How to call Oracle's stored procedure
In Oracle, the method of calling a stored procedure is "declare...begin the stored procedure call and start calling the procedure in sequence END;"; the stored procedure includes three parts: process declaration, execution process part and stored procedure exception. In this part, stored procedures can have parameterless procedures and parameterized procedures.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, Oracle version 12c, Dell G3 computer.
How to call Oracle's stored procedure
Oracle stored procedure contains three parts: process declaration, execution process part, and stored procedure exception.
Oracle stored procedures can have parameterless stored procedures and parameterized stored procedures.
Oracle stored procedure creation syntax
create or replace procedure 存储过程名称
(
--定义输入、输出参数--
参数名1 in 参数类型,
参数名2 in 参数类型,
参数名3 in 参数类型,
参数名4 out 参数类型
)
as
--定义变量--
--变量名 变量数据类型;如:
-- numCount integer;
begin
--处理方法-
end;Above we create a function that handles addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division calculations, then we can also build storage Procedure
/*****
** 创建加、减、乘、除计算的存储过程
**输入参数: 数字1,数字2,计算类型
**输出参数: 数字3
*****/
create or replace procedure Proc_Test
(
--定义输入、输出参数--
num_A in integer,
num_B in integer,
numType in integer,
num_C out integer
)
as
--定义变量--
-- numCount integer;
-- numStr varchar(20);
begin
--判断计算类型--
if numType=1 then
num_C := num_A + num_B;
elsif numType=2 then
num_C := num_A - num_B;
elsif numType=3 then
num_C := num_A * num_B;
elsif numType=4 then
num_C := num_A / num_B;
else
--其它处理
dbms_output.put_line('其它处理');
end if;
end;So how to call the stored procedure
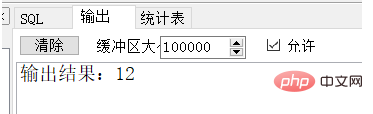
declare num_C integer; begin --调用存储过程--- Proc_Test(3,4,3,num_C); dbms_output.put_line('输出结果:'|| num_C ); end;
Output result
Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to call Oracle's stored procedure. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to uninstall MySQL and clean residual files
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
How to uninstall MySQL and clean residual files
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
To safely and thoroughly uninstall MySQL and clean all residual files, follow the following steps: 1. Stop MySQL service; 2. Uninstall MySQL packages; 3. Clean configuration files and data directories; 4. Verify that the uninstallation is thorough.
 MySQL vs. Oracle: Licensing, Features, and Benefits
May 08, 2025 am 12:05 AM
MySQL vs. Oracle: Licensing, Features, and Benefits
May 08, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The main difference between MySQL and Oracle is licenses, features, and advantages. 1. License: MySQL provides a GPL license for free use, and Oracle adopts a proprietary license, which is expensive. 2. Function: MySQL has simple functions and is suitable for web applications and small and medium-sized enterprises. Oracle has powerful functions and is suitable for large-scale data and complex businesses. 3. Advantages: MySQL is open source free, suitable for startups, and Oracle is reliable in performance, suitable for large enterprises.
 MySQL and Oracle: Exploring Performance and Scalability
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and Oracle: Exploring Performance and Scalability
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The difference between MySQL and Oracle in performance and scalability is: 1. MySQL performs better on small to medium-sized data sets, suitable for fast scaling and efficient reading and writing; 2. Oracle has more advantages in handling large data sets and complex queries, suitable for high availability and complex business logic. MySQL extends through master-slave replication and sharding technologies, while Oracle achieves high availability and scalability through RAC.
 MySQL vs. Oracle: Understanding Licensing and Cost
May 03, 2025 am 12:19 AM
MySQL vs. Oracle: Understanding Licensing and Cost
May 03, 2025 am 12:19 AM
MySQL uses GPL and commercial licenses for small and open source projects; Oracle uses commercial licenses for enterprises that require high performance. MySQL's GPL license is free, and commercial licenses require payment; Oracle license fees are calculated based on processors or users, and the cost is relatively high.
 How to learn Java without taking detours. Share methods and techniques for efficiently learning Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to learn Java without taking detours. Share methods and techniques for efficiently learning Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
The key to learning Java without taking detours is: 1. Understand core concepts and grammar; 2. Practice more; 3. Understand memory management and garbage collection; 4. Join online communities; 5. Read other people’s code; 6. Understand common libraries and frameworks; 7. Learn to deal with common mistakes; 8. Make a learning plan and proceed step by step. These methods can help you master Java programming efficiently.
 MongoDB vs. Oracle: Exploring NoSQL and Relational Approaches
May 07, 2025 am 12:02 AM
MongoDB vs. Oracle: Exploring NoSQL and Relational Approaches
May 07, 2025 am 12:02 AM
In different application scenarios, choosing MongoDB or Oracle depends on specific needs: 1) If you need to process a large amount of unstructured data and do not have high requirements for data consistency, choose MongoDB; 2) If you need strict data consistency and complex queries, choose Oracle.
 What to learn Java? A summary of Java learning routes and essential knowledge points
May 20, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
What to learn Java? A summary of Java learning routes and essential knowledge points
May 20, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
Learning Java requires learning basic syntax, object-oriented programming, collection frameworks, exception handling, multithreading, I/O streaming, JDBC, network programming, and advanced features such as reflection and annotation. 1. The basic syntax includes variables, data types, operators and control flow statements. 2. Object-oriented programming covers classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation and abstraction. 3. The collection framework involves ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, and HashMap. 4. Exception handling ensures program robustness through try-catch block. 5. Multithreaded programming requires understanding of thread life cycle and synchronization. 6. I/O streams are used for data reading, writing and file operations. 7. JDBC is used to interact with databases. 8. Network programming passes S
 Connection and data visualization of Oracle databases with BI tools such as Tableau
May 19, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Connection and data visualization of Oracle databases with BI tools such as Tableau
May 19, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
To connect Oracle database to Tableau for data visualization, you need to follow the following steps: 1. Configure Oracle database connection in Tableau, use ODBC or JDBC drivers; 2. Explore data and create visualizations, such as bar charts, etc.; 3. Optimize SQL queries and indexes to improve performance; 4. Use Oracle's complex data types and functions to implement through custom SQL queries; 5. Create materialized views to improve query speed; 6. Use Tableau's interactive functions such as dashboard for in-depth analysis.







