

Microsoft inadvertently set a new record last November when it mitigated a 3.47 Tbps DDoS (distributed denial of service) attack.
In a blog post, the Redmond giant shared Azure DDoS protection data for the third quarter of 2021. The company noted that the second half of 2021 saw an increase in the number of DDoS attacks. DDoS is a popular attack method that anyone can use due to the low price of attack services.
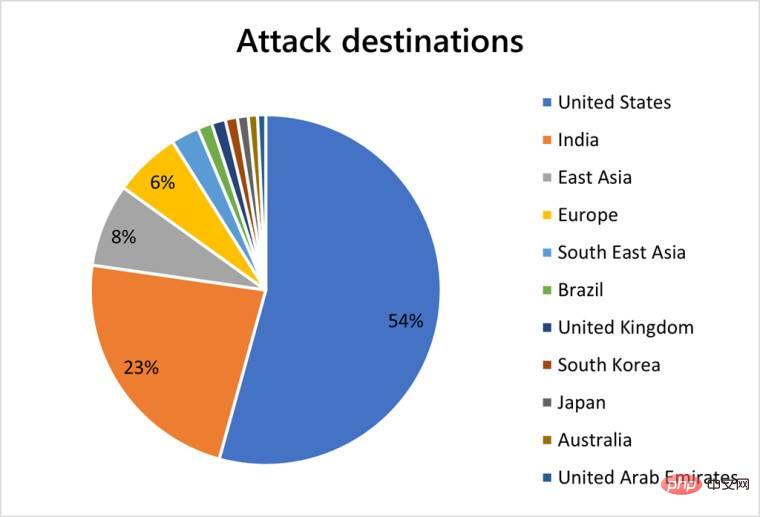
In the second half of 2021, Microsoft mitigated an average of 1,955 attacks per day, a 40% increase from the first half. However, this pales in comparison to the 4,296 attacks mitigated on August 10, 2021. Overall, the company managed to protect its users from more than 359,713 unique attacks in the second half of 2021. While doing so, Microsoft also set new records by protecting Azure servers against DDoS attacks with a throughput of 3.47 Tbps and a packet rate of 340 million packets per second (pps). The attack originated from more than 10,000 sources across the globe, including countries such as the United States, China, South Korea, Russia, Thailand, India, Vietnam, Iran, Indonesia, and Taiwan.
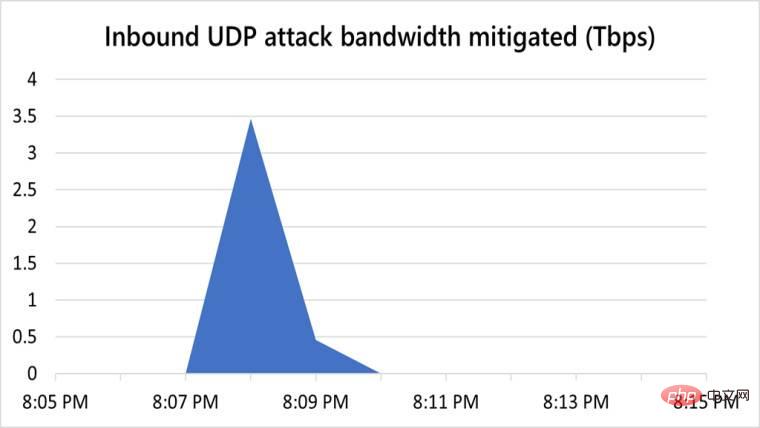
Additionally, the company discovered two other attacks in December with throughput exceeding 2.5 Tbps, both of which occurred again in Asia. Microsoft also noted that there has been a huge uptick in DDoS attacks in East Asia, including Hong Kong and India. A lot of this has to do with the rise of gaming, especially in countries like Hong Kong and South Korea. At the same time, the rise of digital adoption in India has increased “the overall cyber risks faced by the region.”
While Microsoft now has a track record of mitigating the largest DDoS attacks, it's important to note other recent major DDoS attacks. These include an attack mitigated by the Google Security Reliability Team in 2017 with a throughput of 2.54Tbps, and an attack on Amazon Web Services in 2020 with a throughput of 2.3Tbps.
The above is the detailed content of Microsoft sets defense record in response to 3.47 Tbps DDoS attack. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




