None):
print(temp.val, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
else:
print("The list is empty.")
newList = LinkedList()
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(5)
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(4)
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(3)
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(2)
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(1)
newList.Print_the_LL()
newList.print_middle_element()
The linked list elements are: 1 2 3 4 5 the middle element is 3
The above is the detailed content of Python program to get the middle element of a linked list, completed in a single iteration. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to implement linked list in go
How to implement linked list in go
 How to solve the invalid mysql identifier error
How to solve the invalid mysql identifier error
 How to find the greatest common divisor in C language
How to find the greatest common divisor in C language
 What does bean refer to in java?
What does bean refer to in java?
 How to check for plagiarism on CNKI Detailed steps for checking for plagiarism on CNKI
How to check for plagiarism on CNKI Detailed steps for checking for plagiarism on CNKI
 vlookup matches two columns of data
vlookup matches two columns of data
 What is Avalanche
What is Avalanche
 HTML image code collection
HTML image code collection




