
Sort algorithm is an algorithm that arranges the components of a list in a specific order. The most commonly used orders are numerical order and dictionary order.
Cardix Sorting is a non-comparative sorting algorithm. The radix sort algorithm is the preferred algorithm for unsorted lists.
It sorts elements by initially grouping individual numbers of the same place value. The idea of radix sort is to sort bit by bit from least significant digit (LSD) to most significant digit (MSD) in increasing/decreasing order. Radix sort is a small method that is used many times when sorting very large lists of names alphabetically. Specifically, the name list was initially sorted according to the first letter of each name, i.e., the names were organized into twenty-six categories.
Let us review the illustration below to get a clear understanding of how the radix sort algorithm works. Obviously, the number of passes/iterations depends on the size of the highest individual number.
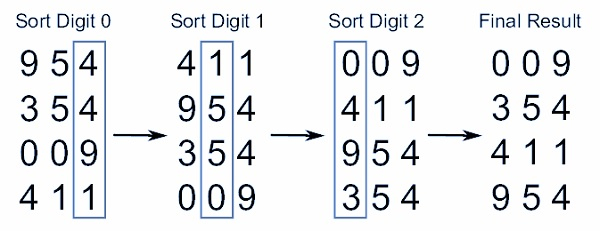
In the above example, the main column is entered. The remaining columns show A sequentially sorted list of numerical positions of increasing importance.
Complexity analysis of radix sort O(m.n).
However, if we look at both values, the size of the keys is relatively small compared to the number of keys. For example, if we had a six-digit key, we could have 1,000,000 completely different records.
Here we tend to see that the size of the key does not matter and the algorithm is linear quality O(n)
Radix_sort (list, n) shift = 1 for loop = 1 to keysize do for entry = 1 to n do bucketnumber = (list[entry].key / shift) mod 10 append (bucket[bucketnumber], list[entry]) list = combinebuckets() shift = shift * 10
This is a C program that implements radix sorting.
Live demonstration
#include<stdio.h>
int get_max (int a[], int n){
int max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] > max)
max = a[i];
return max;
}
void radix_sort (int a[], int n){
int bucket[10][10], bucket_cnt[10];
int i, j, k, r, NOP = 0, divisor = 1, lar, pass;
lar = get_max (a, n);
while (lar > 0){
NOP++;
lar /= 10;
}
for (pass = 0; pass < NOP; pass++){
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){
bucket_cnt[i] = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
r = (a[i] / divisor) % 10;
bucket[r][bucket_cnt[r]] = a[i];
bucket_cnt[r] += 1;
}
i = 0;
for (k = 0; k < 10; k++){
for (j = 0; j < bucket_cnt[k]; j++){
a[i] = bucket[k][j];
i++;
}
}
divisor *= 10;
printf ("After pass %d : ", pass + 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf ("%d ", a[i]);
printf ("</p><p>");
}
}
int main (){
int i, n, a[10];
printf ("Enter the number of items to be sorted: ");
scanf ("%d", &n);
printf ("Enter items: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf ("%d", &a[i]);
}
radix_sort (a, n);
printf ("Sorted items : ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf ("%d ", a[i]);
printf ("</p><p>");
return 0;
}Enter number of items to be sorted 6 Enter items:567 789 121 212 563 562 After pass 1 : 121 212 562 563 567 789 After pass 2 : 212 121 562 563 567 789 After pass 3 : 121 212 562 563 567 789 Sorted items : 121 212 562 563 567 789
The above is the detailed content of C program for radix sort. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




