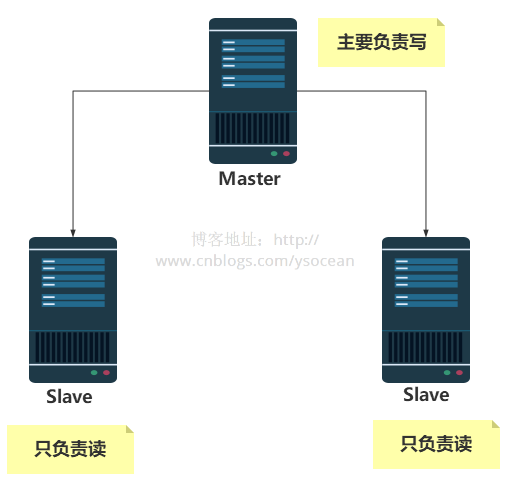
Introducing Redis earlier, we all operate on a server, which means that reading, writing and backup operations are all performed on a Redis server. As the number of project visits increases, the Redis server Operations are also becoming more frequent. Although Redis is very fast in reading and writing, it will also cause a certain delay to a certain extent. In order to solve the problem of large access volume, one method usually adopted is the master-slave architecture Master/ Slave and Master are mainly for writing, and Slave is mainly for reading. After the Master node is updated, it will automatically synchronize to the slave Slave node according to the configuration.
Next we will introduce how to build a master-slave architecture.
ps: Here I am simulating multiple Redis servers on one machine. Compared with the actual production environment, the basic configuration is the same, only the IP address and port number change.
First, copy the redis.conf configuration file into three copies and simulate three Redis servers by modifying the ports.
Then we modify these three redis.conf files respectively.
①、Modify daemonize yes
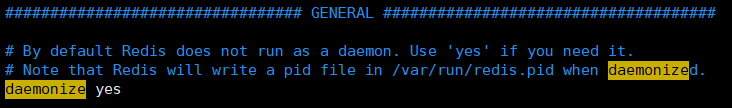
Indicates that the specified Redis will be started as a daemon process (background startup)
②. Configure the PID file path pidfile
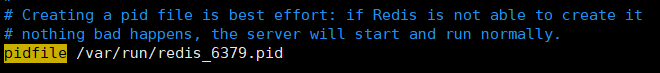
Indicates that when redis is running as a daemon process, it will write the pid to /var/redis by default In the /run/redis_6379.pid file
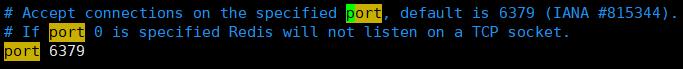
③、Configure port port
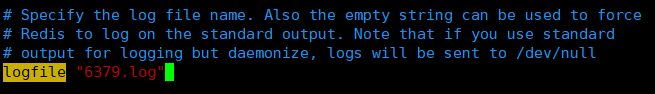
④、Configure log file name
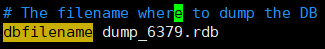
⑤、Configure the rdb file name
Change 6380redis.conf, 6381Redis.conf is configured once, and the configuration is complete.
Next we start these three services respectively.
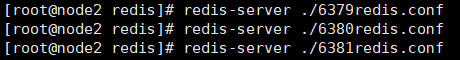
Use the command to check whether Redis is started:
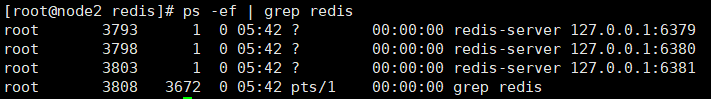
Next, enter the three Redis clients through the following commands Terminal:
1 2 3 |
|
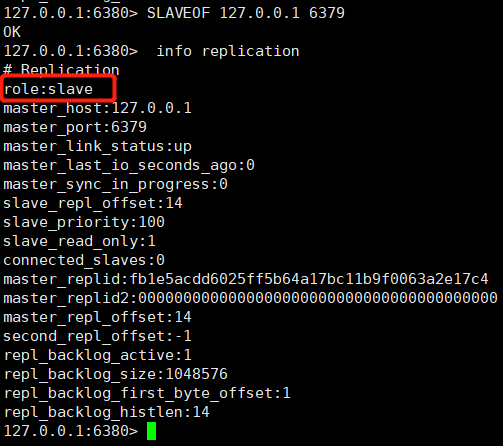
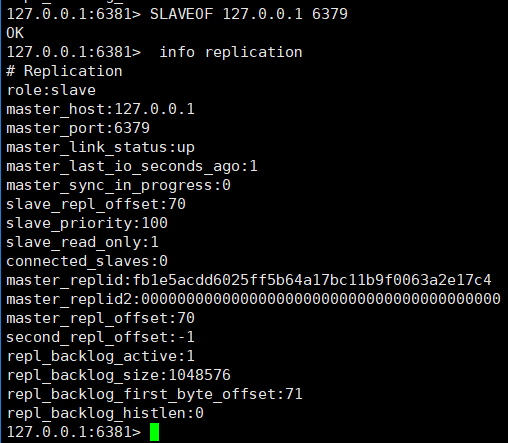
①、View the node role through the info replication command
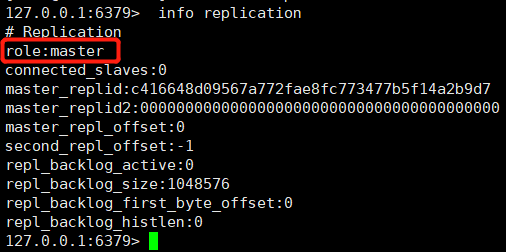
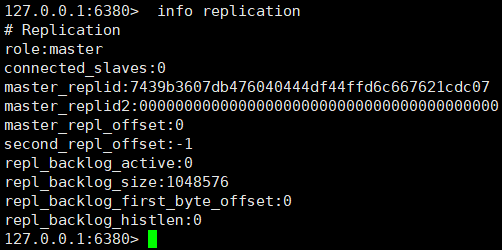
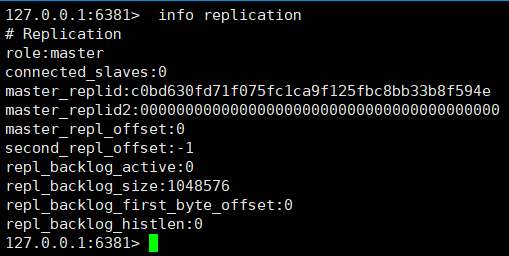
We found that these three nodes all play the role of Master. How to convert nodes 6380 and 6381 to slave node role?
②. Select port 6380 and port 6381 and execute the command: SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6379
Let’s look at the 6379 node information:
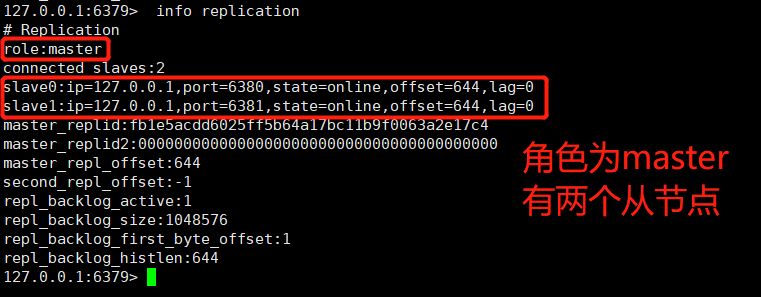
Once the service is restarted, the master-slave relationship previously set through the command will become invalid. This relationship can be permanently saved by configuring the redis.conf file.
①.Incremental replication
The master node executes the set k1 v1 command. Can the slave node get k1? ?
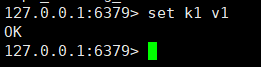
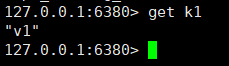
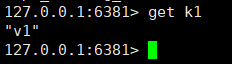
It can be seen from the picture above that it can be obtained.
②、Full copy
By executing SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6379, if there are still some keys before the master node 6379, then after executing the command, the slave node will copy the previous Have you copied all the information?
The answer is yes, I won’t post the test results here.
③. Master-slave read and write separation
Can the master node execute write commands, and can the slave node execute write commands?
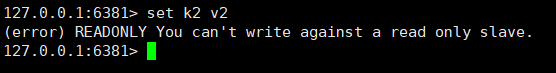
The reason here is the configuration of slave-read-only in the configuration file 6381redis.conf

If After we change it to no, it is possible to execute the write command.
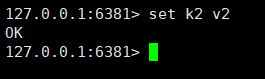
But the data of the slave node write command cannot be obtained from the slave node or the master node.
④. Master node downtime
If the master node Master hangs up, will the roles of the two slave nodes change?
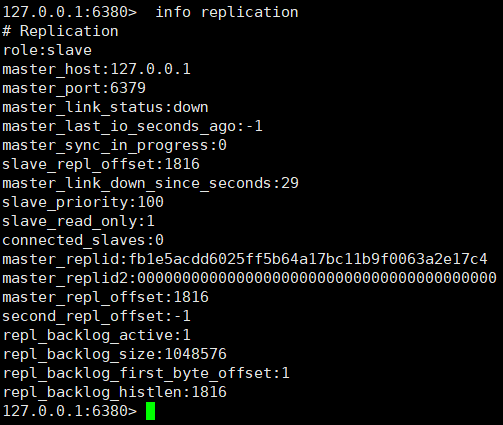
It can be seen from the above figure that after the master node Master hangs up, the role of the slave node will not change.
⑤. Recovery after the master node goes down
After the master node Master hangs up, start the host Master immediately. Does the master node still play the role of Master?
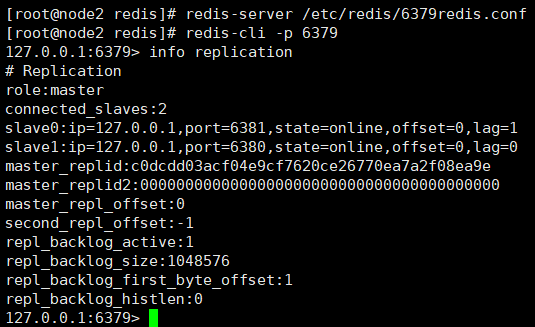
That is to say, after the master node hangs up, it restarts and resumes its role as the master node.
Through the previous configuration, there is only one master node Master. Once the master node hangs up, the slave node cannot take on the task of the master node, and the entire system cannot run. The sentinel mode was born from this, because the slave node can automatically take over the responsibilities of the master node, solving the problem of master node downtime.
The sentry mode is to monitor whether redis is running well as expected from time to time (at least to ensure that the master node exists). If there is a problem with a host, the sentry will automatically remove a slave machine under the host. Set it as a new host and let other slaves establish a master-slave relationship with the new host.
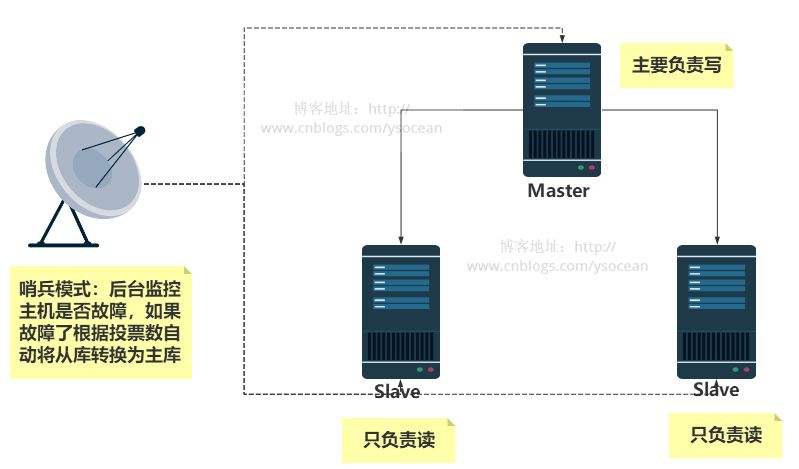
Steps to build sentinel mode:
①Create a new sentinel.conf file in the configuration file directory. The name must not be wrong, and then configure the corresponding content
1 |
|

Configure the monitored name, IP address, port number, and number of votes respectively. When the master machine goes down, the slave machine needs to vote to decide who will take over as the master machine. When the number of votes reaches 1, it is not enough to become the master machine. It must exceed 1 to become the master machine.
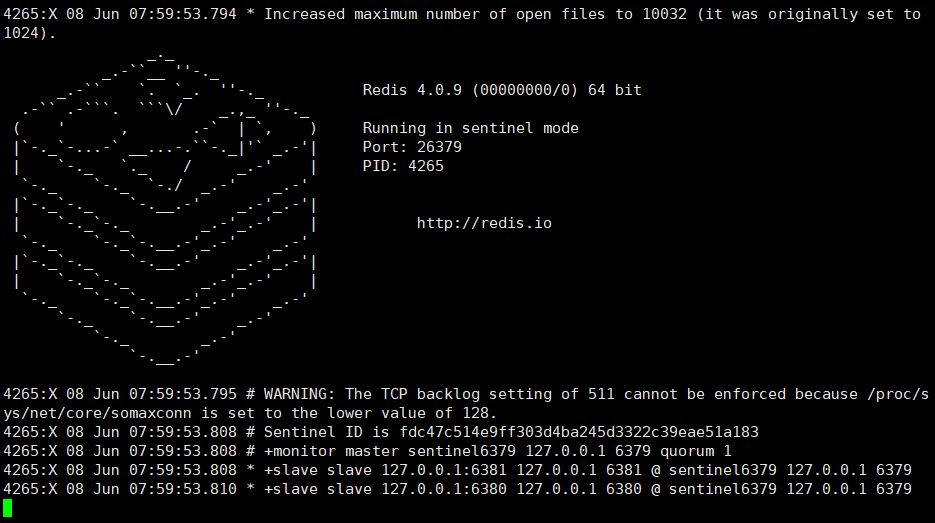
②. Start the sentinel
Startup interface:
Next, we kill host 6379, and then see what changes occur on the slave node.
After killing the master node, we checked the background print log and found that 6381 voted to become the master node.
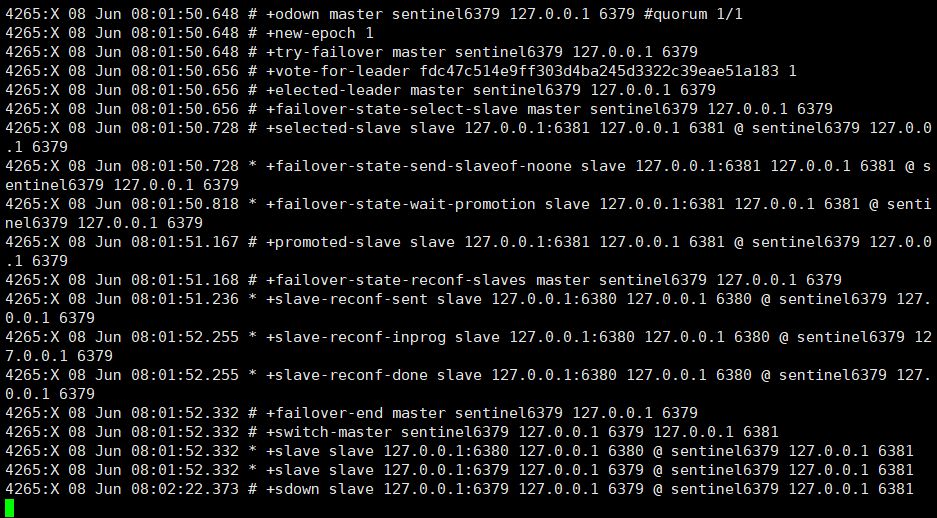
At this time we check the node information of the slave node 6381:
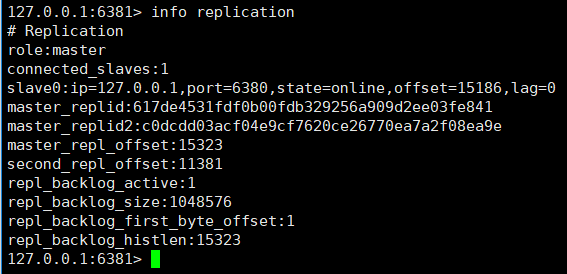
The 6381 node automatically becomes the master node.
PS: Sentinel mode also has a single point of failure problem. If the Sentinel machine hangs up, monitoring will no longer be possible. The solution is for Sentinel to also establish a cluster. Redis Sentinel mode supports clusters.
The replication function of Redis includes two operations: synchronization (sync) and command propagate (command propagate).
①、Old version synchronization
When the slave node issues a SLAVEOF command to require the slave server to copy the master server, the slave server completes it by sending a SYNC command to the master server. Steps to execute this command: 1. Send the SYNC command from the slave server to the master server
2. The master server that receives the SYNC command executes the BGSAVE command, generates an RDB file in the background, and uses a The buffer records all write commands executed from the beginning
3. When the BGSAVE command of the master server is completed, the master server will send the RDB file generated by the BGSAVE command to the slave server, and the slave server will receive the RDB file and Update the server status to the status recorded in the RDB file.
4. The master server also sends all write commands in the buffer to the slave server, and the slave server executes the corresponding commands.
When the synchronization operation is completed, the master server will modify the command accordingly. At this time, the status of the slave server and the master server will be inconsistent.
In order to keep the status of the master server and the slave server consistent, the master server needs to perform a command propagation operation on the slave server. The master server will send its own write command to the slave server for execution. After the slave server executes the corresponding command, the status of the master and slave servers continues to be consistent.
Summary: Through synchronization operations and command propagation functions, the master-slave consistency feature can be well guaranteed.
But we consider a problem. If the slave server suddenly disconnects during synchronization with the master server, and the master server performs some write operations at this time, the slave server restores the connection. If we are synchronizing , then you must regenerate an RDB file from the master server and load it to the slave server. Although consistency can be ensured, the status of the master and slave servers is actually consistent before the connection is disconnected. The inconsistency is when the slave server is disconnected. The master server has executed some write commands, so after the slave server restores the connection, can it only disconnect the write commands instead of the entire RDB snapshot?
The synchronization operation is actually a very time-consuming operation. The master server needs to first generate an RDB file through the BGSAVE command, and then needs to send the file to the slave server. After receiving the file from the slave server, it then loads the file, and during loading, the slave server cannot process other commands.
In order to solve this problem, Redis has used the new synchronization command
since version 2.8 to replace the SYNC command. The partial resynchronization function of this command is used to solve the efficiency problem of re-replication after disconnection. That is to say, when the slave server reconnects to the master server after being disconnected, the master server only sends the write commands executed after the disconnection to the slave server. The slave server only needs to receive and execute these write commands to maintain master-slave consistency.6. Disadvantages of master-slave replication
1 |
##redis-sentinel /etc/redis/sentinel.conf |
The above is the detailed content of How Redis implements master-slave replication. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases? Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis? How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency? What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store? What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis



