
The new features of es6 are: 1. let and const; 2. symbol; 3. Template string; 4. Destructuring expression; 5. Object aspects, such as Map and Set; 6. Function aspects, such as parameters Default value and arrow function; 7. class keyword; 8. promise and proxy; 9. Modularization; 10. Operator.

What are the new features of es6?
https: //m.sbmmt.com/js-tutorial-499866.html
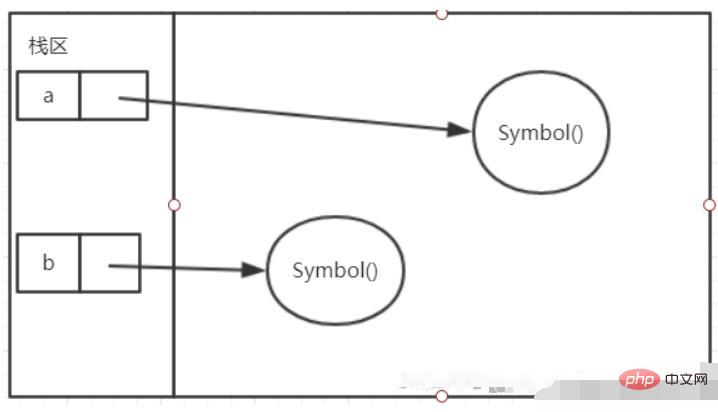
const a = Symbol(); console.log(a); //Symbol() //因为Symbol是基本数据类型,而不是对象,不能 new 。 const a = new Symbol();//报错,Symbol is not a constructor
const a = Symbol();const b = Symbol();
to define;backtickcan be done directly;Determine whether the string contains the parameter string and return a boolean value., determine whether the string starts or ends with the parameter string. Returns a boolean value. These two methods can have a second parameter, a number, indicating the position to start the search.let str = 'blue,red,orange,white';str.includes('blue'); //truestr.startsWith('blue'); //true str.endsWith('blue'); //false
The method returns a new string the specified number of times.console.log('hello'.repeat(2)); //'hellohello'
, use the parameter string to complete the string from the front or back according to the given length, and return a new string.let arr = 'hell';console.log(arr.padEnd(5,'o')); //'hello'console.log(arr.padEnd(6,'o')); //'helloo'console.log(arr.padEnd(6)); //'hell ',如果没有指定将用空格代替 console.log(arr.padStart(5,'o')); //'ohell'
arrayorobject, and then assigns values to the variables in it.
String, and the newMapandSetadded in ES6 can all use destructuring expressions
let [a,b,c] = [1,2,3];console.log(a,b,c); //1,2,3 let [a,b,c] = [1,,3];console.log(a,b,c); //1,undefined,3 let [a,,b] = [1,2,3];console.log(a,b);//1,3 let [a,..b] = [1,2,3]; //...是剩余运算符,表示赋值运算符右边除第一个值外剩余的都赋值给b console.log(a,b); //1,[2,3]
let obj = { name: "ren", age: 12, sex: "male" };let { name, age, sex } = obj;console.log(name, age, sex); //'ren' 12 'male'let { name: myName, age: myAge, sex: mySex } = obj; //自定义变量名console.log(myName, myAge, mySex); //'ren' 12 'male'
or ES6symbolvalues, while Map can be any value.
, which stores the number of key-value pairs, while the object object has no similar attribute.
let myMap = new Map([['name','ren'],['age',12]]);console.log(myMap); //{'name'=>'ren','age'=>12}myMap.set('sex','male');console.log(myMap); //{'name'=>'ren','age'=>12,'sex'=>'male'}console.log(myMap.size); //3myMap.get('name'); //'ren'myMap.has('age'); //truemyMap.delete('age'); //truemyMap.has('age'); //falsemyMap.get('age'); //undefined
each element is unique
.
let mySet = new Set([1,2,3]); //里面要传一个数组,否则会报错console.log(mySet); //{1,2,3}mySet.add(4);console.log(mySet); //{1,2,3,4}mySet.delete(1); //truemySet.has(1); //falseconsole.log(mySet); //{2,3,4}
, you can easilyachieve duplication of arrays
let arr = [1,1,2,3,4,4];let mySet = new Set(arr); let newArr = Array.from(mySet);console.log(newArr); //[1,2,3,4]
Array.from()是内置对象Array的方法,实例数组不能调用includes()参数:数值 -------- 返回值:true/falsemap()、filter()参数:函数-------- 返回值:数组forEach()参数:函数-------- 返回值:undefinedfind()参数:函数-------- 返回值:数值some()、every()参数:函数-------- 返回值:true/falseArray.from()方法可以将可迭代对象转换为新的数组。
let arr = [1, 2, 3];let obj = { double(n) { return n * 2; }}console.log(Array.from(arr, function (n){ return this.double(n);}, obj)); // [2, 4, 6]
参数:数值 -------- 返回值:true/falseincludes()方法------是查看数组中是否存在这个元素,存在就返回true,不存在就返回false
let arr = [1,33,44,22,6,9]let ary = arr.includes(22)console.log(ary)
参数:函数-------- 返回值:数组map()方法-----要利用原数组经过运算后的数组,或者从对象数组中拿某个属性filter()方法------是将符合挑选的筛选出来成为一个新数组,新数组不会影响旧数组。
参数:函数-------- 返回值:undefined
forEach()方法------是循环遍历数组中的每一项,没有返回值
find()方法---------是查找数组中符合条件的第一个元素,直接将这个元素返回出来
let arr = [1,33,44,2,6,9]let a1= []arr.forEach((v, i)=>{ if (v > 10) { a1.push(arr[i]) } })console.log(a1) [33,44]let a2= arr.find(v => v > 10)console.log(a2)
参数:函数-------- 返回值:数值
find()方法----------是查找数组中符合条件的第一个元素,直接将这个元素返回出来
let arr = [1,33,44,2,6,9]let a= arr.find(v => v > 10)console.log(a) // 33
参数:函数-------- 返回值:true/false
some()方法------找到一个符合条件的就返回true,所有都不符合返回false。every()方法------数组所有值都符合条件才会返回true,有一个不符合返回false。
let arr = [1,2,3,4,6,11]let newarr = arr.some(function(v){ return v > 10})console.log(newarr) //truelet newarr2 = arr.every(function(v){ return v > 10})console.log(newarr2) //false
在 ES6 中,添加了Object.is()、Object.assign()、Object.keys()、Object.values()、Object.entries()等方法。
Object.is()方法用来判断两个值是否为同一个值,返回一个布尔类型的值。const obj1 = {};const obj2 = {};console.log(Object.is(obj1, obj2)); // falseconst obj3 = {};const value1 = obj3;const value2 = obj4;console.log(Object.is(value1, value2)); // true
Object.assign()方法用于将所有可枚举属性的值从一个或多个源对象分配到目标对象,并返回目标对象。------难理解看实例const obj1 = { a: 1 };const obj2 = { b: 2 };const obj3 = { a:5 , c: 3 };//对象合并,把后面对像合并到第一个对象,对象里相同的属性会覆盖Object.assign(obj1, obj2, obj3);console.log(obj1); // { a: 5, b: 2 , c:3}
箭头函数实现了一种更加简洁的书写方式。箭头函数内部没有arguments,也没有prototype属性,所以不能用new关键字调用箭头函数。
let add = (a,b) => { return a+b;}let print = () => { console.log('hi');}let fn = a => a * a; //当只有一个参数时,括号可以省略,函数体只有单行return语句时,大括号也可以省略。
var age = 123; let obj = { age:456, say:() => { console.log(this.age); //this指向window } };obj.say(); //123
class作为对象的模板被引入ES6,你可以通过class关键字定义类。class的本质依然是一个函数。
extends关键字实现。constructor中调用super()讲不清楚,等我学会了,后面在讲
ES6使用关键字import导入模块(文件),有两种常用的方式:
import ‘模块名称’ from ‘路径’;import ‘路径’;
ES6 通过 export 和export default 导出模块。
let name = 'ren',age = 12;export {name,age}; //注意:变量需要用大括号包裹,然后才能向外输出
模块化优点
1.防止命名冲突
2.复用性强
...扩展运算符
可选链?.
函数绑定运算符::
若本文对你有帮助 点个赞 点个关注
推荐学习:《react视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What are the new features of es6?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 es6 new features
es6 new features What are the new features of es6
What are the new features of es6 The role of c++this pointer
The role of c++this pointer java regular expression matching string
java regular expression matching string The difference between JD.com's self-operated flagship store and its official flagship store
The difference between JD.com's self-operated flagship store and its official flagship store Is the matcha platform formal?
Is the matcha platform formal? What types of files can be identified based on
What types of files can be identified based on BigDecimal method to compare sizes
BigDecimal method to compare sizes



