Cross-domain access control
Cross-domain access
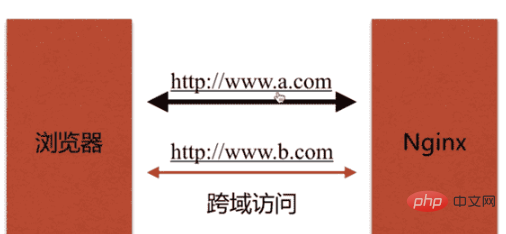
##Why does the browser prohibit cross-domain access
Not safe, prone to CSRF attacks!
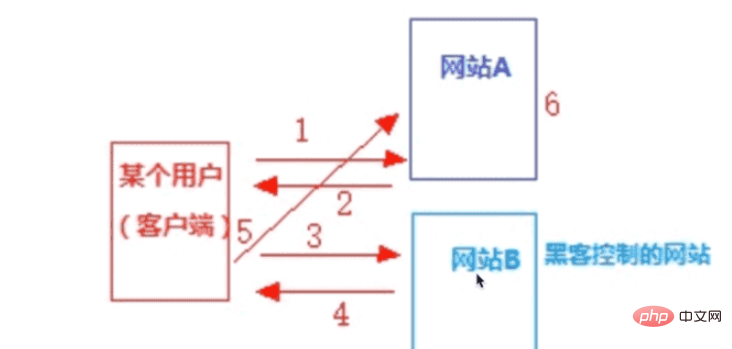
If website b controlled by a hacker adds malicious information in the response header to allow the client to access website a, a csrf attack will occur
How nginx configures cross-domain access
add_header syntax
- syntax:add_header name value [always];
- default:—
- context:http, server, location, if in location
Syntax explanation:
- add_header name value [always];
- name represents the key returned by the response header
- value represents the response header The value corresponding to the returned key
- add_header cross-domain configuration
location ~ .*\.(htm|html)$ { add_header access-control-allow-origin *; add_header access-control-allow-methods get,post,put,delete,options; root /opt/app/code; }
Copy after login
Anti-hotlinking
Anti-hotlinking purpose
- #Prevent resources from being misappropriated.
- Prevent abnormal user access, occupy website resources, affect website performance, and will inevitably affect normal user access
Based on http_referer anti-hotlinking Configuration module
ngx_http_referer_module module is used to prevent requests with invalid values in the "referer" header field from accessing the site.
Example
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.example.com example.* www.example.org/galleries/ ~\.google\.; if ($invalid_referer) { return 403; }
Copy after login
referer_hash_bucket_size syntax
##syntax: referer_hash_bucket_size size;
referer_hash_bucket_size size; indicates that the setting is valid The storage size of the reference hash table.
referer_hash_max_size Syntax
syntax: referer_hash_max_size size;
referer_hash_max_size size; means setting the maximum size of the effective referrer hash table .
valid_referers syntax
syntax: valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | string ...;
- ## Syntax explanation:
valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | string ...;
- none indicates that the "referer" field is missing in the request header;
- blocked means that the "referer" field appears in the request header, but its value has been removed by the firewall or proxy server; these values are strings that do not begin with "http://" or "https://";
- server_names means the "referer" request header field contains a server name;
- string means defining the server name and optional uri prefix. The server name can contain "*" at the beginning or end. The server port in the "referer" field was ignored during the check;
touch test_referer.html (In the /op/app/code directory)
imooc1
张彪

Copy after login
If the anti-hotlink configuration is not transferred from the www.zhangbiao.com domain name, an error will be reported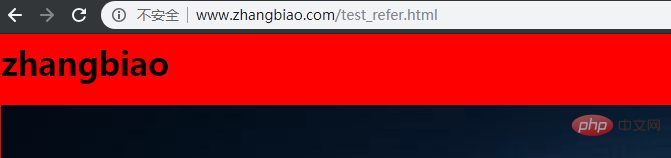
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ { valid_referers none blocked www.zhangbiao.com; if ($invalid_referer) { return 403; } root /opt/app/code/images; } location ~ /test_refer.html { root /opt/app/code; }
Copy after login
Access
http://192.168.1.112/test_refer.html
Copy after login
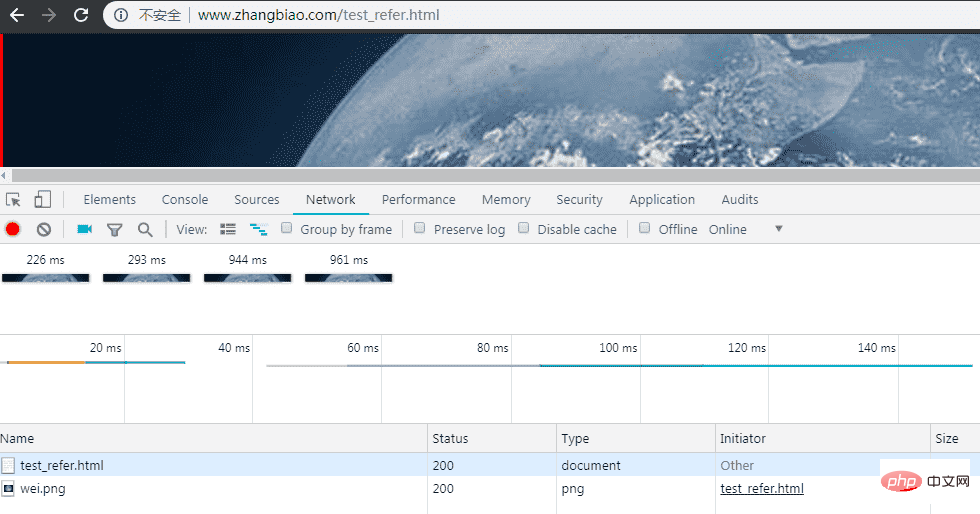
##Access
http://www.zhangbiao.com/test_refer.html
Copy after login
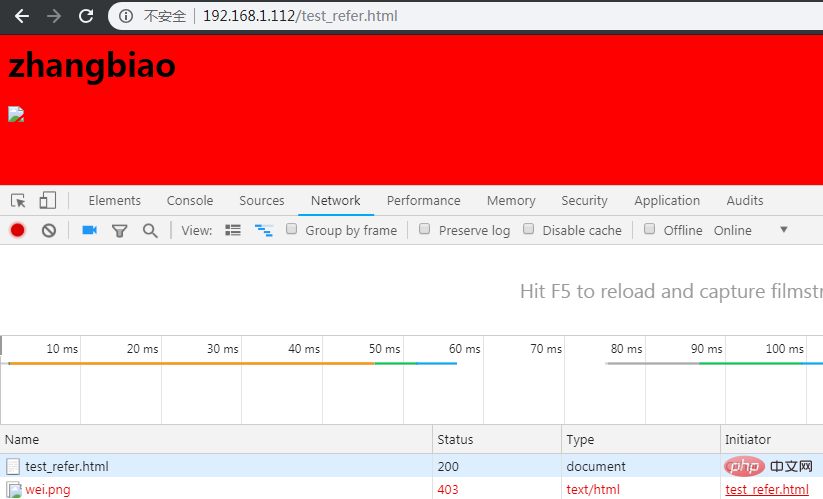
##Allow other websites to access your website resource configuration
The above is the detailed content of How to configure Nginx cross-domain access and anti-leeching. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




 ##Allow other websites to access your website resource configuration
##Allow other websites to access your website resource configuration





