
This article brings you relevant knowledge about data volumes in docker. Data volumes can share or reuse data between containers. Changes in the data volumes will not be included in the update of the image. , hope it helps everyone.

Recommended learning: "docker video tutorial"
Using docker When a container is created, a series of data files will be generated. These data files will disappear when the docker container is deleted, but some of the generated content is expected to be saved for other purposes. Docker will apply and run the environment When packaged and released into containers, programmers hope that some of the data generated during the running process can be persisted, and we hope to be able to share data between containers.
Generally speaking, the docker container data volume can be regarded as a commonly used USB disk. It exists in one or more containers and is mounted to the container by docker, but it does not belong to the joint file system. Docker does not The data volumes mounted on the container will be deleted when it is deleted.
Data volumes can share or reuse data between containers
Changes in data volumes can take effect immediately
In data volumes Changes will not be included in the update of the image
The data volume will always exist by default, even if the container is deleted
The life cycle of the data volume continues until no container uses it
Data volumes: Data Volumes The data in the container is directly mapped to the local host environment
Data volume container:Data Volume Containers Use specific containers to maintain data volumes
Syntax
Copy host files to the container
docker cp [OPTIONS] SRC_PATH CONTAINER:DEST_PATH
Copy files in the container to the host
docker cp [OPTIONS] CONTAINER:SRC_PATH DEST_PATH
Common parameters
-L: Keep the link in the source target
Basic use
Copy the host file to the container
docker cp /data/index.html nginx:/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
Copy the file in the container to the host
docker cp nginx:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf /data
Data volume (Data Volumes) is a special directory that can be used by one or more containers. It maps the host operating system directory directly into the container.
Notes on data volumes
To mount a data volume, it is best to create a startup container through run instead of create/start. After the create/start command creates a startup container, It is quite troublesome to mount the data volume again and requires modifying many configuration files, but it is not impossible.
Docker official website recommends mounting directories as much as possible instead of mounting files
Data volume type
Host data volume: directly on the host in the file system but the container can access (bind mount)
named data volume: a data volume managed by Docker on the disk, but this volume has a name.
Anonymous data volume: A data volume managed by Docker on the disk. It is not easy to find because there is no name. Docker manages these files.
Host data volume
bind mounts: The data in the container is stored anywhere in the host file system, even in some important system directories or files middle. Processes other than docker can also modify them arbitrarily.
When using bind mounts, the host directory or file is mounted into the container. The container will use or modify the host's data according to the absolute path of the mounting directory or file. Directories or files in the host do not need to exist in advance and will be automatically created when needed.
Using bind mounts is very good in terms of performance, but it depends on the host having a properly structured file system.
Containers that use bind mounts can modify the host file system through the process inside the container, including creating, modifying and deleting important system files and directories. Although this function is very powerful, it will obviously also cause security problems. The impact on aspects, including the impact on processes other than Docker on the host
Notes
If you mount an empty data volume to a non-empty directory in the container, then in this directory The files will be copied to the data volume
If you mount a non-empty data volume to a directory in the container, the directory in the container will display the data in the data volume. If the directory in the original container has data, the original data will be hidden
Basic use
Syntax
docker run -v /宿主机绝对路径目录:/容器内目录 镜像名
Basic use
docker run -itd --name mysql --restart always --privileged=true -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin -v /data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql mysql:5.7.31 --character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_general_ci
Container directory permissions
Pass -v to the path inside the container: ro rw Change read and write permissions ro:readonly read-only
rw:readwrite readable and writable
docker run -it -v / Host absolute path directory:/Container directory:ro Image name
docker run -it -v/Host absolute path directory:/Container directory:rw Image name
For example:
docker run -d -P --name nginx05 -v nginx1:/etc/nginx:ro nginx docker run -d -P --name nginx05 -v nginx2:/etc/nginx:rw nginx
ro As long as you see ro, it means that this path can only be operated through the host, and cannot be operated inside the container!
Named data volume
Basic use
docker run -itd --name nginx -p 80:80 -v lagouedu-nginx:/etc/nginx nginx:1.19.3-
alpine
View the docker data volume docker volume ls
View the lagouedu-nginx host directory
docker volume inspect lagouedu-nginx
Enter the docker data volume default directory
cd /var/lib/docker/volumes/lagouedu-nginx
View files
ls
All files docker saves in the _data directory by default cd _data
Delete container
docker rm $(docker stop $(docker ps -aq))
查看挂载数据是否还存在,通过查看数据,发现删除容器后,宿主机中的数据还存在
ls
匿名数据卷
基本使用
docker run -itd --name nginx -p 80:80 -v /etc/nginx nginx:1.19.3-alpine 查看docker数据卷 docker volume ls
查看宿主机目录
docker volume inspect dbd07daa4e40148b11....
进入docker数据卷默认目录
cd /var/lib/docker/volumes/dbd07daa4e40148b11....
查看文件
ls
所有的文件docker默认保存在_data目录中 cd _data
删除容器
docker rm $(docker stop $(docker ps -aq))
查看挂载数据是否还存在,通过查看数据,发现删除容器后,宿主机中的数据还存在
ls
run命令
常用参数
--volumes-from
如果用户需要在多个容器之间共享一些持续更新的数据,最简单的方式是使用数据卷容器。数据卷容器
也是一个容器,但是它的目的是专门用来提供数据卷供其他容器挂载。
发现创建好的数据卷容器是处于停止运行的状态,因为使用 —volumes-from 参数所挂载数据卷的容器 自己并不需要保持在运行状态。
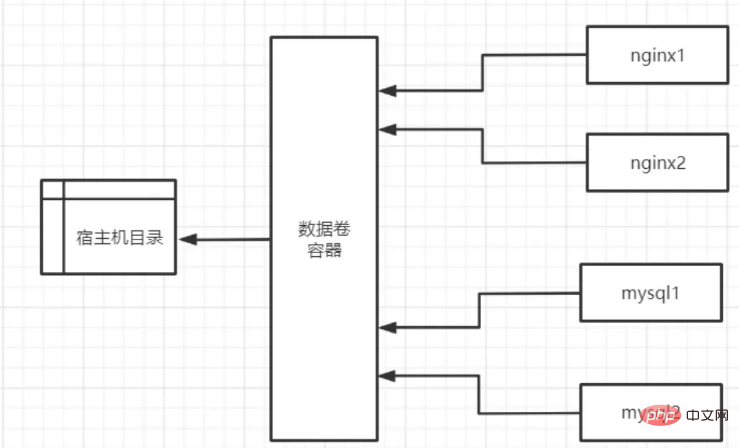
基本使用
docker run -d --name data-volume -v /data/nginx:/usr/share/nginx/html -v /data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql centos:7.8.2003 docker run -itd --name nginx01 -p 80:80 --volumes-from data-volume nginx:1.19.3- alpine echo "nginx" > /data/nginx/index.html http://192.168.198.100 docker run -itd --name nginx02 -p 81:80 --volumes-from data-volume nginx:1.19.3- alpine http://192.168.198.100:81 docker run -itd --name mysql01 --restart always --privileged=true -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin --volumes-from data-volume mysql:5.7.31 -- character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_general_ci docker run -itd --name mysql02 --restart always --privileged=true -p 3307:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin --volumes-from data-volume mysql:5.7.31 -- character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_general_ci
推荐学习:《docker视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of The most detailed tutorial on organizing docker data volumes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The difference between k8s and docker
The difference between k8s and docker
 What are the methods for docker to enter the container?
What are the methods for docker to enter the container?
 What should I do if the docker container cannot access the external network?
What should I do if the docker container cannot access the external network?
 What is the use of docker image?
What is the use of docker image?
 The computer has Internet access but the browser cannot open the web page
The computer has Internet access but the browser cannot open the web page
 How to use btbook magnetic search
How to use btbook magnetic search
 windows ultimate
windows ultimate
 How to create a WeChat clone on Huawei mobile phone
How to create a WeChat clone on Huawei mobile phone