 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How to solve the problem when SpringBoot is deployed to external Tomcat and cannot be registered to the Nacos server
How to solve the problem when SpringBoot is deployed to external Tomcat and cannot be registered to the Nacos server
How to solve the problem when SpringBoot is deployed to external Tomcat and cannot be registered to the Nacos server
What happened
Recently, I have done a project bidding demonstration (POC) environment support, which needs to be integrated with the Nacos server. Considering that existing projects already have Nacos-related dependencies, isn't that simple? Create a new server, configure it and restart it a few times, right? However, things are far from being as simple as thought. The same code can be successfully registered when run in my local IDE, but cannot be deployed in the demo environment Tomcat War.
After the remote Debug code, it was found that the threads of the Nacos client were started, but the registration was not successful.
Thinking
I thought it might be related to the Tomcat deployment mode, so I checked the official issue and StackOverFlow
The event is published as part of Spring Boot starting the embedded Tomcat instance . If you're deploying to an external container, there's no embedded container to start and, therefore, no event is published. – Andy Wilkinson
Roughly speaking, only when Spring Boot starts the embedded Tomcat successfully, The WebServerInitializedEvent event will be released. The Nacos client will wait for this event to occur before registering itself with the server. And because it is deployed in external Tomcat, the embedded Tomcat will not be initialized, so this event will not be triggered.
So the solution is to call part of the code for events such as Nacos and let them start registration.
Nacos's automatic registration class is NacosAutoServiceRegistration, which inherits Spring Cloud's AbstractAutoServiceRegistration, bind(WebServerInitializedEvent) in AbstractAutoServiceRegistration, etc. Method listens for events, sets the port number and starts registration. Here this.port is obtained from the event and needs to be obtained by ourselves.
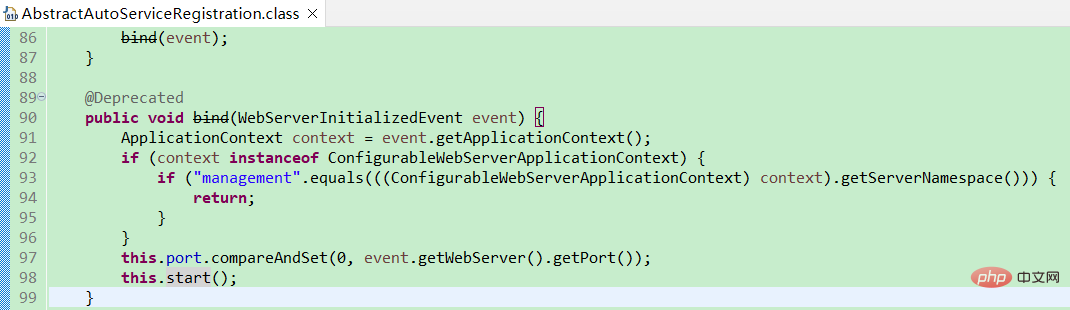
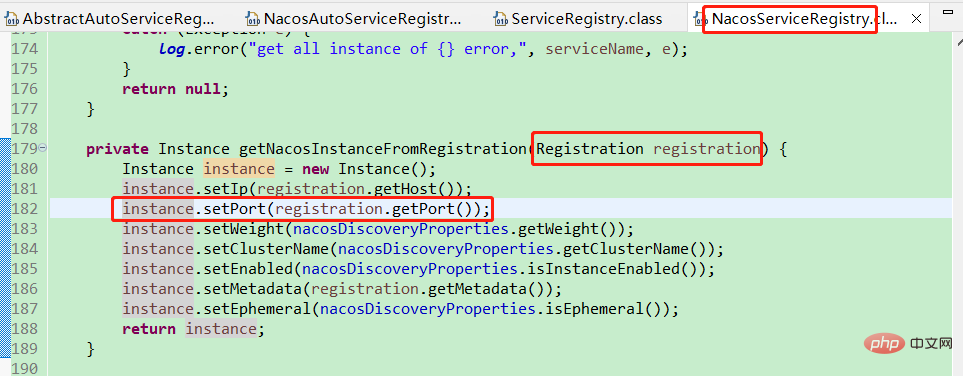
The location where the port is set is visible. It is taken from org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.Registration. Just set it. That's it.
Solution
I wrote a complete configuration class and placed it under the ISSUE, which is posted directly below.
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.management.MBeanServer;
import javax.management.MalformedObjectNameException;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import javax.management.Query;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.registry.NacosAutoServiceRegistration;
import com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.registry.NacosRegistration;
@Configuration
public class NacosWarDeployConfig {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NacosWarDeployConfig.class);
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Autowired
private NacosRegistration registration;
@Autowired
private NacosAutoServiceRegistration nacosAutoServiceRegistration;
@PostConstruct
public void nacosServerRegister() {
if (registration != null) {
registration.setPort(getTomcatPort());
nacosAutoServiceRegistration.start();
}
}
public int getTomcatPort() {
try {
return getProvideTomcatPort();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("obtain provide tomcat port failed, fallback to embeded tomcat port.");
}
return getEmbeddedTomcatPort();
}
private int getProvideTomcatPort() throws MalformedObjectNameException, NullPointerException {
MBeanServer beanServer = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
Set<ObjectName> objectNames = beanServer.queryNames(new ObjectName("*:type=Connector,*"),
Query.match(Query.attr("protocol"), Query.value("HTTP/1.1")));
String port = objectNames.iterator().next().getKeyProperty("port");
return Integer.valueOf(port);
}
private int getEmbeddedTomcatPort() {
return env.getProperty("server.port", Integer.class, 8080);
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem when SpringBoot is deployed to external Tomcat and cannot be registered to the Nacos server. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to check the number of concurrent connections in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:12 AM
How to check the number of concurrent connections in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:12 AM
How to check the number of concurrent Tomcat connections: Visit the Tomcat Manager page (http://localhost:8080/manager/html) and enter your user name and password. Click Status->Sessions in the left navigation bar to see the number of concurrent connections at the top of the page.
 Where is the root directory of the tomcat website?
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:27 AM
Where is the root directory of the tomcat website?
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The Tomcat website root directory is located in Tomcat's webapps subdirectory and is used to store web application files, static resources, and the WEB-INF directory; it can be found by looking for the docBase attribute in the Tomcat configuration file.
 Where is the tomcat installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:48 AM
Where is the tomcat installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:48 AM
Tomcat installation directory: Default path: Windows: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 9.0macOS:/Library/Tomcat/Tomcat 9.0Linux:/opt/tomcat/tomcat9 Custom path: You can specify it during installation. Find the installation directory: use whereis or locate command.
 How to configure domain name in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:52 AM
How to configure domain name in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:52 AM
To configure Tomcat to use a domain name, follow these steps: Create a server.xml backup. Open server.xml and add the Host element, replacing example.com with your domain name. Create an SSL certificate for the domain name (if required). Add an SSL connector in server.xml, change the port, keystore file, and password. Save server.xml. Restart Tomcat.
 How to deploy multiple projects in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:33 AM
How to deploy multiple projects in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:33 AM
To deploy multiple projects through Tomcat, you need to create a webapp directory for each project and then: Automatic deployment: Place the webapp directory in Tomcat's webapps directory. Manual deployment: Manually deploy the project in Tomcat's manager application. Once the project is deployed, it can be accessed by its deployment name, for example: http://localhost:8080/project1.
 How to check the port number of tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:00 AM
How to check the port number of tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:00 AM
The Tomcat port number can be viewed by checking the port attribute of the <Connector> element in the server.xml file. Visit the Tomcat management interface (http://localhost:8080/manager/html) and view the "Status" tab. Run "catalina.sh version" from the command line and look at the "Port:" line.
 How to run two projects with different port numbers in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to run two projects with different port numbers in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Running projects with different port numbers on the Tomcat server requires the following steps: Modify the server.xml file and add a Connector element to define the port number. Add a Context element to define the application associated with the port number. Create a WAR file and deploy it to the corresponding directory (webapps or webapps/ROOT). Restart Tomcat to apply changes.
 Tomcat disappears as soon as it starts up, what should I do?
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:39 AM
Tomcat disappears as soon as it starts up, what should I do?
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:39 AM
Common reasons for Tomcat startup flashing include: 1. Port conflict; 2. Insufficient system resources; 3. Configuration file errors; 4. Java environment issues; 5. Security restrictions; 6. Process conflicts; 7. Other reasons, see Tomcat Log for more clues.






