What is the centos shutdown command?
centos shutdown command: 1. "halt" command, you can shut down immediately; 2. "poweroff" command, you can shut down immediately; 3. "shutdown -h now" command, you can shut down immediately; 4. "shutdown" -h number" command, you can specify the minutes to automatically shut down; 5. "init 0".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: CentOS 6 system, Dell G3 computer.
Linux centos restart command:
reboot- ##shutdown -r now
Immediately Restart (for root user) - shutdown -r 10
Automatically restart after 10 minutes (for root user) - shutdown -r 20:35
Restart when the time is 20:35 (for root users)
Linux centos Shutdown command:
halt
Shut down immediatelypoweroff
Shut down immediately- shutdown -h now
Shut down immediately (for root users) shutdown -h 10
Automatically shut down after 10 minutesinit 0
Shutdown
shutdown - c command cancel
1. shutdown
shutdown command safely shuts down the system. Some users will shut down Linux by directly cutting off the power supply, which is very dangerous. Because Linux is different from Windows, there are many processes running in the background, so forced shutdown may cause the data of the process to be lost, put the system in an unstable state, and even damage the hardware equipment in some systems. When using the shutdown command before shutting down the system, the system administrator will notify all logged-in users that the system will be shut down. And the login command will be frozen, that is, new users can no longer log in. It is possible to shut down directly or delay shutting down for a certain period of time. It may also restart. This is determined by the fact that all processes will receive signals sent by the system. This gives programs like vi time to save the document currently being edited, and programs like mail and news can exit normally, etc. shutdown performs its job by sending a signal [signal] to the init program, asking it to change the runlevel. Runlevel 0 is used to shut down [halt], runlevel 6 is used to reactivate [reboot] the system, and runlevel 1 is used to allow the system to enter management work. Status; This is the default, assuming neither -h nor -r parameters are given to shutdown. To understand what actions were taken during the shutdown (halt) or restart (reboot) process, you can see the runlevels-related information in this file /etc/inittab. shutdown Parameter description: [-t] Tell init how long to shut down before changing to other runlevels. [-r] Restart the calculator. [-k] does not actually shut down, but only sends a warning signal to each login [login]. [-h] Turn off the power after shutdown [halt]. [-n] No need to init, but shut down by yourself. Using this option is discouraged, and the consequences of this option are often not always what you expect. [-c] cancel current processCancel the shutdown program currently being executed. So of course this option has no time parameter, but you can enter a message to explain it, and this message will be sent to each user. [-f] Ignore fsck when restarting the calculator [reboot]. [-F] Force fsck when restarting the calculator [reboot]. [-time] Set the time before shutdown [shutdown].2. Halt—the simplest shutdown command
In fact, halt is to call shutdown -h. When halt is executed, the application process is killed, the sync system call is executed, and the kernel is stopped after the file system write operation is completed. Parameter description: [-n] Prevent sync system calls. It is used after patching the root partition with fsck to prevent the kernel from overwriting the patched one with an old version of the superblock. Super block. [-w] is not a real restart or shutdown, it just writes wtmp [/var/log/wtmp] records. [-d] Do not write wtmp records [included in option [-n]]. [-f] Force shutdown or restart without calling shutdown. [-i] Before shutting down (or restarting), turn off all network interfaces. [-p] This option is the default option. Just call poweroff when shutting down.3. init
init is the ancestor of all processes. Its process number is always 1, so sending the TERM signal to init will terminate all user processes and daemons. Process etc. shutdown uses this mechanism. init defines 8 runlevels (runlevel),init 0 is shutdown, init 1 is restart.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the centos shutdown command?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 .NET Core Quick Start Tutorial 1. The beginning: Talking about .NET Core
May 07, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
.NET Core Quick Start Tutorial 1. The beginning: Talking about .NET Core
May 07, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
1. The Origin of .NETCore When talking about .NETCore, we must not mention its predecessor .NET. Java was in the limelight at that time, and Microsoft also favored Java. The Java virtual machine on the Windows platform was developed by Microsoft based on JVM standards. It is said to be the best performance Java virtual machine at that time. However, Microsoft has its own little abacus, trying to bundle Java with the Windows platform and add some Windows-specific features. Sun's dissatisfaction with this led to a breakdown of the relationship between the two parties, and Microsoft then launched .NET. .NET has borrowed many features of Java since its inception and gradually surpassed Java in language features and form development. Java in version 1.6
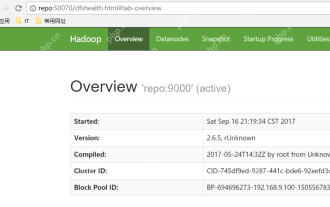 Hadoop pseudo-distributed cluster construction
May 07, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Hadoop pseudo-distributed cluster construction
May 07, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Software preparation I am using a virtual machine with CentOS-6.6, with the host name repo. Refer to the steps to install a Linux virtual machine in Windows, I installed JDK in that virtual machine, refer to the guide to installing JDK in Linux. In addition, the virtual machine is configured with a key-free login itself, and the settings for configuring key-free login between each virtual machine are referenced. The download address of Hadoop installation package is: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/apache/hadoop/common/. I am using hadoop 2.6.5 version. Upload the Hadoop installation package to the server and unzip [root@repo~]#tarzxv
 Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Integrating Postman applications on CentOS can be achieved through a variety of methods. The following are the detailed steps and suggestions: Install Postman by downloading the installation package to download Postman's Linux version installation package: Visit Postman's official website and select the version suitable for Linux to download. Unzip the installation package: Use the following command to unzip the installation package to the specified directory, for example /opt: sudotar-xzfpostman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz-C/opt Please note that "postman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz" is replaced by the file name you actually downloaded. Create symbols
 CentOS: What Led to the Decision to End Support
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:10 AM
CentOS: What Led to the Decision to End Support
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:10 AM
RedHatendedsupportforCentOStoshifttowardsacommerciallyfocusedmodelwithCentOSStream.1)CentOStransitionedtoCentOSStreamforRHELdevelopment.2)ThisencourageduserstomovetoRHEL.3)AlternativeslikeAlmaLinux,RockyLinux,andOracleLinuxemergedasreplacements.
 How to optimize HDFS configuration on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to optimize HDFS configuration on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Optimizing the performance of Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) on CentOS systems can be achieved through a variety of methods, including adjusting system kernel parameters, optimizing HDFS configuration files, and improving hardware resources. The following are detailed optimization steps and suggestions: Adjust the system kernel parameters to increase the limit on the number of files opened by a single process: Use the ulimit-n65535 command to temporarily adjust. If it needs to take effect permanently, please edit the /etc/security/limits.conf and /etc/pam.d/login files. Optimize TCP parameters: Edit /etc/sysctl.conf file, add or modify the following content: net.ipv4.tcp_tw
 CentOS: A Community-Driven Linux Distribution
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:03 AM
CentOS: A Community-Driven Linux Distribution
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:03 AM
CentOS is a stable, enterprise-grade Linux distribution suitable for server and enterprise environments. 1) It is based on RedHatEnterpriseLinux and provides a free, open source and compatible operating system. 2) CentOS uses the Yum package management system to simplify software installation and updates. 3) Support advanced automation management, such as using Ansible. 4) Common errors include package dependency and service startup issues, which can be solved through log files. 5) Performance optimization suggestions include the use of lightweight software, regular cleaning of the system and optimization of kernel parameters.
 CentOS: Security, Stability, and Performance
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:11 AM
CentOS: Security, Stability, and Performance
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:11 AM
CentOS is the first choice for server and enterprise environments for its superior security, stability and performance. 1) Security provides forced access control through SELinux to improve system security. 2) Stability is supported by the LTS version for up to 10 years to ensure the stability of the system. 3) Performance significantly improves system response speed and resource utilization by optimizing kernel and system configuration.
 How to customize the interface of GitLab on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
How to customize the interface of GitLab on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
Customize the GitLab interface on CentOS system to easily create a personalized workspace! The following steps will guide you how to change the interface language and customize the homepage style: Interface language settings Log in to GitLab: Access your GitLab server address in your browser and log in. Access settings: Click on your user avatar in the upper right corner and select "Settings". Go to User Interface Settings: In the menu on the left, find "Preferences" and select "UserInterface". Select language: In the "User Interface" drop-down menu, select "Chinese(Simplified)",







