How to use Quartz to implement scheduled tasks in Java?
Scheduler will create a new Job instance based on JobDetail every time it is executed, so as to avoid the problem of concurrent access (the instance of jobDetail is also new)
Quzrtz scheduled tasks are executed concurrently by default, no It will wait for the last task to be executed, and it will be executed as long as the interval is up. If the scheduled task is executed for too long, it will occupy resources for a long time and cause other tasks to be blocked.
@DisallowConcurrentExecution: On the job class, concurrent execution is prohibited Multiple instances of the same job definition (defined by JobDetail).
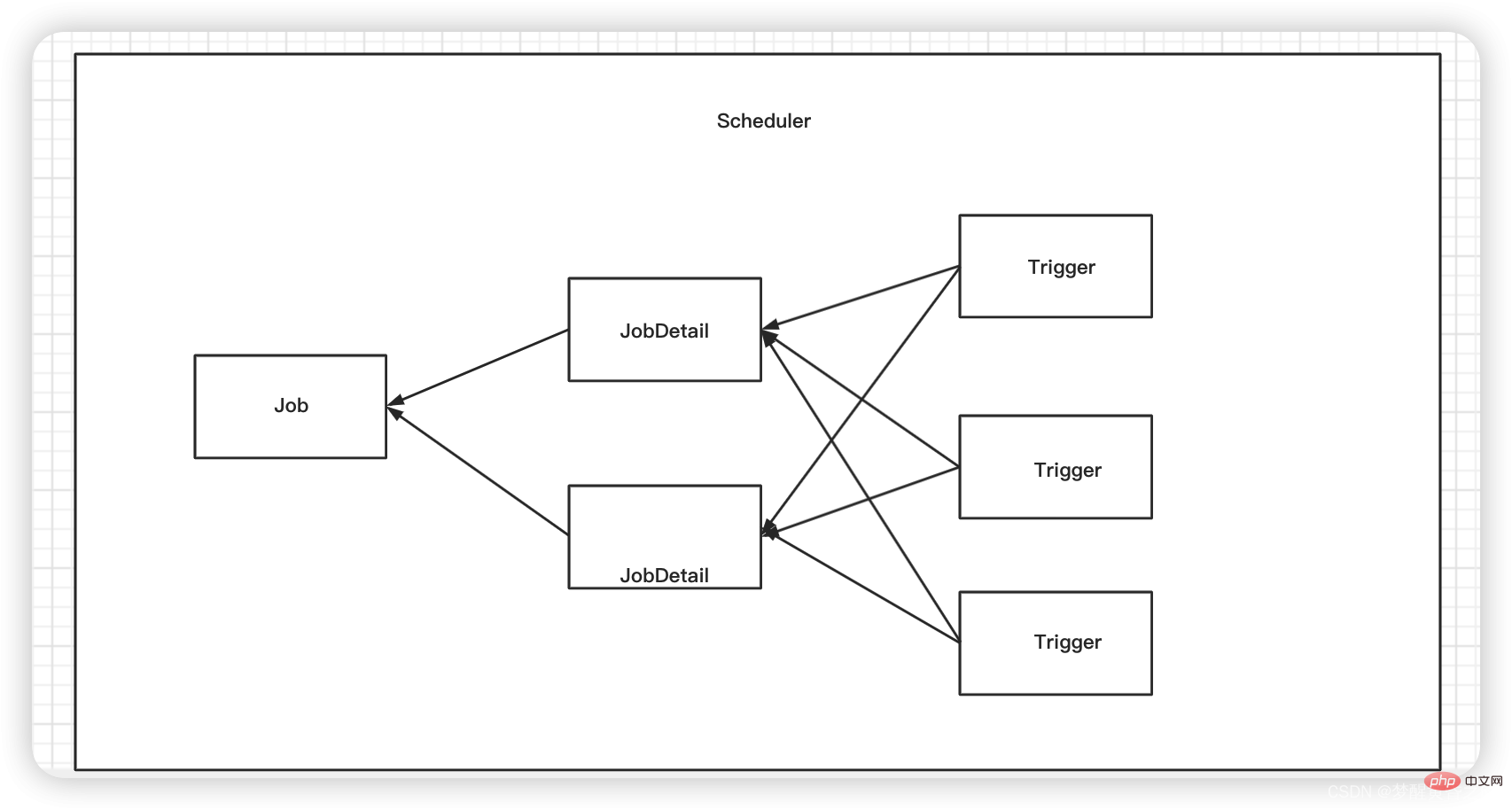
scheduler: It can be understood as a work container or workplace for scheduled tasks. All scheduled tasks are placed in it and can be opened and stop.
trigger: It can be understood as the work rule configuration of a scheduled task. For example, it is called every few minutes, or it is specified to be executed at that time point every day.
jobDetail: Scheduled task information, such as configuring the name of the scheduled task, group, etc.
job: The place where the real business processing logic of scheduled tasks is located.
Simple example
TestClient.Java
import org.quartz.*;
import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory;
public class TaskClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(TaskJob.class)
.withIdentity("job1", "group1") //设置JOB的名字和组
.build();
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity("trigger1", "trigger1")
.startNow()
.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(1)
.repeatForever())
.build();
try {
Scheduler scheduler = StdSchedulerFactory.getDefaultScheduler();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,trigger);
scheduler.start();
} catch (SchedulerException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}TaskJob.Java
import cn.hutool.core.date.DateUtil;
import org.quartz.Job;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionException;
public class TaskJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext jobExecutionContext) throws JobExecutionException {
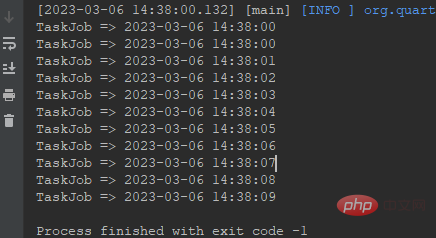
System.out.println("TaskJob => " + DateUtil.now());
}
}
import org.quartz.*;
import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory;
public class TaskClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(TaskJob.class)
.withIdentity("job1", "group1")
.usingJobData("job","jobDetail1.JobDataMap.Value")
.build();
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity("trigger1", "trigger1")
.usingJobData("trigger","trigger.JobDataMap.Value")
.startNow()
.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(1)
.repeatForever())
.build();
try {
Scheduler scheduler = StdSchedulerFactory.getDefaultScheduler();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,trigger);
scheduler.start();
} catch (SchedulerException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}TaskJob.javaimport org.quartz.Job;
import org.quartz.JobDataMap;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionException;
public class TaskJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
JobDataMap jobDataMap = context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap();
JobDataMap triggerMap = context.getTrigger().getJobDataMap();
JobDataMap mergeMap = context.getMergedJobDataMap();
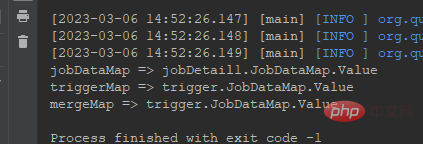
System.out.println("jobDataMap => " + jobDataMap.getString("job"));
System.out.println("triggerMap => " + triggerMap.getString("trigger"));
System.out.println("mergeMap => " + mergeMap.getString("trigger"));
}
}
Assign values through attributes
import org.quartz.*;
import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory;
public class TaskClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(TaskJob.class)
.withIdentity("job1", "group1")
.usingJobData("job","jobDetail1.JobDataMap.Value")
.usingJobData("name","jobDetail1.name.Value") //通过 setName 自动赋值
.build();
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity("trigger1", "trigger1")
.usingJobData("trigger","trigger.JobDataMap.Value")
.usingJobData("name","trigger.name.Value") //如果 Trigger 有值,会覆盖 JobDetail
.startNow()
.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(1)
.repeatForever())
.build();
try {
Scheduler scheduler = StdSchedulerFactory.getDefaultScheduler();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,trigger);
scheduler.start();
} catch (SchedulerException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}import org.quartz.*;
public class TaskJob implements Job {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
System.out.println("name => " + name);
}
}Non-concurrent execution@DisallowConcurrentExecution job class prohibits concurrent execution of multiple instances of the same job definition (JobDetail definition). import cn.hutool.core.date.DateUtil;
import org.quartz.*;
@DisallowConcurrentExecution
public class TaskJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) {
System.out.println("Time => " + DateUtil.now());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}@PersistJobDataAfterExecutionPersistent JobDataMap in JobDetail (invalid for datamap in trigger), if a task is not import cn.hutool.core.date.DateUtil;
import org.quartz.*;
//持久化JobDetail中的JobDataMap(对 trigger 中的 datamap 无效),如果一个任务不是
@PersistJobDataAfterExecution
public class TaskJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) {
JobDataMap triggerMap = context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap();
triggerMap.put("count", triggerMap.getInt("count") + 1);
System.out.println("Time => " + DateUtil.now() + " count =>" + triggerMap.getInt("count"));
}
}Clientimport org.quartz.*;
import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory;
public class TaskClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(TaskJob.class)
.withIdentity("job1", "group1")
.usingJobData("job","jobDetail1.JobDataMap.Value")
.usingJobData("name","jobDetail1.name.Value") //通过 setName 自动赋值
.usingJobData("count",0) //通过 setName 自动赋值
.build();
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity("trigger1", "trigger1")
.usingJobData("trigger","trigger.JobDataMap.Value")
.usingJobData("name","trigger.name.Value") //如果 Trigger 有值,会覆盖 JobDetail
.startNow()
.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(1)
.repeatForever())
.build();
try {
Scheduler scheduler = StdSchedulerFactory.getDefaultScheduler();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,trigger);
scheduler.start();
} catch (SchedulerException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to use Quartz to implement scheduled tasks in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to implement a simple TCP client in Java?
Aug 08, 2025 pm 03:56 PM
How to implement a simple TCP client in Java?
Aug 08, 2025 pm 03:56 PM
Importjava.ioandjava.net.SocketforI/Oandsocketcommunication.2.CreateaSocketobjecttoconnecttotheserverusinghostnameandport.3.UsePrintWritertosenddataviaoutputstreamandBufferedReadertoreadserverresponsesfrominputstream.4.Usetry-with-resourcestoautomati
 Deploying a Java Application to Kubernetes with Docker
Aug 08, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
Deploying a Java Application to Kubernetes with Docker
Aug 08, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
Containerized Java application: Create a Dockerfile, use a basic image such as eclipse-temurin:17-jre-alpine, copy the JAR file and define the startup command, build the image through dockerbuild and run locally with dockerrun. 2. Push the image to the container registry: Use dockertag to mark the image and push it to DockerHub and other registries. You must first log in to dockerlogin. 3. Deploy to Kubernetes: Write deployment.yaml to define the Deployment, set the number of replicas, container images and resource restrictions, and write service.yaml to create
 VS Code shortcut to focus on explorer panel
Aug 08, 2025 am 04:00 AM
VS Code shortcut to focus on explorer panel
Aug 08, 2025 am 04:00 AM
In VSCode, you can quickly switch the panel and editing area through shortcut keys. To jump to the left Explorer panel, use Ctrl Shift E (Windows/Linux) or Cmd Shift E (Mac); return to the editing area to use Ctrl ` or Esc or Ctrl 1~9. Compared to mouse operation, keyboard shortcuts are more efficient and do not interrupt the encoding rhythm. Other tips include: Ctrl KCtrl E Focus Search Box, F2 Rename File, Delete File, Enter Open File, Arrow Key Expand/Collapse Folder.
 Fixed: Windows Update Failed to Install
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:16 PM
Fixed: Windows Update Failed to Install
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:16 PM
RuntheWindowsUpdateTroubleshooterviaSettings>Update&Security>Troubleshoottoautomaticallyfixcommonissues.2.ResetWindowsUpdatecomponentsbystoppingrelatedservices,renamingtheSoftwareDistributionandCatroot2folders,thenrestartingtheservicestocle
 How to use a while loop in Java
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:04 PM
How to use a while loop in Java
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:04 PM
AwhileloopinJavarepeatedlyexecutescodeaslongastheconditionistrue;2.Initializeacontrolvariablebeforetheloop;3.Definetheloopconditionusingabooleanexpression;4.Updatethecontrolvariableinsidethelooptopreventinfinitelooping;5.Useexampleslikeprintingnumber
 What is the process of serialization for a Java object?
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
What is the process of serialization for a Java object?
Aug 08, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
Javaserializationconvertsanobject'sstateintoabytestreamforstorageortransmission,anddeserializationreconstructstheobjectfromthatstream.1.Toenableserialization,aclassmustimplementtheSerializableinterface.2.UseObjectOutputStreamtoserializeanobject,savin
 What is a HashMap in Java?
Aug 11, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
What is a HashMap in Java?
Aug 11, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
AHashMapinJavaisadatastructurethatstoreskey-valuepairsforefficientretrieval,insertion,anddeletion.Itusesthekey’shashCode()methodtodeterminestoragelocationandallowsaverageO(1)timecomplexityforget()andput()operations.Itisunordered,permitsonenullkeyandm
 python numpy array example
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:13 AM
python numpy array example
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:13 AM
The use of NumPy arrays includes: 1. Creating arrays (such as creating from lists, all zeros, all ones, and ranges); 2. Shape operations (reshape, transpose); 3. Vectorization operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, broadcast, mathematical functions); 4. Indexing and slicing (one-dimensional and two-dimensional operations); 5. Statistical calculations (maximum, minimum, mean, standard deviation, summing and axial operations); these operations are efficient and do not require loops, and are suitable for large-scale numerical calculations. Finally, you need to practice more.







