
RBAC是英文Role-based Access Control的首字母缩写,中文意思是基础角色的权限控制,它是一种思想,根据 RBAC 思想进行数据表设计,更好的完成不同角色的对应的权限控制。
如何使用RBAC思想进行数据表的设计
如果我们的项目允许一个后台管理用户可能有1个或者2个及2个以上的多个角色,按照下面进行设计:
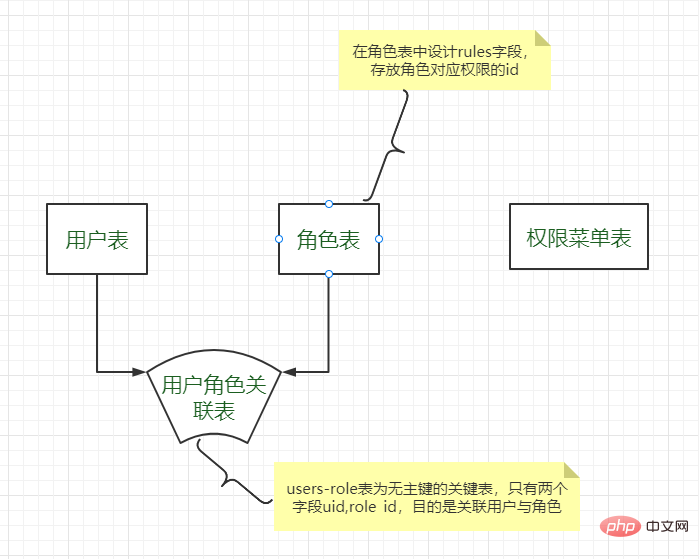
权限菜单表,角色表,用户表是互相独立的。设计表的顺序是权限菜单表,角色表,用户表,用户-角色关联表。
1. 首先是权限菜单表设计如下:
注意:权限菜单可以是多级菜单,添加pid字段,方便无限极递归分类。
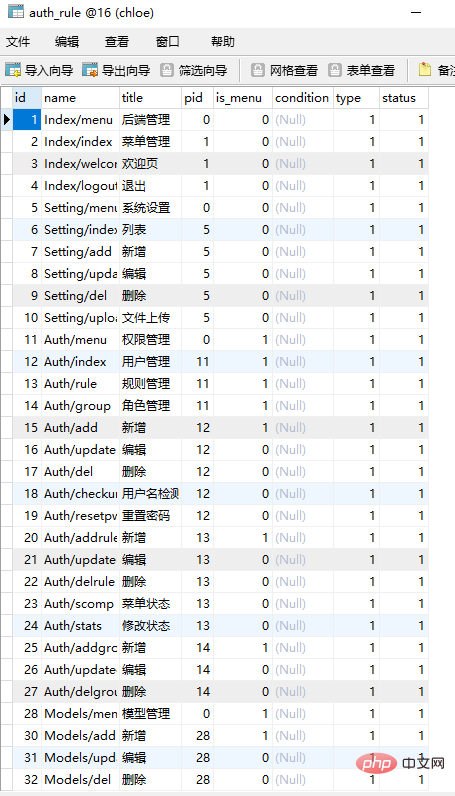
2. 角色表设计如下:
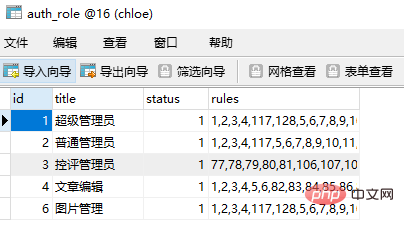
3. 用户表设计如下:
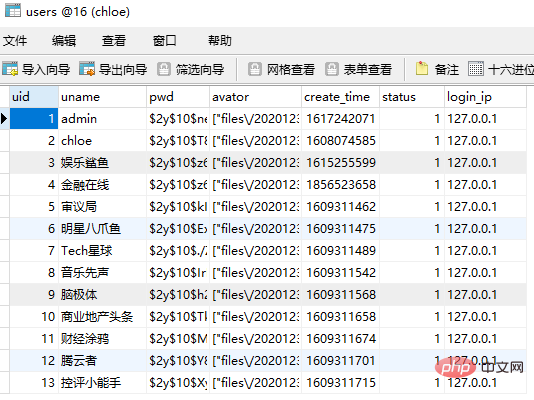
4. 最后是用户-角色关联表设计如下:
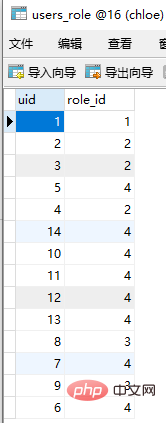
当超级管理员在后台需要添加新用户时,不仅需要insert数据进用户表,也需要在用户-角色表中添加用户和角色的关系。与之对应,删除用户时,也需要将用户-角色表中对应的用户-角色关系删除。
public function add() { if(request()->isPost()){ $role_id = input('post.role_id'); $data = [ 'uname'=>input('post.uname'), 'pwd'=>password_hash(input('post.pwd'),PASSWORD_BCRYPT), 'login_ip'=>request()->ip(), 'status'=>input('post.status'), 'create_time'=>time(), ]; $uid = Db::name('users')->insertGetId($data); if($uid){ $data = [ 'uid'=>$uid, 'role_id'=>$role_id ]; $id = Db::name('users_role')->insertGetId($data); if($id) { echo 'true'; exit; }else{ echo 'false'; exit; } }else{ echo 'false'; exit; } }else{ //获取所有角色 $role = Db::name('auth_role')->field('id,title')->order('id','asc')->where('status',1)->select(); return view('add',['role'=>$role]); } }
这样以来我们根据用户登录以后session中储存的uid判断当前登录用户的身份信息,根据获取到的uid查询用户-角色关联表查询到用户的角色id, 然后到角色表获取到该用户可操作的权限菜单。
封装中间控制器Common.php
check(request()->controller().'/'.request()->action(),$sess_auth)){ historyTo('抱歉~你没有操作该栏目的权限,请联系管理员!'); exit; } } } }
lib\Auth;/**权限认证类**/
true, // 认证开关 'auth_type' => 1, // 认证方式,1为实时认证;2为登录认证。 'auth_role' => 'auth_role', // 用户组数据表名 'users_role' => 'users_role', // 用户-用户组关系表 'auth_rule' => 'auth_rule', // 权限规则表 'auth_user' => 'users', // 用户信息表 ]; public function __construct() { if (Config::get('app.auth')) { $this->_config = array_merge($this->_config, Config::get('app.auth')); } } /** * 检查权限 * @param string|array $name 需要验证的规则列表,支持逗号分隔的权限规则或索引数组 * @param integer $uid 认证用户ID * @param string $relation 如果为 'or' 表示满足任一条规则即通过验证;如果为 'and' 则表示需满足所有规则才能通过验证 * @param string $mode 执行check的模式 * @param integer $type 规则类型 * @return boolean 通过验证返回true;失败返回false */ public function check($name, $uid, $relation = 'or', $mode = 'url', $type = 1) { if (!$this->_config['auth_on']) { return true; } $authList = $this->getAuthList($uid, $type); if (is_string($name)) { $name = strtolower($name); if (strpos($name, ',') !== false) { $name = explode(',', $name); } else { $name = [$name]; } } $list = []; if ($mode === 'url') { $REQUEST = unserialize(strtolower(serialize($_REQUEST))); } foreach ($authList as $auth) { $query = preg_replace('/^.+\?/U', '', $auth); if ($mode === 'url' && $query != $auth) { parse_str($query, $param); // 解析规则中的param $intersect = array_intersect_assoc($REQUEST, $param); $auth = preg_replace('/\?.*$/U', '', $auth); if (in_array($auth, $name) && $intersect == $param) { $list[] = $auth; } } elseif (in_array($auth, $name)) { $list[] = $auth; } } if ($relation === 'or' && !empty($list)) { return true; } $diff = array_diff($name, $list); if ($relation === 'and' && empty($diff)) { return true; } return false; } /** * 根据用户ID获取用户组,返回值为数组 * @param integer $uid 用户ID * @return array 用户所属用户组 ['uid'=>'用户ID', 'group_id'=>'用户组ID', 'title'=>'用户组名', 'rules'=>'用户组拥有的规则ID,多个用英文,隔开'] */ public function getGroups($uid) { static $groups = []; if (isset($groups[$uid])) { return $groups[$uid]; } $user_groups = Db::name($this->_config['users_role']) ->alias('ur') ->where('ur.uid', $uid) ->where('ar.status', 1) ->join($this->_config['auth_role'].' ar', "ur.role_id = ar.id") ->field('uid,role_id,title,rules') ->select(); $groups[$uid] = $user_groups ?: []; return $groups[$uid]; } /** * 获得权限列表 * @param integer $uid 用户ID * @param integer $type 规则类型 * @return array 权限列表 */ protected function getAuthList($uid, $type) { static $_authList = []; $t = implode(',', (array)$type); if (isset($_authList[$uid.$t])) { return $_authList[$uid.$t]; } if ($this->_config['auth_type'] == 2 && Session::has('_AUTH_LIST_'.$uid.$t)) { return Session::get('_AUTH_LIST_'.$uid.$t); } // 读取用户所属用户组 $groups = $this->getGroups($uid); $ids = []; // 保存用户所属用户组设置的所有权限规则ID foreach ($groups as $g) { $ids = array_merge($ids, explode(',', trim($g['rules'], ','))); } $ids = array_unique($ids); if (empty($ids)) { $_authList[$uid.$t] = []; return []; } $map = [ ['id', 'in', $ids], ['type', '=', $type], ['status', '=', 1] ]; // 读取用户组所有权限规则 $rules = Db::name($this->_config['auth_rule'])->where($map)->field('condition,name')->select(); // 循环规则,判断结果。 $authList = []; foreach ($rules as $rule) { if (!empty($rule['condition'])) { // 根据condition进行验证 $user = $this->getUserInfo($uid); // 获取用户信息,一维数组 $command = preg_replace('/\{(\w*?)\}/', '$user[\'\\1\']', $rule['condition']); // dump($command); // debug @(eval('$condition=('.$command.');')); if ($condition) { $authList[] = strtolower($rule['name']); } } else { // 只要存在就记录 $authList[] = strtolower($rule['name']); } } $_authList[$uid.$t] = $authList; if ($this->_config['auth_type'] == 2) { Session::set('_AUTH_LIST_'.$uid.$t, $authList); } return array_unique($authList); } /** * 获得用户资料,根据自己的情况读取数据库 */ protected function getUserInfo($uid) { static $user_info = []; $user = Db::name($this->config['auth_user']); // 获取用户表主键 $_pk = is_string($user->getPk()) ? $user->getPk() : 'uid'; if (!isset($user_info[$uid])) { $user_info[$uid] = $user->where($_pk, $uid)->find(); } return $user_info[$uid]; } }
这样就能实现路由操作权限的实时检测,比如我们让首页控制器继承中间控制器:
alias('u')->where('u.uid',$uid) ->leftJoin('users_role ur','ur.uid = u.uid') ->leftJoin('auth_role ar','ar.id = ur.role_id') ->field('u.uid,u.uname,ar.rules') ->select()->toArray(); // dd($res); $rules = implode(",",array_column($res,'rules')); // dd( $rules); //in查询 根据获取到的rules id 选权限列表 $res = Db::name('auth_rule')->field('id,name,title,pid')->order('id','asc')->where('is_menu',1) ->where('id','in',$rules)->select(); // dump($res); //这里使用扩展类Rule中封装的无限极分类方法 $rlist = Rule::Rulelayer($res); // dd($rlist); $data = [ 'uid'=>$uid, 'uname'=>$uname, 'rlist'=>$rlist, 'create_time'=>1617252175 ]; return view('index', $data); } }
最终实现的效果如图:
The above is the detailed content of RBAC permission control implementation principle - design of permission table, user table and association table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!