How to check what the process is doing in linux
How to check what the process is doing in Linux: 1. ps command, which can list all processes of the current user; 2. top command, which can display the system's process status in real time; 3. htop command, which is an improvement of top version, which can provide more interactive functions; 4. pstree command, which can display the relationship between processes in a tree structure; 5. lsof command, which can display open files and network connections in the current system.

The operating environment of this article: Linux 5.18.14 system, DELL G3 computer.
1. In the Linux system, you can use the following command to view the running processes in detail:
1. ps command: The ps command can list all the processes of the current user. process. Commonly used parameters include -a, -u, -x, etc. For example, use the ps -aux command to list the detailed information of all processes, including process ID, parent process ID, user, CPU usage, memory usage, etc.
2. top command: The top command can display the process status of the system in real time. The process list can be refreshed in real time via an interactive interface and sorted in various ways. You can use the top -c command to display the complete command line of a process.
3. htop command: htop is an improved version of top, which can provide more interactive functions and can be operated using the mouse. htop can also display detailed information about processes.
4. pstree command: The pstree command can display the relationship between processes in a tree structure. You can use the pstree -p command to display the PID of the process.
5. lsof command: The lsof command can display open files and network connections in the current system. Use the -l parameter to display detailed information about the process, including the PID of the process and the user of the process.
In short, the above commands can be used to view running processes, and different commands are suitable for different occasions. Just choose the appropriate command according to your needs.
2. The meaning of each process status
1. R: Running
means that the process is running or waiting in the allow queue.
2. S: Interrupt
Indicates that the process is sleeping. When a certain condition is formed or a signal is received, it will leave the interrupt state.
3. D: Uninterruptible
Indicates that the process does not respond to system asynchronous signals and cannot be interrupted even with the kill command.
4. Z: Zombie
Indicates that the process has been terminated, but the process descriptor still exists until the parent process calls the wait(4) system function and releases the process.
5. T: Stop
means that the process stops running after receiving the stop signal.
3. Status
[root@mycentos ~]# ps aux USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.0 0.1 191120 3588 ? Ss 2021 25:59 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --system --deserialize 19 root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2021 0:00 [kthreadd] root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 2021 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2021 1:51 [ksoftirqd/0] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2021 0:00 [migration/0] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2021 0:00 [rcu_bh] 1、USER:进程的所有者 2、PID: 进程ID号 3、%CPU:运算器占用率 4、%MEM:内存占用率 5、VSZ: 虚拟内存使用量,单位KB 6、RSS: 占用的固定内存量,单位KB 7、TTY: 所在终端 8、STAT:进程状态 9、START: 进程被启动的时间 10、TIME: 实际使用CPU的时间 11、COMMEND: 命令名称和参数
4. The top command is used to dynamically monitor process activity and system load information.
The top command is quite powerful and can dynamically view the system operation and maintenance status.
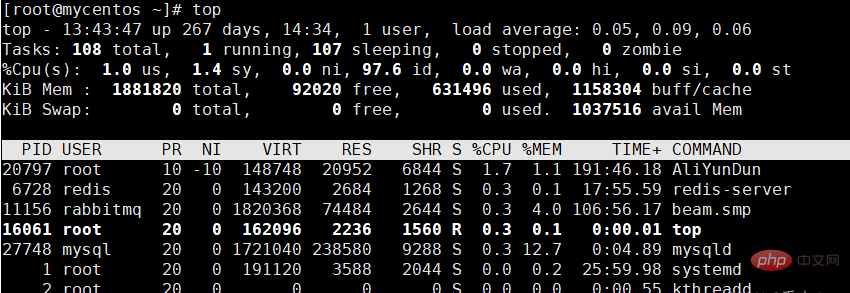
1. The meaning of each line of top
[root@mycentos ~]# top
top - 13:45:38 up 267 days, 14:36, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.06, 0.05
Tasks: 107 total, 1 running, 106 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 1.3 us, 1.3 sy, 0.0 ni, 97.3 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 1881820 total, 92160 free, 631276 used, 1158384 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 0 total, 0 free, 0 used. 1037740 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
20797 root 10 -10 148748 20952 6844 S 2.0 1.1 191:48.06 AliYunDun
6728 redis 20 0 143200 2684 1268 S 0.3 0.1 17:55.69 redis-server
11156 rabbitmq 20 0 1820368 74484 2644 S 0.3 4.0 106:56.41 beam.smp
29954 polkitd 20 0 52812 2340 700 S 0.3 0.1 40:13.73 redis-server
1 root 20 0 191120 3588 2044 S 0.0 0.2 26:00.01 systemd
备注:
top 命令执行结果的前5行为系统整体的统计信息
1、第1行:系统时间、运行时间、登录终端数量、系统负载(3个数值分别表示:
1分钟,5分钟,15分钟内的平均负载值,数值越小意味着负载越低)。
2、第2行:进程总数、运行中的进程数、睡眠中的进程数、停止的进程数、僵死的进程数。
3、第3行:用户占用资源百分比、系统内核占用资源百分比、改变过优先级的进程资源百分比、
空闲的资源百分比。(这一行中的数据均为 cpu 数据并以百分比格式显示,
比如:"97.3 id"表示有 97.3%的CPU处理器资源处于空闲)
4、第4行:物理内存总量、内存空闲量、内存使用量、作为内核缓存的内存量。
5、第5行:虚拟内存总量、虚拟内存空闲量、虚拟内存使用量、已被提前加载的内存量。5. View the process ID of a service
[root@mycentos ~]# pidof mysqld
27748
备注:
pidof 服务名称
pidof 命令用于查询某个指定服务进程的PID 值。 每个进程的进程号(PID)是唯一的,
因此可以通过PID来区分不同的进程。The above is the detailed content of How to check what the process is doing in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Linux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.
 How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.
 Using Docker with Linux: A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Using Docker with Linux: A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Using Docker on Linux can improve development and deployment efficiency. 1. Install Docker: Use scripts to install Docker on Ubuntu. 2. Verify the installation: Run sudodockerrunhello-world. 3. Basic usage: Create an Nginx container dockerrun-namemy-nginx-p8080:80-dnginx. 4. Advanced usage: Create a custom image, build and run using Dockerfile. 5. Optimization and Best Practices: Follow best practices for writing Dockerfiles using multi-stage builds and DockerCompose.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
The steps to start an Oracle listener are as follows: Check the listener status (using the lsnrctl status command) For Windows, start the "TNS Listener" service in Oracle Services Manager For Linux and Unix, use the lsnrctl start command to start the listener run the lsnrctl status command to verify that the listener is started
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status
 How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
This article introduces two methods of configuring a recycling bin in a Debian system: a graphical interface and a command line. Method 1: Use the Nautilus graphical interface to open the file manager: Find and start the Nautilus file manager (usually called "File") in the desktop or application menu. Find the Recycle Bin: Look for the Recycle Bin folder in the left navigation bar. If it is not found, try clicking "Other Location" or "Computer" to search. Configure Recycle Bin properties: Right-click "Recycle Bin" and select "Properties". In the Properties window, you can adjust the following settings: Maximum Size: Limit the disk space available in the Recycle Bin. Retention time: Set the preservation before the file is automatically deleted in the recycling bin




