1. Introduction to Redis
REmote DIctionary Server (Redis) is a key-value storage system written by Salvatore Sanfilippo. Redis is an open source log-type Key-Value database written in ANSI C language, abides by the BSD protocol, supports the network, can be memory-based and persistent, and provides APIs in multiple languages. It is often called a data structure server because values can be of types such as String, Map, List, Sets and Sorted Sets.
Everyone knows that redis is a no sql database based on key-value, so let’s first learn about key-related knowledge points
1. Any binary sequence can be used as a key
2. Redis has unified rules to design keys
3. The maximum length allowed for key-value is 512MB
2. Supported languages
ActionScript Bash C C# C++ Clojure Common LispCrystal D Dart Elixir emacs lisp Erlang Fancy gawk GNU Prolog Go Haskell Haxe Io Java Javascript Julia Lua Matlab mruby Nim Node.js Objective-C OCaml Pascal Perl PHP Pure Data Python R Racket Rebol Ruby Rust Scala Scheme Smalltalk Swift Tcl VB VCL
3. What are the application scenarios of Redis? ?
1. The most commonly used one is session cache
2. Message queue, such as payment
3. Activity ranking or count
4 , publish, subscribe to messages (message notifications)
5. Product list, comment list, etc.
4. Redis installation
About redis installation and related For an introduction to knowledge points, please refer to Nosql database service redis
The approximate installation steps are as follows:
Redis is developed in c language, and installing redis requires a c language compilation environment
If you don’t have gcc, you need to install it online: yum install gcc-c
Step 1: Get the source package: wget http://download.redis.io/rele...
Step 2 : Decompress redis: tar zxvf redis-3.0.0.tar.gz
Step 3: Compile. Enter the redis source code directory (cd redis-3.0.0). Execute make
Step 4: Installation. make install PREFIX=/usr/local/redis
The PREFIX parameter specifies the installation directory of redis
5. Redis data type
Redis supports a total of five Data types
1, string(string)
2, hash(hash)
3, list(list)
4, set (Set)
5, zset (sorted set ordered set)
string(string)
The most basic data type of Redis is key Value pairs, where one key corresponds to a value. It should be noted that a key-value pair can store up to 512MB.
127.0.0.1:6379> set key "hello world" OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get key "hello world" 127.0.0.1:6379> getset key "nihao" "hello world" 127.0.0.1:6379> mset key1 "hi" key2 "nihao" key3 "hello" OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get key1 "hi" 127.0.0.1:6379> get key2 "nihao" 127.0.0.1:6379> get key3 "hello"
Introduction to related commands
set sets the value for a Key
get gets the value corresponding to a key
getset sets the value (value) for a Key and returns the corresponding value
mset sets the value (value) for multiple keys
hash (hash)
redis hash is a collection of key-value pairs, a mapping table of string type fields and values, suitable for storing objects
127.0.0.1:6379> hset redishash 1 "001" (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> hget redishash 1 "001" 127.0.0.1:6379> hmset redishash 1 "001" 2 "002" OK 127.0.0.1:6379> hget redishash 1 "001" 127.0.0.1:6379> hget redishash 2 "002" 127.0.0.1:6379> hmget redishash 1 2 1) "001" 2) "002"
Introduction to related commands
hset configures the field in the hash corresponding to the Key as value. If the hash does not exist, it will be automatically created.
hget obtains the value of the field configuration in a certain hash
hmset configures multiple field values in the same hash in batches
hmget obtains multiple field values in the same hash in batches
list(list)
is a simple string list in redis, which is sorted in insertion order
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush word hi (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> lpush word hello (integer) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> rpush word world (integer) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> lrange word 0 2 1) "hello" 2) "hi" 3) "world" 127.0.0.1:6379> llen word (integer) 3
Related command introduction
lpush inserts elements to the left of the specified list and returns after insertion The length of the list
rpush inserts an element to the right side of the specified list and returns the length of the inserted list
llen returns the length of the specified list
lrange returns the specified range in the specified list The element value
set(set)
is an unordered set of string type and cannot be repeated
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd redis redisset (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd redis redisset1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd redis redisset2 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers redis 1) "redisset1" 2) "redisset" 3) "redisset2" 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd redis redisset2 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers redis 1) "redisset1" 2) "redisset" 3) "redisset2" 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers redis 1) "redisset1" 2) "redisset3" 3) "redisset" 4) "redisset2" 127.0.0.1:6379> srem redis redisset (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers redis 1) "redisset1" 2) "redisset3" 3) "redisset2"
Introduction to related commands
sadd adds a string element to the set collection corresponding to key, returns 1 if successful, returns 0 if the element exists
smembers Returns all elements in the specified set
srem Delete an element of the specified set
zset (sorted set ordered set)
is an ordered set of string type and cannot be repeated
Each element in the sorted set needs to specify a score, and the elements are sorted in ascending order according to the score. If multiple elements have the same score, they are sorted in ascending order in lexicographic order. The sorted set is therefore very suitable for ranking
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 0 001 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 0 002 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 0 003 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zcount nosql 0 0 (integer) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> zcount nosql 0 3 (integer) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> zrem nosql 002 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zcount nosql 0 3 (integer) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> zscore nosql 003 "0" 127.0.0.1:6379> zrangebyscore nosql 0 10 1) "001" 2) "003" 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 1 003 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 1 004 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zrangebyscore nosql 0 10 1) "001" 2) "003" 3) "004" 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 3 005 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd nosql 2 006 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> zrangebyscore nosql 0 10 1) "001" 2) "003" 3) "004" 4) "006" 5) "005"
Related command introduction
zadd Add 1 or more elements to the specified sorteset
zrem Delete 1 or more elements from the specified sorteset Element
zcount View the number of elements within the specified score range in the specified sorteset
zscore View the elements with the specified score in the specified sorteset
zrangebyscore View the specified score in the specified sorteset All elements within the range
6, key value related commands
127.0.0.1:6379> exists key (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> exists key1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> exists key100 (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> get key "nihao,hello" 127.0.0.1:6379> get key1 "hi" 127.0.0.1:6379> del key1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> get key1 (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379> rename key key0 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get key(nil) 127.0.0.1:6379> get key0 "nihao,hello" 127.0.0.1:6379> type key0 string
exists #Confirm whether the key exists
del #Delete key
expire #Set Key expiration time (in seconds)
persist #Remove Key expiration time configuration
rename #Rename key
type #Type of return value
7. Redis service Related commands
127.0.0.1:6379> select 0 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> info # Server redis_version:3.0.6 redis_git_sha1:00000000 redis_git_dirty:0 redis_build_id:347e3eeef5029f3 redis_mode:standalone os:Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 x86_64 arch_bits:64 multiplexing_api:epoll gcc_version:4.8.5 process_id:31197 run_id:8b6ec6ad5035f5df0b94454e199511084ac6fb12 tcp_port:6379 uptime_in_seconds:8514 uptime_in_days:0 hz:10 lru_clock:14015928 config_file:/usr/local/redis/redis.conf -------------------省略N行 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET 0 (empty list or set) 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET 15 (empty list or set)
slect #选择数据库(数据库编号0-15)
quit #退出连接
info #获得服务的信息与统计
monitor #实时监控
config get #获得服务配置
flushdb #删除当前选择的数据库中的key
flushall #删除所有数据库中的key
8、Redis的发布与订阅
Redis发布与订阅(pub/sub)是它的一种消息通信模式,一方发送信息,一方接收信息。
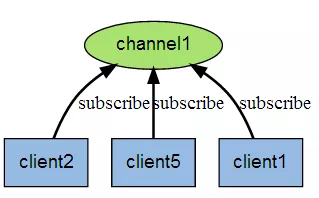
下图是三个客户端同时订阅同一个频道
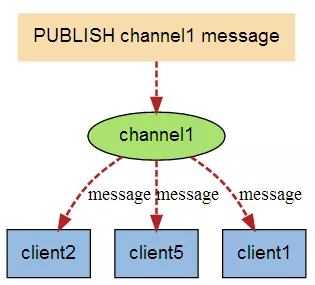
下图是有新信息发送给频道1时,就会将消息发送给订阅它的三个客户端
9、Redis事务
Redis事务可以一次执行多条命令
1、发送exec命令前放入队列缓存,结束事务
2、收到exec命令后执行事务操作,如果某一命令执行失败,其它命令仍可继续执行
3、一个事务执行的过程中,其它客户端提交的请求不会被插入到事务执行的命令列表中
一个事务经历三个阶段
开始事务(命令:multi)
命令执行
结束事务(命令:exec)
127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set key key1 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> get key QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> rename key key001 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> exec 1) OK 2) "key1" 3) OK
10、Redis安全配置
可以通过修改配置文件设备密码参数来提高安全性
#requirepass foobared
去掉注释#号就可以配置密码
没有配置密码的情况下查询如下
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET requirepass 1) "requirepass" 2) ""
配置密码之后,就需要进行认证
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET requirepass (error) NOAUTH Authentication required. 127.0.0.1:6379> AUTH foobared #认证OK 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET requirepass 1) "requirepass" 2) "foobared"
11、Redis持久化
Redis持久有两种方式:Snapshotting(快照),Append-only file(AOF)
Snapshotting(快照)
1、将存储在内存的数据以快照的方式写入二进制文件中,如默认dump.rdb中
2、save 900 1
#900秒内如果超过1个Key被修改,则启动快照保存
3、save 300 10
#300秒内如果超过10个Key被修改,则启动快照保存
4、save 60 10000
#60秒内如果超过10000个Key被修改,则启动快照保存
Append-only file(AOF)
1、使用AOF持久时,服务会将每个收到的写命令通过write函数追加到文件中(appendonly.aof)
2、AOF持久化存储方式参数说明
appendonly yes
#开启AOF持久化存储方式
appendfsync always
#收到写命令后就立即写入磁盘,效率最差,效果最好
appendfsync everysec
#每秒写入磁盘一次,效率与效果居中
appendfsync no
#完全依赖OS,效率最佳,效果没法保证
12、Redis 性能测试
自带相关测试工具
[root@test ~]# redis-benchmark --help Usage: redis-benchmark [-h <host>] [-p <port>] [-c <clients>] [-n <requests> [-k <boolean>] -h <hostname> Server hostname (default 127.0.0.1) -p <port> Server port (default 6379) -s <socket> Server socket (overrides host and port) -a <password> Password for Redis Auth -c <clients> Number of parallel connections (default 50) -n <requests> Total number of requests (default 100000) -d <size> Data size of SET/GET value in bytes (default 2) -dbnum <db> SELECT the specified db number (default 0) -k <boolean> 1=keep alive 0=reconnect (default 1) -r <keyspacelen> Use random keys for SET/GET/INCR, random values for SADD Using this option the benchmark will expand the string __rand_int__ inside an argument with a 12 digits number in the specified range from 0 to keyspacelen-1. The substitution changes every time a command is executed. Default tests use this to hit random keys in the specified range. -P <numreq> Pipeline <numreq> requests. Default 1 (no pipeline). -q Quiet. Just show query/sec values --csv Output in CSV format -l Loop. Run the tests forever -t <tests> Only run the comma separated list of tests. The test names are the same as the ones produced as output. -I Idle mode. Just open N idle connections and wait. Examples: Run the benchmark with the default configuration against 127.0.0.1:6379: $ redis-benchmark Use 20 parallel clients, for a total of 100k requests, against 192.168.1.1: $ redis-benchmark -h 192.168.1.1 -p 6379 -n 100000 -c 20 Fill 127.0.0.1:6379 with about 1 million keys only using the SET test: $ redis-benchmark -t set -n 1000000 -r 100000000 Benchmark 127.0.0.1:6379 for a few commands producing CSV output: $ redis-benchmark -t ping,set,get -n 100000 --csv Benchmark a specific command line: $ redis-benchmark -r 10000 -n 10000 eval 'return redis.call("ping")' 0 Fill a list with 10000 random elements: $ redis-benchmark -r 10000 -n 10000 lpush mylist __rand_int__ On user specified command lines __rand_int__ is replaced with a random integer with a range of values selected by the -r option.</tests></numreq></numreq></keyspacelen></boolean></db></size></requests></clients></password></socket></port></hostname></boolean></requests></clients></port></host>实际测试同时执行100万的请求
[root@test ~]# redis-benchmark -n 1000000 -q PING_INLINE: 152578.58 requests per second PING_BULK: 150308.14 requests per second SET: 143266.47 requests per second GET: 148632.58 requests per second INCR: 145857.64 requests per second LPUSH: 143781.45 requests per second LPOP: 147819.66 requests per second SADD: 138350.86 requests per second SPOP: 134282.27 requests per second LPUSH (needed to benchmark LRANGE): 141302.81 requests per second LRANGE_100 (first 100 elements): 146756.67 requests per second LRANGE_300 (first 300 elements): 148104.27 requests per second LRANGE_500 (first 450 elements): 152671.75 requests per second LRANGE_600 (first 600 elements): 148104.27 requests per second MSET (10 keys): 132731.62 requests per second
13、Redis的备份与恢复
Redis自动备份有两种方式
第一种是通过dump.rdb文件实现备份
第二种使用aof文件实现自动备份
dump.rdb备份
Redis服务默认的自动文件备份方式(AOF没有开启的情况下),在服务启动时,就会自动从dump.rdb文件中去加载数据。
**具体配置在redis.conf
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000**
也可以手工执行save命令实现手动备份
127.0.0.1:6379> set name key OK 127.0.0.1:6379> SAVE OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set name key1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> BGSAVE Background saving started
redis快照到dump文件时,会自动生成dump.rdb的文件
# The filename where to dump the DB dbfilename dump.rdb -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 253 Apr 17 20:17 dump.rdb
SAVE命令表示使用主进程将当前数据库快照到dump文件
BGSAVE命令表示,主进程会fork一个子进程来进行快照备份
两种备份不同之处,前者会阻塞主进程,后者不会。
恢复举例
# Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name.dir /usr/local/redisdata/ #备份文件存储路径 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET dir 1) "dir" 2) "/usr/local/redisdata" 127.0.0.1:6379> set key 001 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set key1 002 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set key2 003 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> save OK
将备份文件备份到其它目录
[root@test ~]# ll /usr/local/redisdata/ total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 49 Apr 17 21:24 dump.rdb [root@test ~]# date Tue Apr 17 21:25:38 CST 2018 [root@test ~]# cp ./dump.rdb /tmp/
删除数据
127.0.0.1:6379> del key1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> get key1 (nil)
关闭服务,将原备份文件拷贝回save备份目录
[root@test ~]# redis-cli -a foobared shutdown [root@test ~]# lsof -i :6379 [root@test ~]# cp /tmp/dump.rdb /usr/local/redisdata/ cp: overwrite ‘/usr/local/redisdata/dump.rdb’? y [root@test ~]# redis-server /usr/local/redis/redis.conf & [1] 31487
登录查看数据是否恢复
[root@test ~]# redis-cli -a foobared 127.0.0.1:6379> mget key key1 key2 1) "001" 2) "002" 3) "003"
AOF自动备份
redis服务默认是关闭此项配置
###### APPEND ONLY MODE ########## appendonly no # The name of the append only file (default: "appendonly.aof") appendfilename "appendonly.aof" # appendfsync always appendfsync everysec # appendfsync no
配置文件的相关参数,前面已经详细介绍过。
AOF文件备份,是备份所有的历史记录以及执行过的命令,和mysql binlog很相似,在恢复时就是重新执次一次之前执行的命令,需要注意的就是在恢复之前,和数据库恢复一样需要手工删除执行过的del或误操作的命令。
AOF与dump备份不同
1、aof文件备份与dump文件备份不同
2、服务读取文件的优先顺序不同,会按照以下优先级进行启动
如果只配置AOF,重启时加载AOF文件恢复数据
如果同时 配置了RBD和AOF,启动是只加载AOF文件恢复数据
如果只配置RBD,启动时将加载dump文件恢复数据
注意:只要配置了aof,但是没有aof文件,这个时候启动的数据库会是空的
14、Redis 生产优化介绍
1、内存管理优化
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 list-max-ziplist-entries 512 list-max-ziplist-value 64 #list的成员与值都不太大的时候会采用紧凑格式来存储,相对内存开销也较小
在linux环境运行Redis时,如果系统的内存比较小,这个时候自动备份会有可能失败,需要修改系统的vm.overcommit_memory 参数,这个参数是linux系统的内存分配策略
0 表示内核将检查是否有足够的可用内存供应用进程使用;如果有足够的可用内存,内存申请允许;否则,内存申请失败,并把错误返回给应用进程。
1 表示内核允许分配所有的物理内存,而不管当前的内存状态如何。
2 表示内核允许分配超过所有物理内存和交换空间总和的内存
Redis官方的说明是,建议将vm.overcommit_memory的值修改为1,可以用下面几种方式进行修改:
(1)编辑/etc/sysctl.conf 改vm.overcommit_memory=1,然后sysctl -p 使配置文件生效
(2)sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1
(3)echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
**2、内存预分配
3、持久化机制**
定时快照:效率不高,会丢失数据
AOF:保持数据完整性(一个实例的数量不要太大2G最大)
优化总结
1)根据业务需要选择合适的数据类型
2)当业务场景不需持久化时就关闭所有持久化方式(采用ssd磁盘来提升效率)
3)不要使用虚拟内存的方式,每秒实时写入AOF
4)不要让REDIS所在的服务器物理内存使用超过内存总量的3/5
5)要使用maxmemory
6)大数据量按业务分开使用多个redis实例
15、Redis集群应用
集群是将多个redis实例集中在一起,实现同一业务需求,或者实现高可用与负载均衡
到底有哪些集群方案呢??
1、haproxy+keepalived+redis集群
1)通过redis的配置文件,实现主从复制、读写分离
2)通过haproxy的配置,实现负载均衡,当从故障时也会及时从集群中T除
3)利用keepalived来实现负载的高可用
2、redis官方Sentinel集群管理工具
Redis集群生产环境高可用方案实战过程
1)sentinel负责对集群中的主从服务监控、提醒和自动故障转移
2)redis集群负责对外提供服务
关于redis sentinel cluster集群配置可参考
3、Redis Cluster
Redis Cluster是Redis的分布式解决方案,在Redis 3.0版本正式推出的,有效解决了Redis分布式方面的需求。Cluster架构可用于实现负载均衡,以解决单机内存、并发和流量等瓶颈问题。
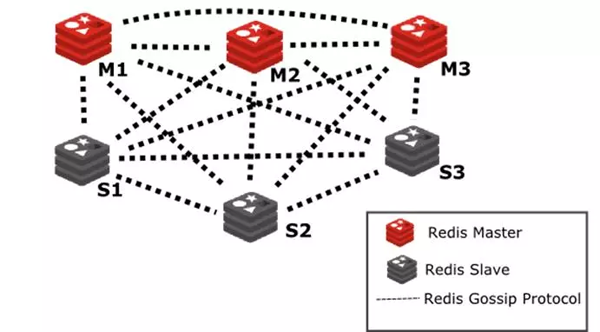
1)官方推荐,毋庸置疑。
2)去中心化,集群最大可增加1000个节点,性能随节点增加而线性扩展。
3)管理方便,后续可自行增加或摘除节点,移动分槽等等。
4)简单,易上手。
The above is the detailed content of What are the introductory knowledge points for Redis?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software
 What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases?
 Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
 How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server
 How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
 What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store?
 What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis




