 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 How to use Redis linked list to solve the problem of oversold products with high concurrency
How to use Redis linked list to solve the problem of oversold products with high concurrency
How to use Redis linked list to solve the problem of oversold products with high concurrency
Implementation Principle
Use redis linked list to do it, because the pop operation is atomic, even if many users arrive at the same time, they will be executed in sequence, which is recommended.
Implementation steps
The first step is to put the product inventory into the queue
/**
* 添加商品数量到商品队列
* @param int $couponId 优惠券ID
*/
function addCoupons($couponId)
{
//1.初始化Redis连接
$redis = new Redis();
if (!$redis->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379)) {
trigger_error('Redis连接出错!!!', E_USER_ERROR);
} else {
echo '连接正常<br>';
}
//根据优惠券ID从数据库中查询该优惠券的库存量
//$sql = "select id, stock from coupon where id = {$couponId}";
$stock = 10; //假设10就是我们从数据库中查询出的该优惠券在数据库中的库存量
//我们现在将这10个库存放入到以该商品ID为key的redis链表中,有几件库存,就存入多少次1,链表长度代表商品库存数
for($i = 0; $i < $stock; $i++) {
$redis->lPush("secKill:".$couponId.":stock", 1);
}
$redis->close();
}
$couponId = 11211;
addCoupons($couponId);We call this method, and then check redis, 10 elements have been added to the linked list
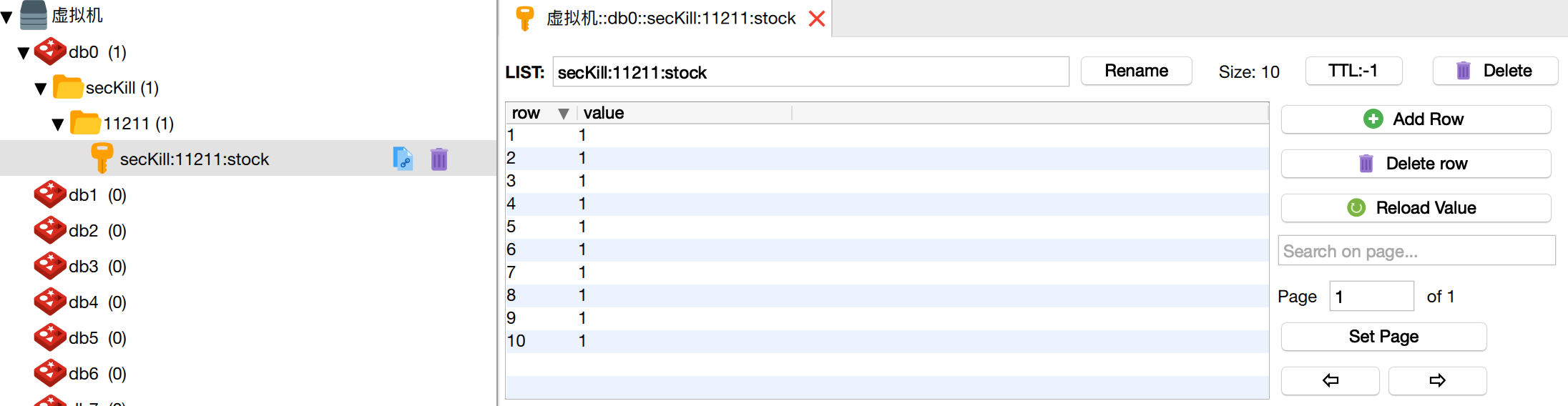
The second step is to start the rush purchase and set the cache cycle of the inventory.
This step is determined according to your own business. If the business stipulates, this coupon will be released 2 minutes for users to grab, then use the expire() method to set a validity period for the linked list. Even if it is not sold out within the validity period, there is still stock and users will not be allowed to grab it (because our company’s business does not grab coupons The coupon sets the validity period, so I don’t need to do this step)
//设置链表有效期是两分钟 $redis->expire('key', 120);
The third step, the client performs the instant snap-up operation
/**
* 抢优惠券(秒杀)
* @param int $couponId 商品ID
* @param int $uid 用户ID
* @return bool
*/
function secKill($couponId, $uid)
{
//1.初始化Redis连接
$redis = new Redis();
if (!$redis->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379)) {
trigger_error('Redis连接出错!!!', E_USER_ERROR);
} else {
echo '连接正常<br>';
}
//将已经成功抢购的用户添加到该以该商品ID为key的集合(set)中
//如果用户已经在集合中,说明用户已经成功秒杀过一次了,不允许再次参与秒杀
if ($redis->sIsMember('secKill:'.$couponId.':uid', $uid)) {
echo '秒杀失败';
return false;
}
//秒杀商品的库存key
$key = 'secKill:'.$couponId.':stock';
//从以该优惠券ID为key的链表中弹出一个值,如果有值,证明优惠券还有库存
$isSockNotEmpty = $redis->lPop($key);
//判断库存,如果库存大于0,则减库存,将该成功秒杀用户加入哈希表,如果小于等于0,秒杀结束
if ($isSockNotEmpty != 1) {
echo '秒杀已结束';
return false;
}
//抢券成功,将优惠券ID和UID放入到队列中,由一个单独的进程队列来消费队列里的数据,向用户推送抢到的优惠券
$redis->lPush('couponOrder', $couponId.'+'.$uid);
//将成功抢券的用户记录到集合中,防止被已抢过的用户再次秒杀
$redis->sAdd('secKill:'.$couponId.':uid', $uid);
$redis->close();
return true;
}
$couponId = 11211;
$uid = mt_rand(1, 100);
secKill($couponId, $uid);The fourth step, the successful flash sale users are entered into the database to persist the data , for purchases where the concurrency is not very large, we can directly write the information into the database after a successful purchase in the third step. For purchases where the concurrency is relatively large, it can be put into the RabbitMQ message queue for consumption (it is recommended to use the RabbitMQ queue instead of redis because RabbitMQ can guarantee that messages are 100% consumed, while redis is relatively less stable and reliable)
//此处代码省略 //根据自己的业务场景看看是入数据库还是放入rabbitMQ消息队列中消费
Now we use the ab tool to simulate coupon grabbing behavior under high concurrency (2000 requests, 100 concurrency)
ab -n 2000 -c 100 www.test.com/
Then we use Redis Desktop Manager to view the Redis results
Similarly, there are already 10 pieces of information containing user uid and coupon id in the couponOrder queue. This information can be used by the queue Consumption.
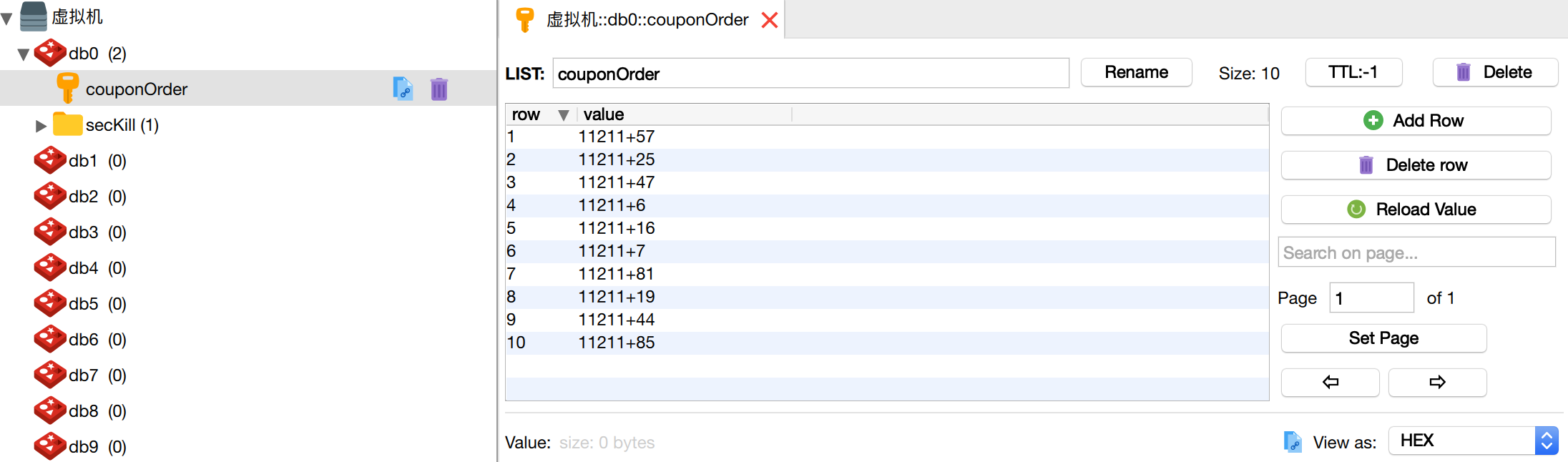
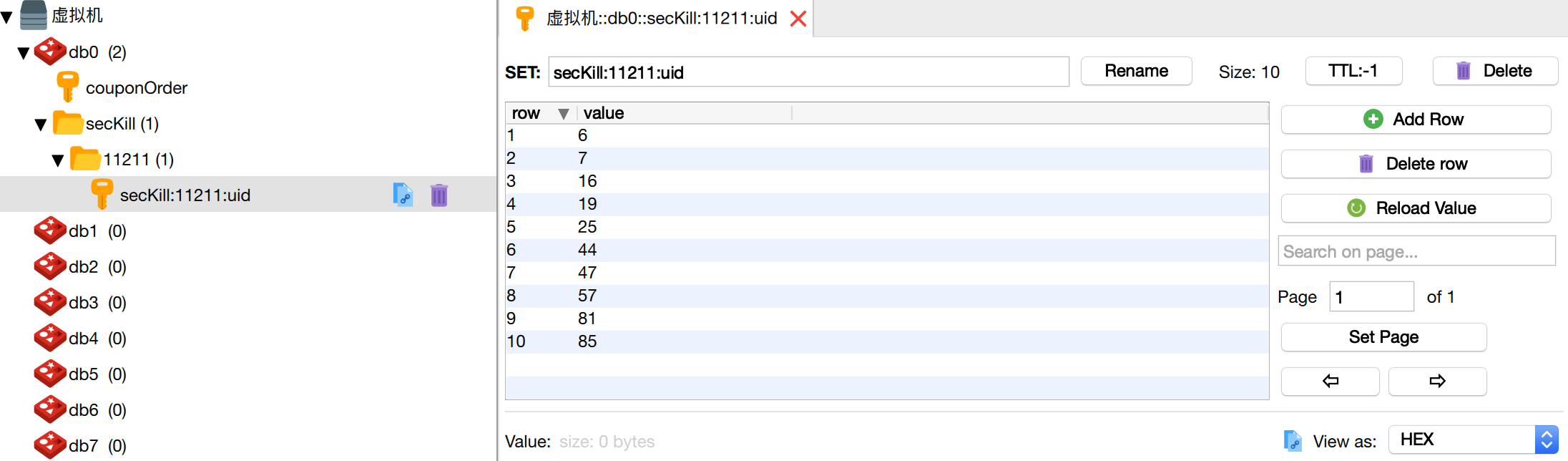
#At the same time, the UID information of 10 users is also saved in the user coupon collection.
The above is the detailed content of How to use Redis linked list to solve the problem of oversold products with high concurrency. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
The steps for troubleshooting and repairing Redis master-slave replication failures include: 1. Check the network connection and use ping or telnet to test connectivity; 2. Check the Redis configuration file to ensure that the replicaof and repl-timeout are set correctly; 3. Check the Redis log file and find error information; 4. If it is a network problem, try to restart the network device or switch the alternate path; 5. If it is a configuration problem, modify the configuration file; 6. If it is a data synchronization problem, use the SLAVEOF command to resync the data.
 Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
The quick location and processing steps for Redis cluster node failure are as follows: 1. Confirm the fault: Use the CLUSTERNODES command to view the node status. If the fail is displayed, the node will fail. 2. Determine the cause: Check the network, hardware, and configuration. Common problems include memory limits exceeding. 3. Repair and restore: Take measures based on the reasons, such as restarting the service, replacing the hardware or modifying the configuration. 4. Notes: Ensure data consistency, select appropriate failover policies, and establish monitoring and alarm systems.
 Methods and strategies to solve the problem of split brain in Redis cluster
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Methods and strategies to solve the problem of split brain in Redis cluster
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Effective solutions to the problem of split brain in Redis cluster include: 1) Network configuration optimization to ensure connection stability; 2) Node monitoring and fault detection, real-time monitoring with tools; 3) Failover mechanism, setting high thresholds to avoid multiple master nodes; 4) Data consistency guarantee, using replication function to synchronize data; 5) Manual intervention and recovery, and manual processing if necessary.
 Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Redis and RabbitMQ each have their own advantages in performance and joint application scenarios. 1.Redis performs excellently in data reading and writing, with a latency of up to microseconds, suitable for high concurrency scenarios. 2.RabbitMQ focuses on messaging, latency at milliseconds, and supports multi-queue and consumer models. 3. In joint applications, Redis can be used for data storage, RabbitMQ handles asynchronous tasks, and improves system response speed and reliability.
 Configuration suggestions for improving Redis persistence performance
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Configuration suggestions for improving Redis persistence performance
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Methods to improve Redis persistence performance through configuration include: 1. Adjust the save parameters of RDB to reduce the snapshot generation frequency; 2. Set the appendfsync parameter of AOF to everysec; 3. Use AOF and RDB in combination; 4. Use no-appendfsync-on-rewrite parameters to optimize AOF rewrite performance; 5. Enable hybrid persistence mode. These configurations can improve performance while ensuring data security.
 Methods to implement data deduplication using Redis sets (Sets)
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
Methods to implement data deduplication using Redis sets (Sets)
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
The Redis collection is selected to implement data deduplication because it supports quick insertion and search, and it automatically deduplication. 1) The Redis collection is based on an ordered collection structure without repeat elements, and is suitable for scenarios where quick insertion and query are required. 2) But you need to pay attention to its memory usage, because each element occupies memory. 3) It can be optimized for use through shard storage, regular cleaning and combined with other storage.
 How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
To realize text error correction and syntax optimization with AI, you need to follow the following steps: 1. Select a suitable AI model or API, such as Baidu, Tencent API or open source NLP library; 2. Call the API through PHP's curl or Guzzle and process the return results; 3. Display error correction information in the application and allow users to choose whether to adopt it; 4. Use php-l and PHP_CodeSniffer for syntax detection and code optimization; 5. Continuously collect feedback and update the model or rules to improve the effect. When choosing AIAPI, focus on evaluating accuracy, response speed, price and support for PHP. Code optimization should follow PSR specifications, use cache reasonably, avoid circular queries, review code regularly, and use X
 Tools and metrics to monitor the health status of Redis clusters
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Tools and metrics to monitor the health status of Redis clusters
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Through tools such as redis-cli, RedisInsight, Prometheus and Grafana, as well as focusing on memory usage, number of connections, cluster node status, data consistency and performance indicators, the health status of the Redis cluster can be effectively monitored.






