
There are three types of parameter assignment in PHP functions: 1. Value-passing assignment, copying the value of the actual parameter and assigning it to the formal parameter of the function; 2. Reference-passing assignment, copying the memory address of the actual parameter One copy is then passed to the formal parameter of the function, and then the actual parameter value is assigned to the formal parameter; 3. Directly specify the default value for the parameter of the function, the syntax is "function name (parameter variable = 'value')".

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP7.1 version, DELL G3 computer
The parameter assignment of the php function is 3 Type:
1. Value transfer assignment
2. Reference transfer assignment
3.Default parameter value
The following will give you a detailed introduction .
1. Value passing assignment
Value passing is the default value passing method for functions in PHP, also known as "copy passing by value".
As the name suggests, the value assignment method will copy the value of the actual parameter and then pass it to the formal parameter of the function, so operating the value of the parameter in the function will not affect the actual parameters outside the function.
So if you don’t want the function to modify the value of the actual parameter, you can pass it by value.
Example:
<?php
header(&#39;content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8&#39;);
function swap($a, $b){
echo &#39;函数内,交换前 $a = &#39;.$a.&#39;, $b = &#39;.$b.&#39;<br>&#39;;
$temp = $a;
$a = $b;
$b = $temp;
echo &#39;函数内,交换后 $a = &#39;.$a.&#39;, $b = &#39;.$b.&#39;<br>&#39;;
}
$x = 5;
$y = 7;
echo &#39;函数外,交换前 $x = &#39;.$x.&#39;, $y = &#39;.$y.&#39;<br>&#39;;
swap($x, $y);
echo &#39;函数外,交换后 $x = &#39;.$x.&#39;, $y = &#39;.$y;
?>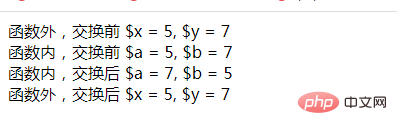
2. Pass-by-reference assignment
Passing parameters by reference means passing the actual parameters Make a copy of the memory address and pass it to the formal parameter of the function, and then assign the actual parameter value to the formal parameter.
Both the actual parameters and the formal parameters point to the same memory address, so the function's operation on the formal parameters will affect the actual parameters outside the function.
Passing by reference is to pass the memory address of the actual parameter to the formal parameter of the function. Therefore, the actual parameters and formal parameters point to the same memory address. At this time, all operations inside the function will affect the values of the actual parameters outside the function. The method of passing by reference is to add a & symbol on the basis of value passing, as shown below:
function name (&参数1, &参数2, ..., &参数3) {
...
} Example:
<?php
header(&#39;content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8&#39;);
function swap(&$a, &$b){
echo &#39;函数内,交换前 $a = &#39;.$a.&#39;, $b = &#39;.$b.&#39;<br>&#39;;
$temp = $a;
$a = $b;
$b = $temp;
echo &#39;函数内,交换后 $a = &#39;.$a.&#39;, $b = &#39;.$b.&#39;<br>&#39;;
}
$x = 5;
$y = 7;
echo &#39;函数外,交换前 $x = &#39;.$x.&#39;, $y = &#39;.$y.&#39;<br>&#39;;
swap($x, $y);
echo &#39;函数外,交换后 $x = &#39;.$x.&#39;, $y = &#39;.$y;
?>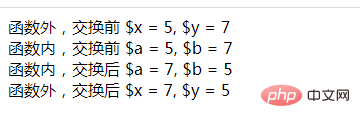
3. Default parameter value
The default parameter is to specify a default value for one or more formal parameters of the function. If the corresponding parameter is not passed in when calling the function value, then the function will use this default value, which can avoid errors when calling without parameters, and can also make some programs more reasonable. If the corresponding parameters are passed in, this default value will be replaced.
The default parameters of the function are as follows:
function name ($str = &#39;默认值&#39;, $url) {
echo $str;
}You need to use = to connect the default values of the shape participants.
Example:
<?php
function add($a, $b=56){
echo $a.&#39; + &#39;.$b.&#39; = &#39;.($a+$b).&#39;<br>&#39;;
}
add(11);
add(37, 29);
?>The default parameters can also be multiple, and the default parameters must be placed to the right of the non-default parameters, and The value of the specified default parameter must be a specific value, such as a number or a string, and cannot be a variable.
<?php
function add($a, $b=33, $c=57){
echo $a.&#39; + &#39;.$b.&#39; + &#39;.$c.&#39; = &#39;.($a+$b+$c).&#39;<br>&#39;;
}
add(11);
add(31, 22);
add(64, 9, 7);
?>
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What are the types of parameter assignments in php functions?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!