Using Python to develop apps requires the use of a Python module – kivy. kivy is an open source, cross-platform Python development framework for development Use innovative apps. In short, this is a Python desktop program development framework (similar to wxpython and other modules). The powerful thing is that kivy supports linux, mac, windows, android, and ios platforms. This is why this module is needed to develop apps.
Although kivy is cross-platform, if you want to use Python code on different platforms, you also need to package the Python code into an executable program for the corresponding platform. Fortunately, there is a packaging tool under the kivy project Project – buildozer, this is the officially recommended packaging tool because it is relatively simple and has a high degree of automation. Other projects such as Python-for-android can also play a similar role and will not be introduced here.
You need to install the kivy development environment on your PC. Here is a demonstration of the installation process under mac and linux.
install kivy for mac
Install some dependent packages:
brew install pkg-config sdl2 sdl2_image sdl2_ttf sdl2_mixer gstreamer
Install cython and kivy:
pip install cython==0.25 pip install kivy
If an error is reported when installing kivy, use the following method to install kivy:
git clone https://github.com/kivy/kivy python setup.py install
Post-installation test:
$python Python 2.7.10 (default, Jul 15 2017, 17:16:57) [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 9.0.0 (clang-900.0.31)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> >>> import kivy [INFO ] [Logger] Record log in /Users/didi/.kivy/logs/kivy_18-05-08_4.txt [INFO ] [Kivy] v1.10.1.dev0, git-5f6c66e, 20180507 [INFO ] [Python] v2.7.10 (default, Jul 15 2017, 17:16:57) [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 9.0.0 (clang-900.0.31)]
Note: If there is no error when importing the kivy module, it means the installation is successful.
First install dependencies:
yum install make mercurial automake gcc gcc-c++ SDL_ttf-devel SDL_mixer-devel khrplatform-devel mesa-libGLES mesa-libGLES-devel gstreamer-plugins-good gstreamer gstreamer-python mtdev-devel python-devel python-pip java-devel
Install cython and kivy:
pip install Cython==0.20 pip install kivy
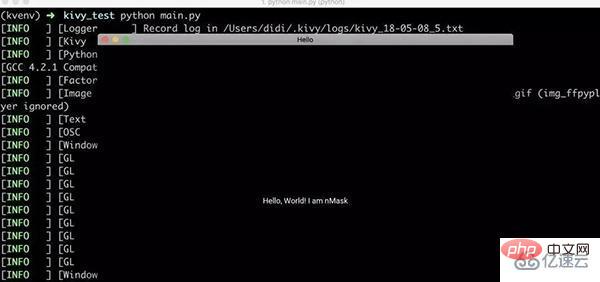
After installing kivy, you can develop an app program. Here is a demonstration of the hello-world program. The more complex usage of kivy is not the focus of this article and will be introduced in writing later.
#! -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from kivy.app import App class HelloApp(App): pass if __name__ == '__main__': HelloApp().run()
Label: text: 'Hello, World! I am nMask'
Simple Note: main.py is the entry function and defines a HelloApp class, which inherits kivy.app; the hello.kv file is a kivy program, which is equivalent to defining the interface style, etc. The naming rule of this file is that the class name is in lowercase and app is removed.
python main.py
Run result:
pip install buildozer
buildozer init
buildozer android debug deploy run
 ##buildozer instructions
##buildozer instructions
Usage: buildozer [--profile] [--verbose] [target]... buildozer --version Available targets: androidAndroid target, based on python-for-android project iosiOS target, based on kivy-ios project android_oldAndroid target, based on python-for-android project (old toolchain) Global commands (without target): distcleanClean the whole Buildozer environment. help Show the Buildozer help. init Create a initial buildozer.spec in the current directory serveServe the bin directory via SimpleHTTPServer setdefault Set the default command to run when no arguments are given versionShow the Buildozer version Target commands: cleanClean the target environment update Update the target dependencies debugBuild the application in debug mode releaseBuild the application in release mode deploy Deploy the application on the device runRun the application on the device serveServe the bin directory via SimpleHTTPServer Target "android_old" commands: adbRun adb from the Android SDK. Args must come after --, or use --alias to make an alias logcat Show the log from the device Target "ios" commands: list_identitiesList the available identities to use for signing. xcodeOpen the xcode project. Target "android" commands: adbRun adb from the Android SDK. Args must come after --, or use --alias to make an alias logcat Show the log from the device p4aRun p4a commands. Args must come after --, or use --alias to make an alias
Error report: You might have missed to install 32bits libs
Solution:
yum -y install --skip-broken glibc.i686 arts.i686 audiofile.i686 bzip2-libs.i686 cairo.i686 cyrus-sasl-lib.i686 dbus-libs.i686 directfb.i686 esound-libs.i686 fltk.i686 freeglut.i686 gtk2.i686 hal-libs.i686 imlib.i686 lcms-libs.i686 lesstif.i686 libacl.i686 libao.i686 libattr.i686 libcap.i686 libdrm.i686 libexif.i686 libgnomecanvas.i686 libICE.i686 libieee1284.i686 libsigc++20.i686 libSM.i686 libtool-ltdl.i686 libusb.i686 libwmf.i686 libwmf-lite.i686 libX11.i686 libXau.i686 libXaw.i686 libXcomposite.i686 libXdamage.i686 libXdmcp.i686 libXext.i686 libXfixes.i686 libxkbfile.i686 libxml2.i686 libXmu.i686 libXp.i686 libXpm.i686 libXScrnSaver.i686 libxslt.i686 libXt.i686 libXtst.i686 libXv.i686 libXxf86vm.i686 lzo.i686 mesa-libGL.i686 mesa-libGLU.i686 nas-libs.i686 nss_ldap.i686 cdk.i686 openldap.i686 pam.i686 popt.i686 pulseaudio-libs.i686 sane-backends-libs-gphoto2.i686 sane-backends-libs.i686 SDL.i686 svgalib.i686 unixODBC.i686 zlib.i686 compat-expat1.i686 compat-libstdc++-33.i686 openal-soft.i686 alsa-oss-libs.i686 redhat-lsb.i686 alsa-plugins-pulseaudio.i686 alsa-plugins-oss.i686 alsa-lib.i686 nspluginwrapper.i686 libXv.i686 libXScrnSaver.i686 qt.i686 qt-x11.i686 pulseaudio-libs.i686 pulseaudio-libs-glib2.i686 alsa-plugins-pulseaudio.i686 python-matplotli
pip install cython==0.25
Solution:
Modify the /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/buildozer/tagets/android.py file:
from distutils.version import LooseVersion 将786行:XXX found how the apk name is really built from the title这一行以下的代码替换为: kivy官方推出了一个buildozer虚拟机镜像,已经安装好了buildozer以及一些依赖文件,为buildozer打包测试提供平台。由于之前我在mac上利用buildozer打包一直报错,后来换成centos也依然没有成功,因此便下载了此虚拟机,测试效果如下: 说明:对于无法解决依赖问题的朋友,可以使用此虚拟机进行程序打包,开发环境还是推荐用自己的本机。 The above is the detailed content of How to use Python to develop apps. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!__sdk_dir = self.android_sdk_dir
build_tools_versions = os.listdir(join(__sdk_dir, 'build-tools'))
build_tools_versions = sorted(build_tools_versions, key=LooseVersion)
build_tools_version = build_tools_versions[-1]
gradle_files = ["build.gradle", "gradle", "gradlew"]
is_gradle_build = any((exists(join(dist_dir, x)) for x in gradle_files)) and build_tools_version >= ’25.0'
buildozer虚拟机