
Computer Vision (Computer Vision), usually referred to as CV, is a research field that uses technology to help computers "see" and "understand" images, such as enabling computers to understand photos or videos. Content.
This article will provide an overall introduction to computer vision. This article is divided into six parts, which are:
Physiologically, vision begins with the excitement of the receptor cells of the visual organ, and is formed after the visual nervous system processes the collected information. We humans use vision to intuitively understand the shape and state of things in front of us. Most of us rely on vision to complete cooking, negotiate obstacles, read street signs, watch videos, and countless other tasks. In fact, if it were not for special groups such as the blind, the vast majority of people obtain external information through vision, and this proportion is as high as 80% - this proportion is not unfounded, according to the famous experimental psychologist Treicher has confirmed through a large number of experiments that 83% of the information humans obtain comes from vision, 11% from hearing, and the remaining 6% comes from smell, touch, and taste. Therefore, for humans, vision is undoubtedly the most important sense.
Not only humans are "visual animals", but for most animals, vision also plays a very important role. Through vision, humans and animals perceive the size, light and shade, color, and movement of external objects, and obtain various information that is important to the survival of the body. Through this information, they can learn what the surrounding world is like and how to interact with the world.

#Before the advent of computer vision, images were in a black box state for computers. To a computer, an image is just a file or a string of data. The computer does not know what the content of the picture is. It only knows what size the picture is, how much memory it occupies, what format it is in, etc.
If computers and artificial intelligence want to play an important role in the real world, they must understand pictures! Therefore, for half a century, computer scientists have been trying to figure out how to make computers see, giving rise to the field of "computer vision."

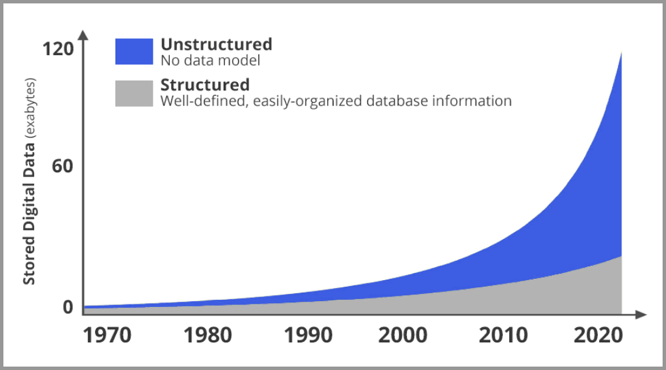
The rapid development of the Internet has also made computer vision particularly important. The figure below is a trend chart of the amount of new data on the network since 2020. Gray graphics are structured data, blue graphics are unstructured data (mostly pictures and videos). It is obvious that the number of pictures and videos is growing at an exponential rate.
The Internet is made up of text and images. Searching for text is relatively simple, but in order to search for images, the algorithm needs to know what the image contains. For a long time, humans did not have enough technology to understand the content of images and videos, and could only rely on manual annotation to obtain descriptions of images or videos. How to enable computers to better understand these image information is a major challenge facing today's computer technology. In order to make full use of image or video data, you need to let the computer "see" the image or video and understand the content.
Computer vision is an important branch in the field of artificial intelligence. Simply put, the problem it solves is to let computers understand the content of images or videos. For example: Is the pet in the picture a cat or a dog? Is the person in the picture Lao Zhang or Lao Wang? What are the people in the video doing? Furthermore, computer vision refers to using cameras and computers instead of human eyes to identify, track and measure targets, and further perform graphics processing to obtain images that are more suitable for human eye observation or transmission to instruments for detection. As a scientific discipline, computer vision studies related theories and technologies, trying to build artificial intelligence systems that can obtain high-level information from images or multi-dimensional data. From an engineering perspective, it seeks to leverage automated systems to mimic the human visual system to complete tasks. The ultimate goal of computer vision is to enable computers to observe and understand the world through vision like humans do, and have the ability to adapt to the environment autonomously. But it is very difficult to truly realize that a computer can perceive the world through a camera, because although the images captured by the camera are the same as what we usually see, for the computer, any image is just an arrangement and combination of pixel values. A bunch of rigid numbers. How to allow computers to read meaningful visual clues from these rigid numbers is a problem that computer vision should solve.
Anyone who has used a camera or mobile phone knows that computers are good at taking photos with amazing fidelity and details. To a certain extent, computers Artificial "vision" is much stronger than the natural visual ability of humans. But just as we usually say "hearing does not mean understanding", "seeing" does not mean "understanding". If you want a computer to truly "understand" images, it is not a simple matter. An image is a large grid of pixels, and each pixel has a color, which is a combination of three primary colors: red, green, and blue. By combining the intensities of three colors - called RGB values - we can get any color. The simplest and most suitable computer vision algorithm for getting started is: to track a colored object, such as a pink ball, we first note the color of the ball, save the RGB value of the center pixel, and then feed the image to the program , letting the program find the pixel closest to this color. The algorithm can start from the upper left corner, examine each pixel, and calculate the difference from the target color. After checking each pixel, the closest part of the pixels is likely to be the pixel where the ball is. This algorithm is not limited to running on this single image, we can run the algorithm on each frame of the video to track the position of the ball. Of course, due to the influence of light, shadow and other factors, the color of the ball will change. It will not be exactly the same as the RGB value we saved, but it will be very close. However, in some extreme cases, such as a football match at night, the tracking effect may be very poor; and if one of the teams' jerseys is the same color as the ball, the algorithm will be completely "fainted." Therefore, unless the environment can be strictly controlled, such color tracking algorithms are rarely put into practical use. Nowadays, more computer vision algorithms used generally involve "Deep Learning" methods and technologies. Among them, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is the most widely used because of its superior performance. Since the knowledge involved in "deep learning" is too extensive, this article will not describe it in more detail. If you want to learn more about "deep learning", you might as well take a look at the introductory AI course - "Intel® OpenVINO™ Tool Suite Elementary Course". It starts with the basic concepts of AI, introduces relevant knowledge of artificial intelligence and vision applications, and helps users quickly understand the basic concepts and application scenarios of the Intel® OpenVINO™ tool suite. The entire course includes video processing, knowledge related to deep learning, inference acceleration for artificial intelligence applications, and Demo demonstrations of the Intel® OpenVINO™ tool suite. It takes you step by step to master deep learning from the shallower to the deeper.
Image classification is to distinguish different categories of images based on the semantic information of the image. It is a computer The core of vision is the basis for other high-level visual tasks such as object detection, image segmentation, object tracking, behavior analysis, and face recognition. For example, in the picture below, through image classification, the computer recognizes person, tree, grass, and sky in the image.
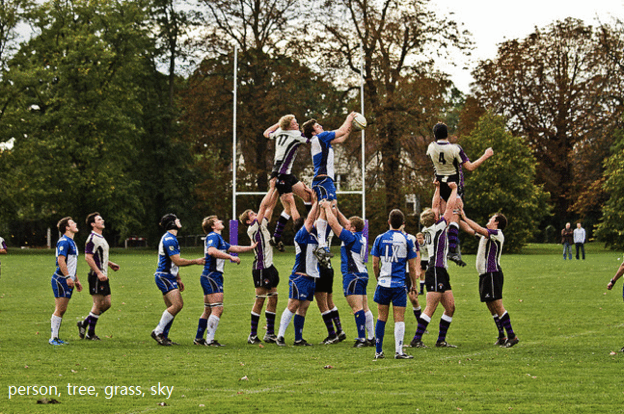

Image classification is widely used in many fields, such as: face recognition and intelligent video analysis in the security field, traffic scene recognition in the transportation field, and Internet-based Image retrieval of content and automatic classification of photo albums, image recognition in the medical field, etc.
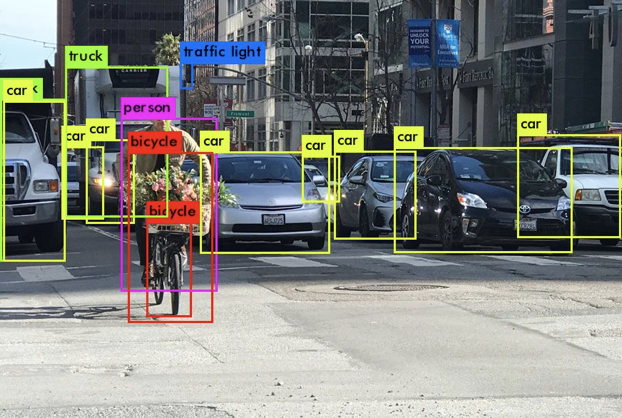
The goal of the target detection task is to give an image or a video frame, let the computer find the positions of all targets in it, and give each target specific categories. As shown in the figure below, taking recognition and detection of people as an example, the borders are used to mark the positions of all people in the image.
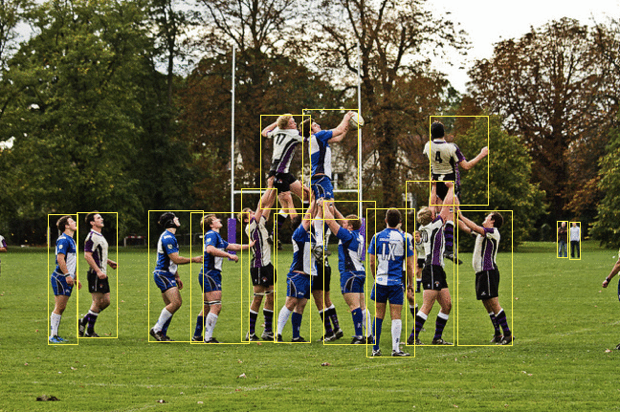

In multi-category target detection, borders of different colors are generally used to mark the positions of different detected objects, as shown in the figure below.
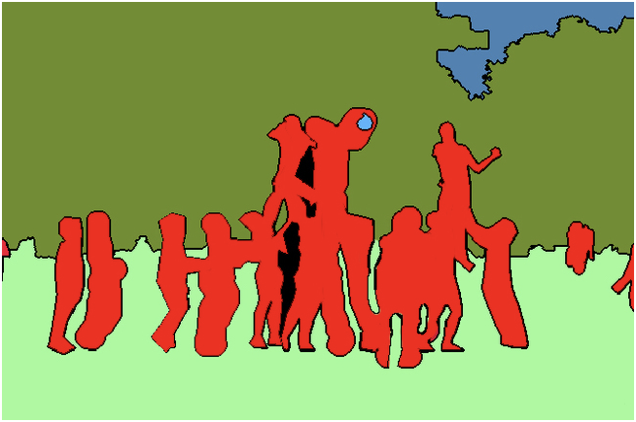
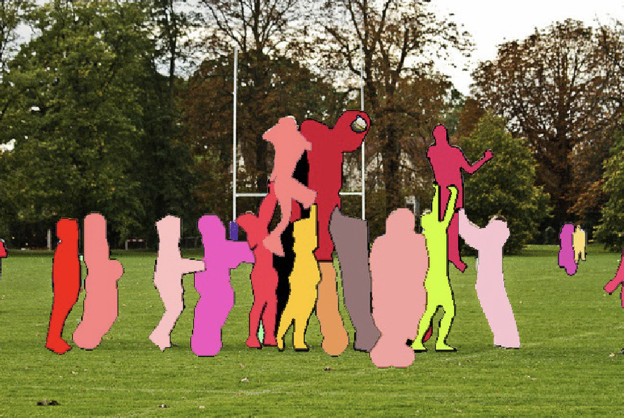
Semantic segmentation is a basic task in computer vision. In semantic segmentation we need to divide the visual input into Different semantic interpretable categories. It divides the entire image into groups of pixels, which are then labeled and classified. For example, we might want to distinguish all pixels in an image that belong to cars and color those pixels blue. As shown below, the image is divided into people (red), trees (dark green), grass (light green), and sky (blue) labels.
Instance segmentation Instance segmentation is a combination of target detection and semantic segmentation. The target is detected in the image (target detection), and then each pixel is labeled (semantic segmentation) ). Comparing the figures above and below, we can see that if human targets are used, semantic segmentation does not distinguish different instances belonging to the same category (all people are marked in red), while instance segmentation distinguishes different instances of the same category (different colors are used to distinguish different people).

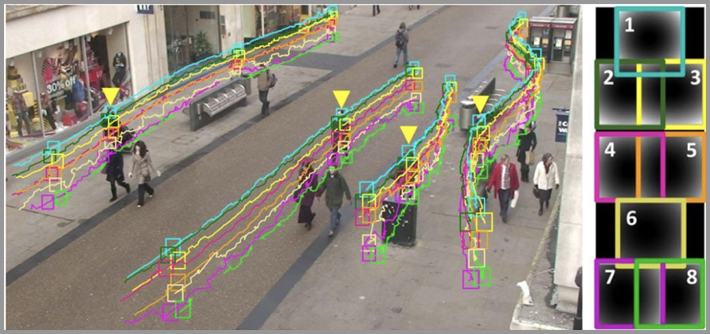
Target tracking Target tracking refers to the detection, extraction, identification and tracking of moving targets in image sequences, obtaining the motion parameters of the moving targets, processing and analysis, and achieving Behavioral understanding of moving targets to complete higher-level detection tasks.
The application scenarios of computer vision are very wide. Here are a few common application scenarios in life. . · Face recognition for access control and Alipay



Currently, computer vision technology is developing rapidly and has preliminary industry scale. The development of computer vision technology in the future mainly faces the following challenges: First, how to better combine it with other technologies in different application fields. Computer vision can make extensive use of big data when solving certain problems. It has gradually matured and can surpass humans, and However, it is impossible to achieve high accuracy on some problems; the second is how to reduce the development time and labor costs of computer vision algorithms. Currently, computer vision algorithms require a large amount of data and manual annotation, and require a long research and development cycle to reach the requirements of the application field. The required accuracy and time-consuming; the third is how to speed up the design and development of new algorithms. With the emergence of new imaging hardware and artificial intelligence chips, the design and development of computer vision algorithms for different chips and data acquisition equipment is also one of the challenges.
Computer vision is one of the fastest growing and most widely used technologies in the field of artificial intelligence. It is like the "eyes" of artificial intelligence, capturing images for all walks of life. and analyze more information. With the change of algorithms, the upgrade of hardware computing power, the explosion of data, and the high-speed network brought about by the development of 5G technology in the future, computer vision will also have a broader development space in terms of applications. Let us wait and see!
The above is the detailed content of One article to understand computer vision, full of useful information. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Computer Languages
Computer Languages Computer application areas
Computer application areas What is the encoding used inside a computer to process data and instructions?
What is the encoding used inside a computer to process data and instructions? The main reason why computers use binary
The main reason why computers use binary What are the main characteristics of computers?
What are the main characteristics of computers? What are the basic components of a computer?
What are the basic components of a computer? What skills are needed to work in the PHP industry?
What skills are needed to work in the PHP industry? What keys do arrows refer to in computers?
What keys do arrows refer to in computers?



