
“This article will briefly study the final execution process of the controller and the two advanced attributes used. One is the clever use of the fastcgi_finish_request method, and the other is the trait feature, super class We have some understanding of the concept, let’s analyze it together.
”
When the method in the controller is executed, the response data is sent to the run method of the App class, and the execution has been completed up to this point.
Are you a little confused about where the data here will eventually be returned?
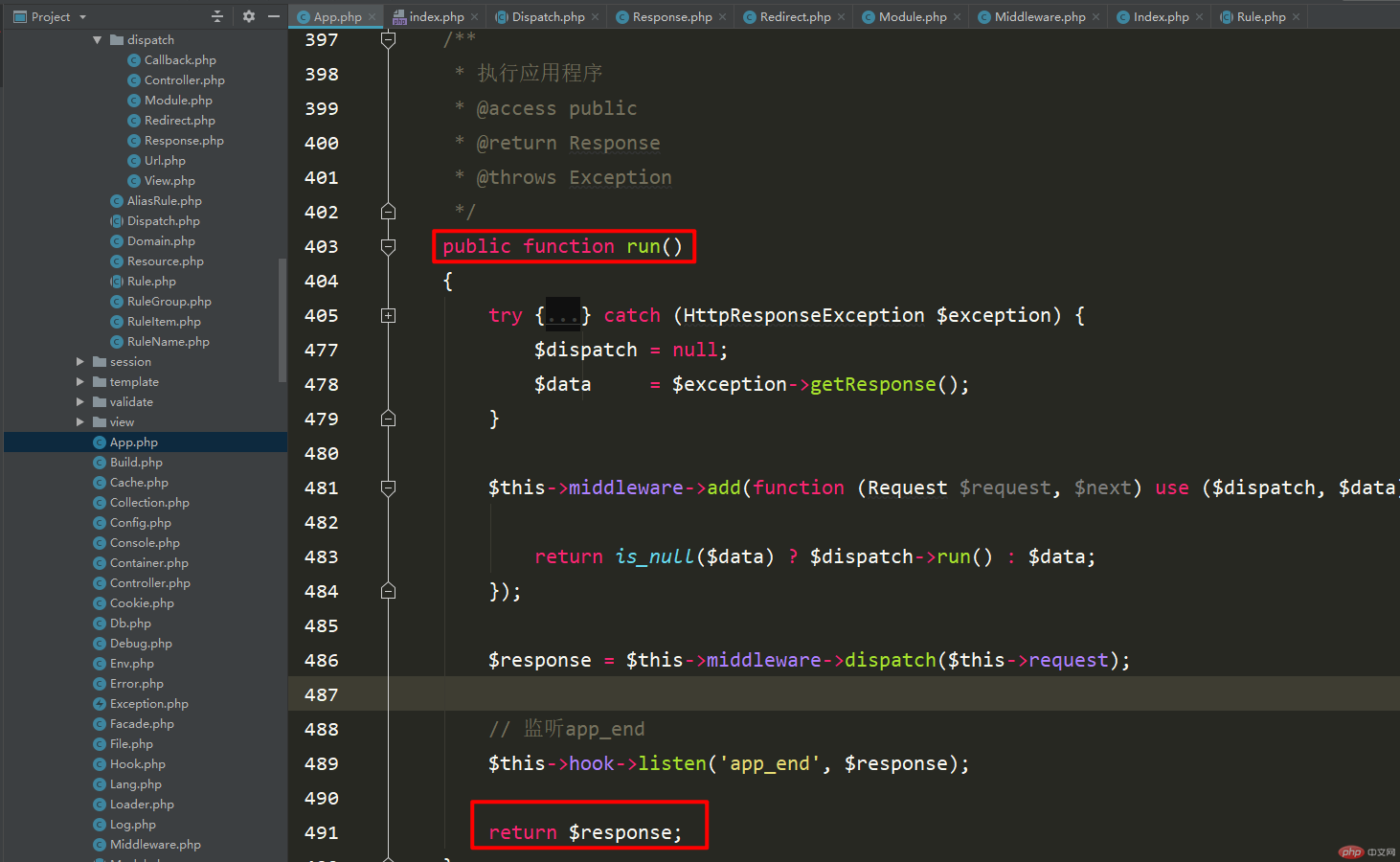
The framework execution process, routing, and controller instantiation written before are all entered from here. of.
So when the run method is executed, the corresponding results will be returned here.
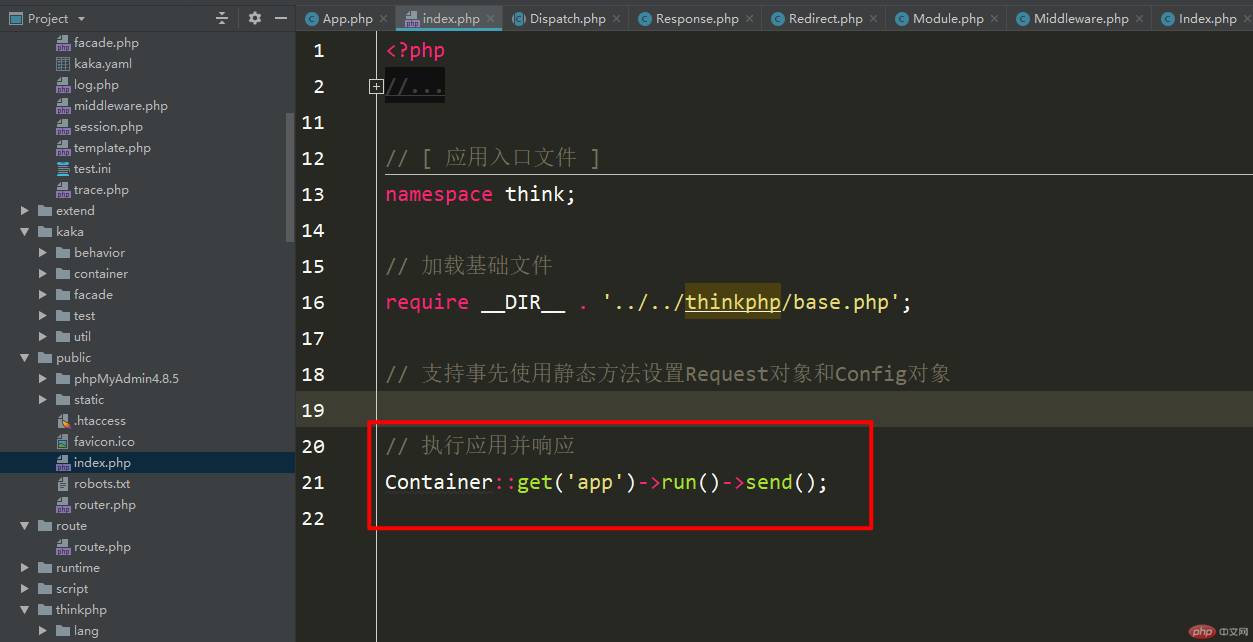
This part of the codeContainer::get('app')You should all know that it returns an instance of the App class.
Then execute the run method through the App class, and then you will have everything mentioned before.
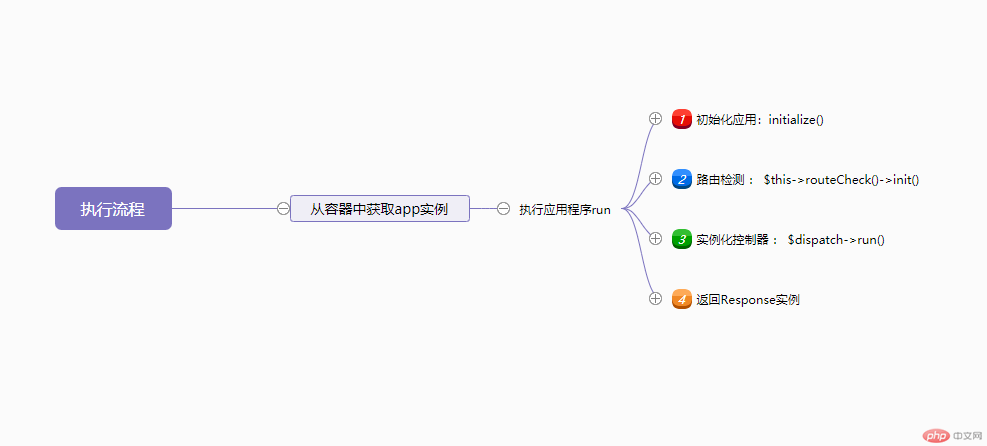
The picture below is a mind map made by Kaka from the middle waist. The front part is not there, and all the knowledge points in the back will be written in this mind map.
After executing the run method, it will be executedContainer::get('app')- >run()->send()send method, how many people would think that the send method is executed in the App class.
Actually no, think back to the response result returned after executing the controller method before?
If you don’t look at it very roughly, you will remember that it is an object instance of Response.
So the send method will be executed in the response class.
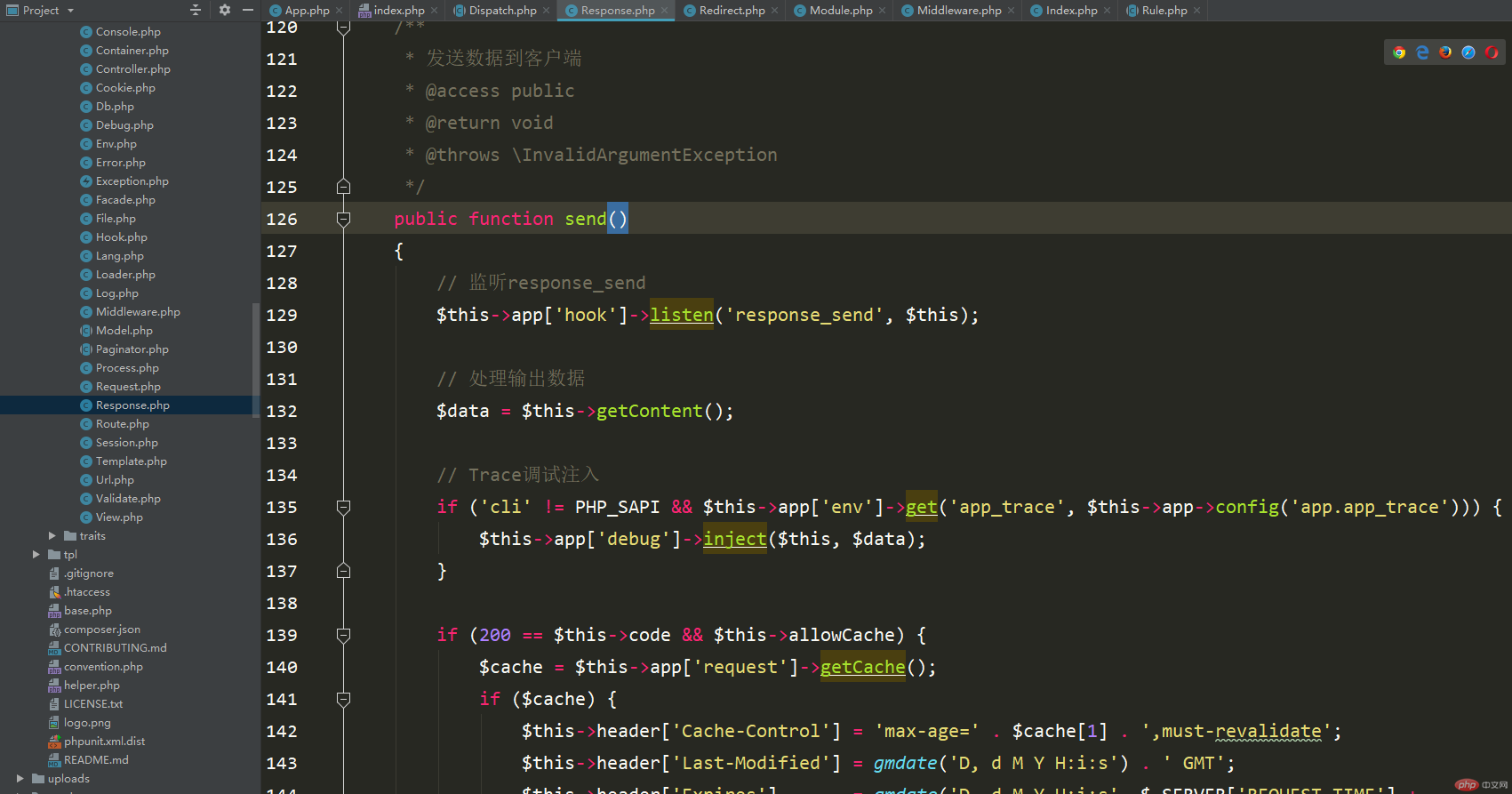
Don’t look at other things first, look at this line of code first$this-> ;app['hook'], now do you know where it is executed?
This form is to access the properties of the object by accessing the array form, which is the ArrayAccess class parsed before. When the accessed attribute does not exist, offsetGet is executed, and then the magic method __get is executed, and finally the instance is returned through the make method. All these operations are performed in the container.
I will not analyze what this line of code is specifically monitoring.
Then you need to look at the line of code that processes the output data$data = $this->getContent();
What this method does is to pass the Data is assigned to the content attribute of this class.
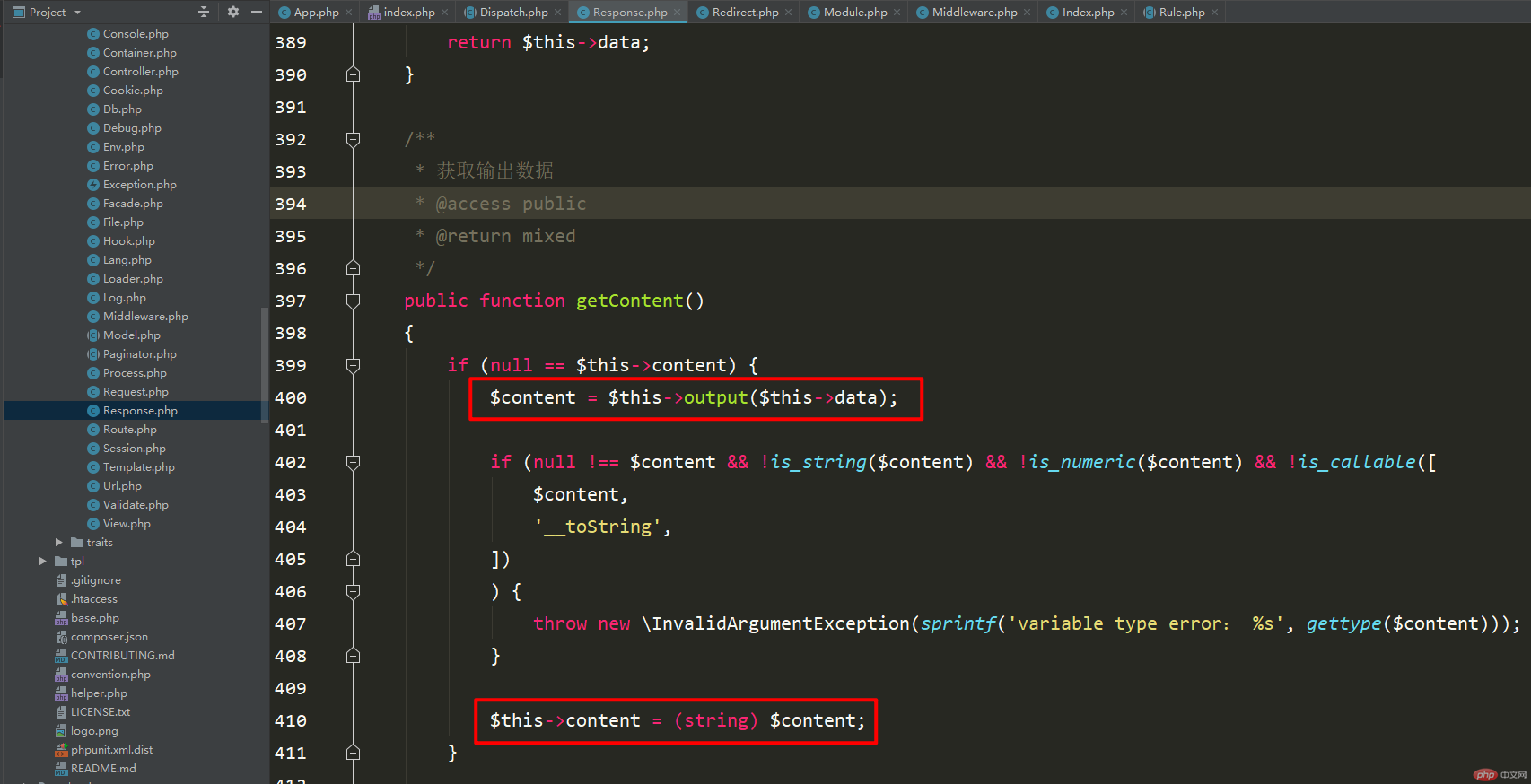
In fact, in this method of getting the output data, please look at the first place circled by Kaka. It feels very no need.
It can be seen that there is no processing of the data at all, it is just returned. Therefore, the framework has good and bad points. Only if you read it will you know, otherwise you will be wrong Know nothing about the tools you use regularly.
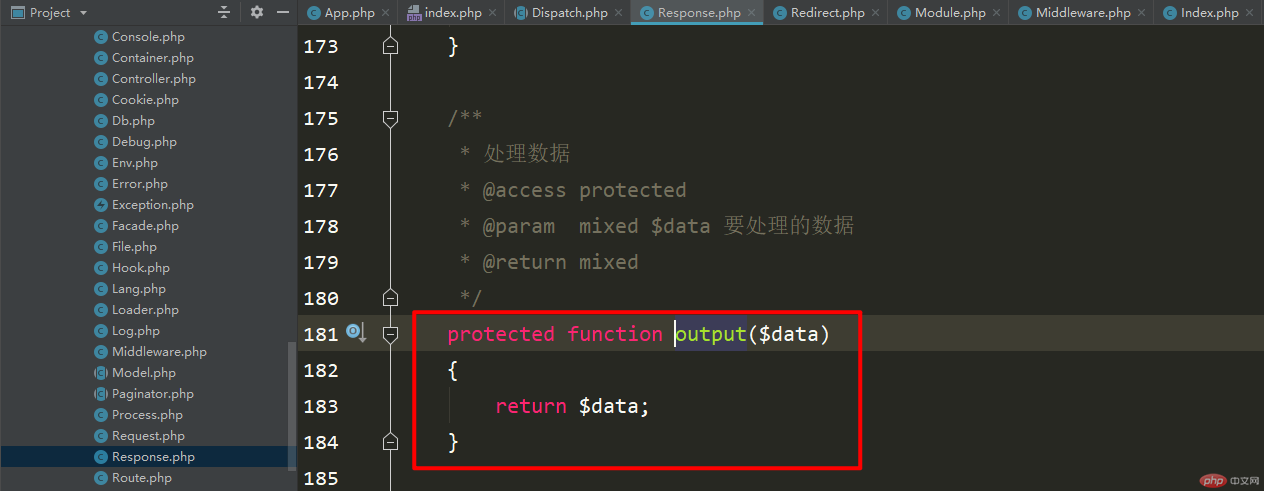
The next step is Trace debugging injection, which is configured through the configuration file and implemented by calling the debug class. I won’t explain it in detail here.
Then there is caching judgment. Caching will be discussed separately in the following article, so it is also passed.
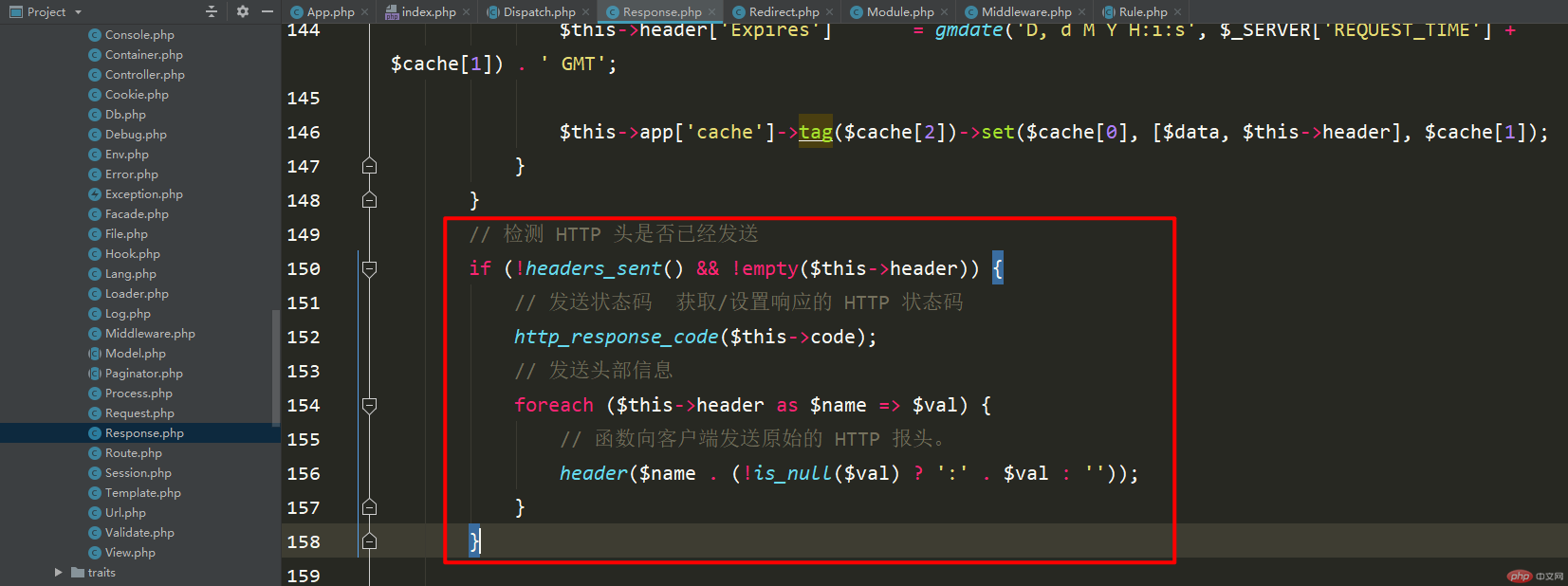
The next step is to set the response header and detect whether the HTTP header has been sent. This is very important, and it is also a knowledge point that is rarely exposed to.
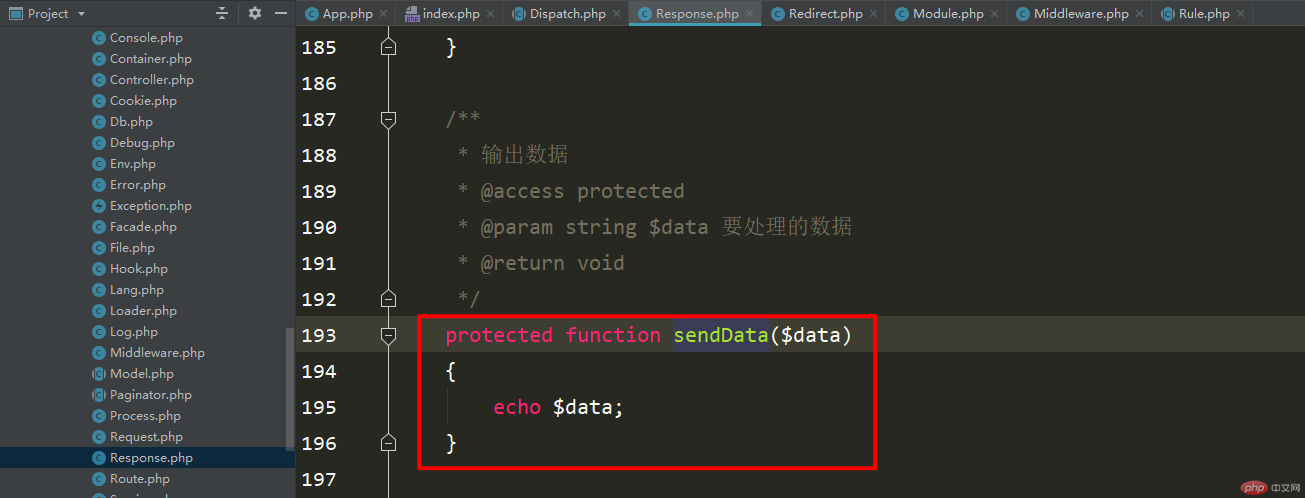
The last step, it’s coming, it’s coming , it came with echo and executed a method$this->sendData($data);
, giving people the feeling that a daughter-in-law has become a mother, and finally arrived. At the terminal, an echo outputted dozens of days of sadness!
In order to reach this echo Kaka, I went through nine or ninety-nine and eighty-one difficulties! The battle has not stopped yet, comrades still need to work hard!
So here we go to the framework execution and then to the application initialization, then to the route detection and the instantiation of the controller. , then return the response instance, and execute the send method through the entry file.
Finally output the data to the terminal, which is an echo thing.
Although the battle here is over, there is still a very important knowledge point below, and Kaka will mention it again to explain it.
passedContainer::get('app')-> in the previous section ;run()->send();The send method is executed in the response class and the data is output.
But after outputting the data, a methodfastcgi_finish_request();is also executed. The comment is to improve the page response. Let’s take a closer look at the mystery.
See this passage on the PHP official website
The script will still occupy a FPM process after fastcgi_finish_request(). So using it excessively for long running tasks may occupy all your FPM threads up to pm.max_children. This will lead to gateway errors on the webserver.
After fastcgi_finish_request(), the script will still occupy the FPM process. So overusing it for long running tasks may tie up all your FPM threads up to pm.max_children. This will cause a gateway error on the web server.
So don’t use this method in your own projects without a thorough understanding of this method.
Next, Kaka will use a case to demonstrate the use of this method. It is just a demonstration. If you need to use it in a project, please read the document carefully and pay attention to the issues.
Case Demonstration
The company has a business that needs to send notifications to users, but because the sending time is too long, it is very time-consuming and may take dozens of seconds. , more seriously it will directly cause the browser connection to time out.
One problem is the user experience. The user’s waiting time process is of course not good.
In order to solve the above two problems, thefastcgi_finish_requestdiscussed today comes in handy.
understand
The understanding of this function is actually to send a response to the browser. The user's waiting time is greatly shortened, but the PHP process is still running.
This achieves a purpose, which is similar to the asynchronous execution we often talk about.
Intuitively speaking, it may take 10 seconds to send an email, but the user is not aware of it. After the user clicks to send the email, it will directly return that the sending is successful, the browser response ends, the user does other things, and the background process continues. Perform the task of sending emails.
Case
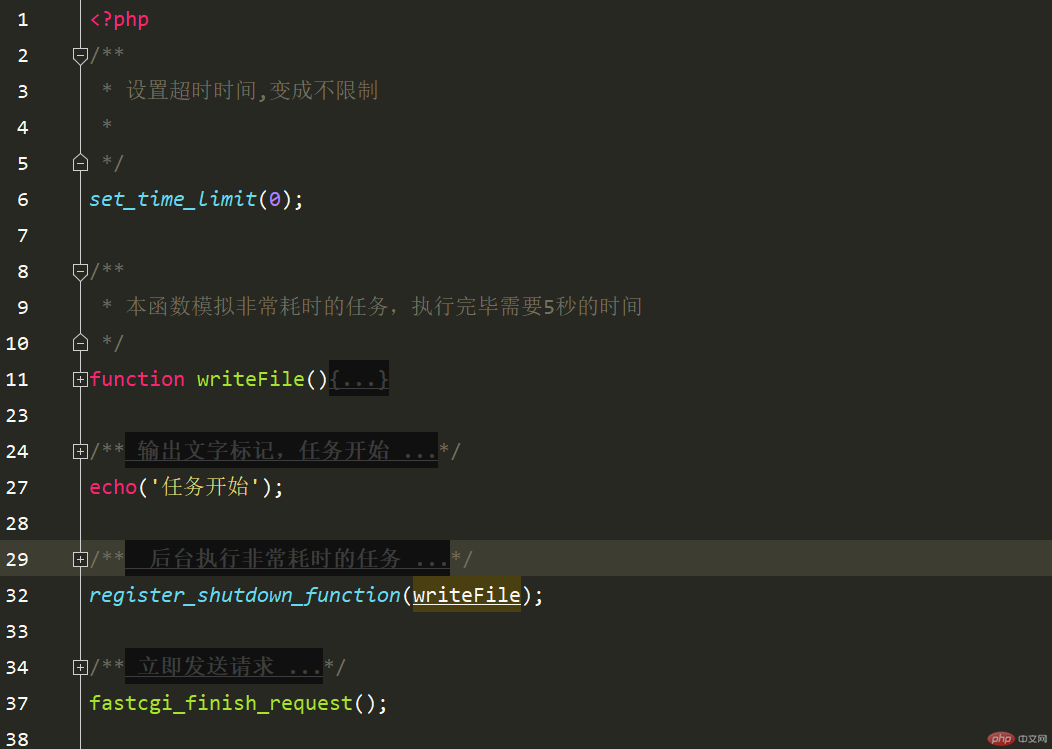
/**
* 设置超时时间,变成不限制
*
*/
set_time_limit(0);
/**
* 本函数模拟非常耗时的任务,执行完毕需要5秒的时间
*/
function writeFile()
{
$path = 'D:/phpstudy_pro/WWW/kaka.txt';
file_put_contents($path,'程序运行开始' . PHP_EOL,FILE_APPEND);
for($i =0;$i 5;$i++) {
file_put_contents($path,time() . PHP_EOL,FILE_APPEND);
sleep(1);
}
file_put_contents($path,'程序运行结束' . PHP_EOL,FILE_APPEND);
}
/**
* 输出文字标记,任务开始
*/
echo('任务开始');
/**
* 后台执行非常耗时的任务
*/
register_shutdown_function(writeFile);
/**
* 立即发送请求
*/
fastcgi_finish_request();
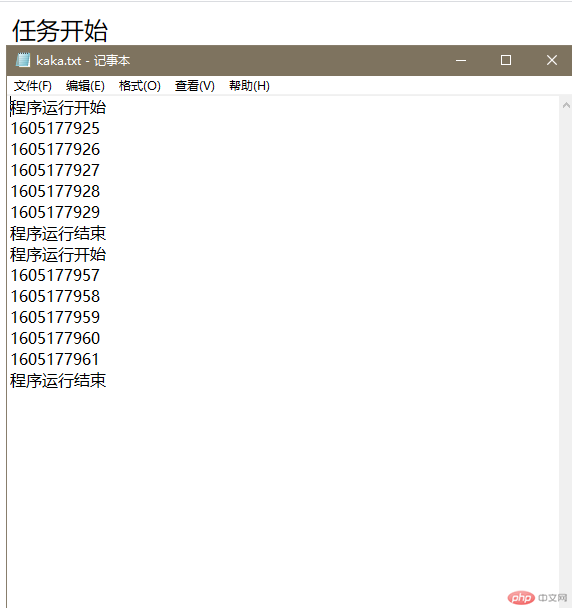
After the above demonstration, the response is very fast. After the browser responds, the background program still executes a timestamp every second.
The above is a brief introduction to thefastcgi_finish_requestmethod. If you are also interested, you can give it a simple try, which will help you better understand the little secrets.
Kaka should have analyzed this feature two years ago,traitis what is often called a super class.
This feature was only added in PHP5.4. This feature is not a frequently used interface nor a class.
This feature is to solve a major weakness of PHP, which is that it can only have single inheritance. However, it cannot be called multiple inheritance. A more rigorous one is just a function similar to multiple inheritance.
Next I will show you a case.
Create test file 1 and return the corresponding class name.
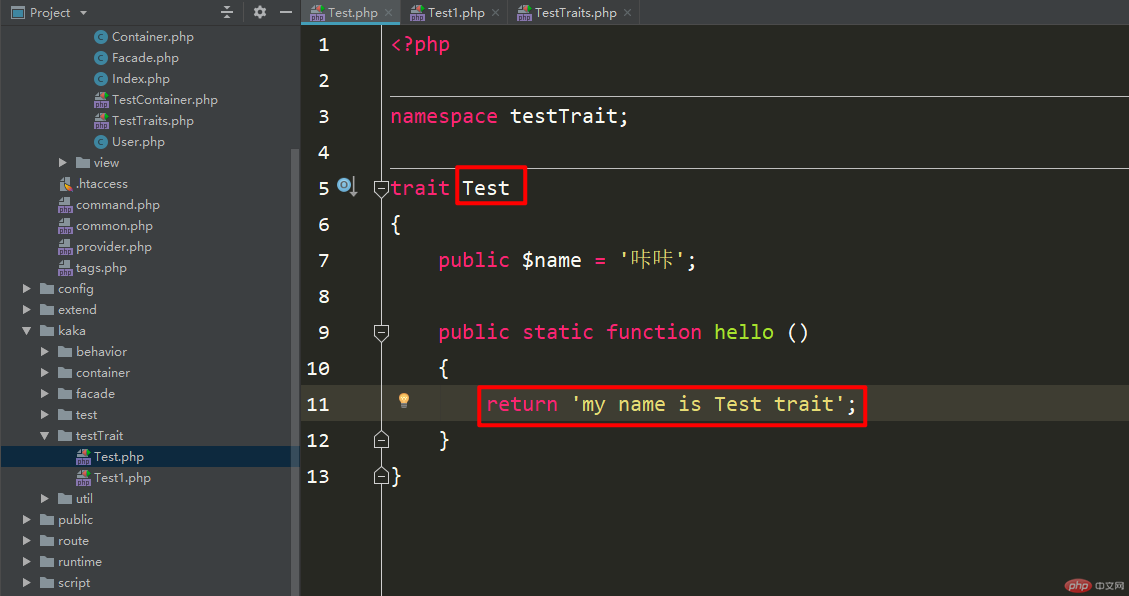
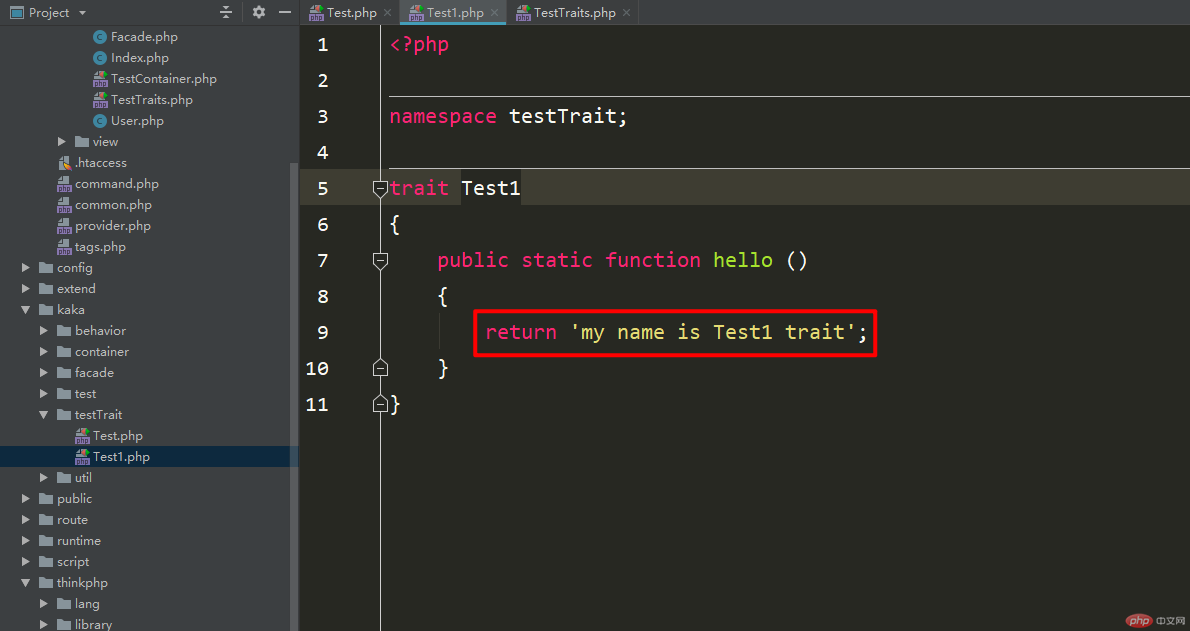
Create the test1 file and return the corresponding class name
Create a controller file to output information.
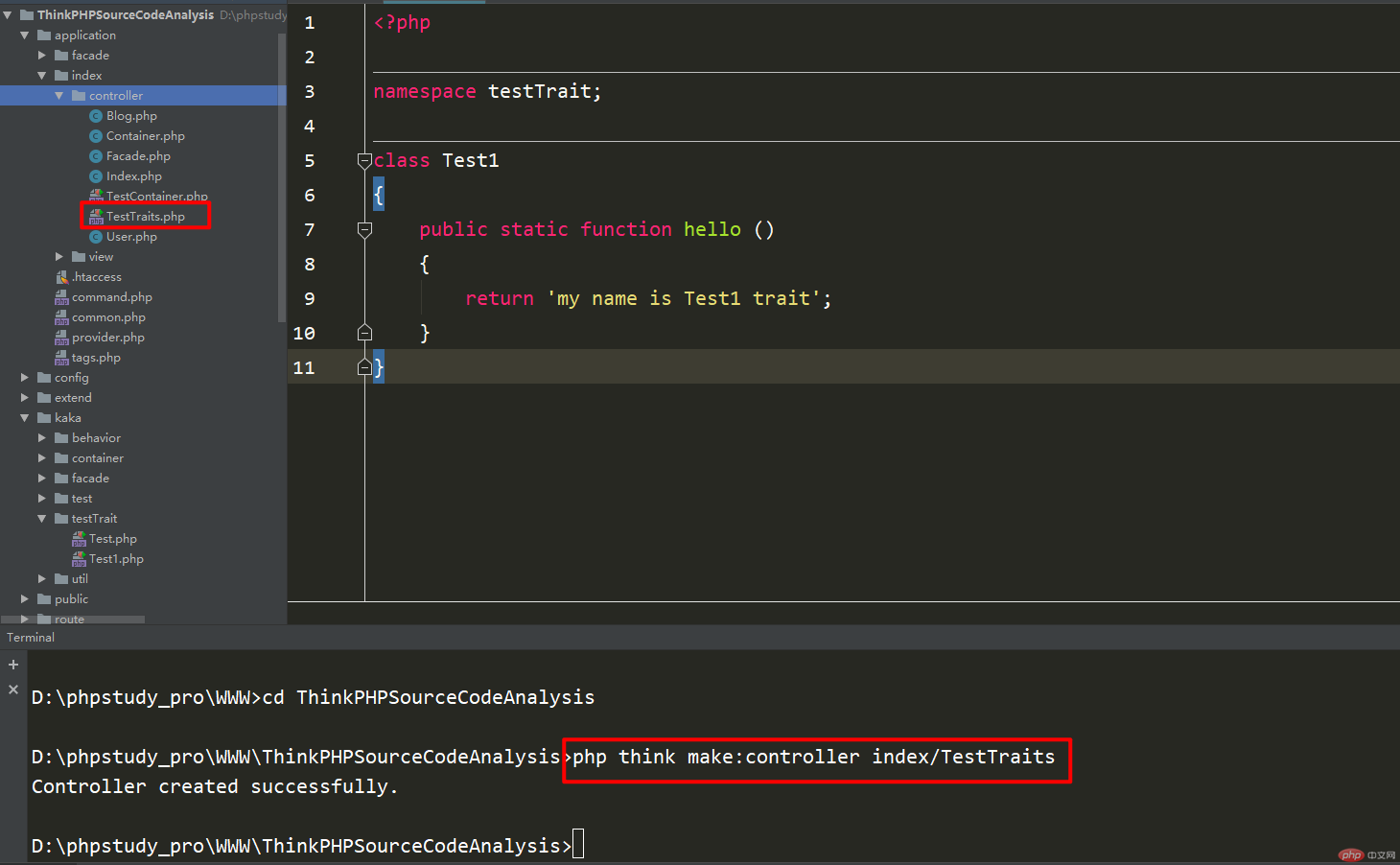
Then introduce the corresponding super class file in the controller. What needs to be noted here is the circle The first box is to directly introduce the super class test file.
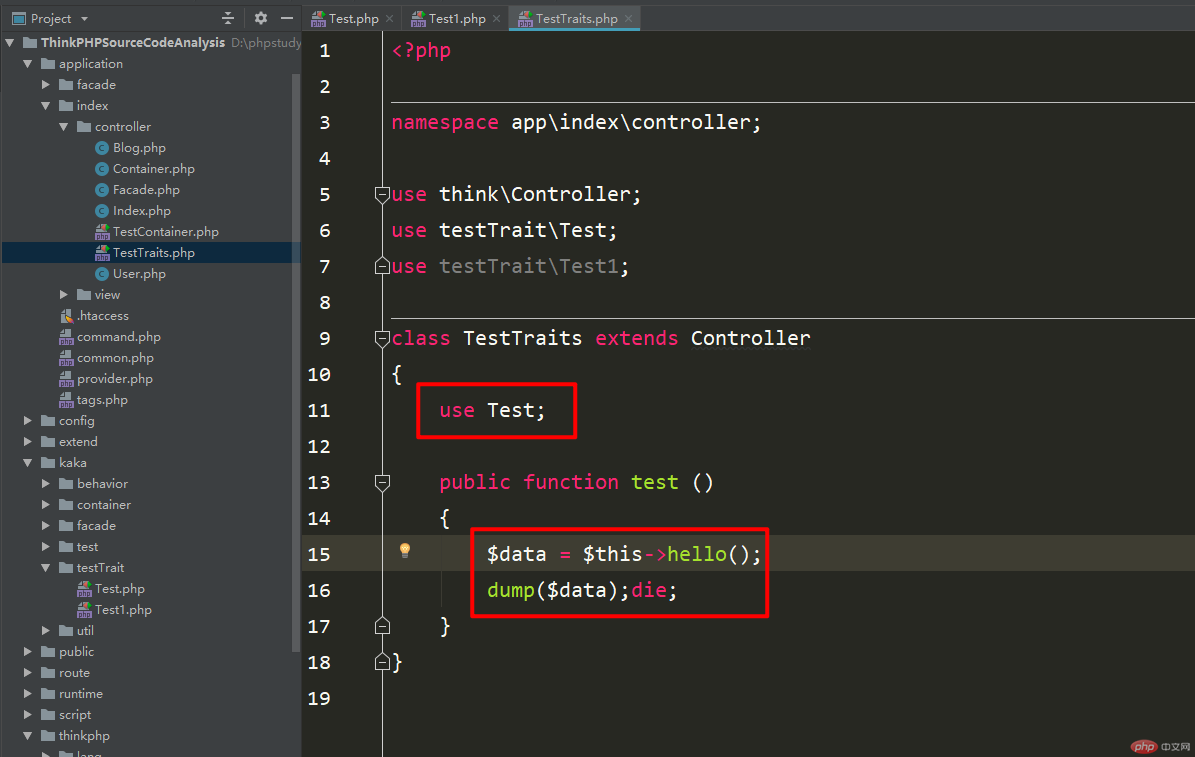
Then you can access it directly and see what will be returned.
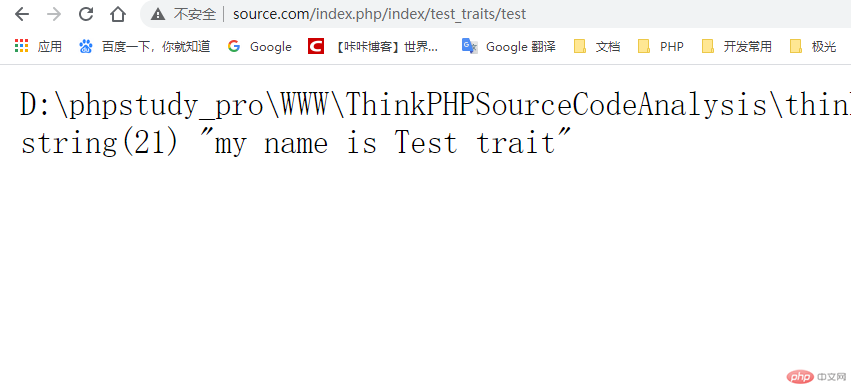
Accessing the result through the above figure, you can see that the method that returns the Test super class file is the same, but this controller is the same The Controller controller is also based on it. This is what the super class mentioned at the beginning of the article just implements a function of multiple inheritance.
But there will be a problem here, please see the error message below.
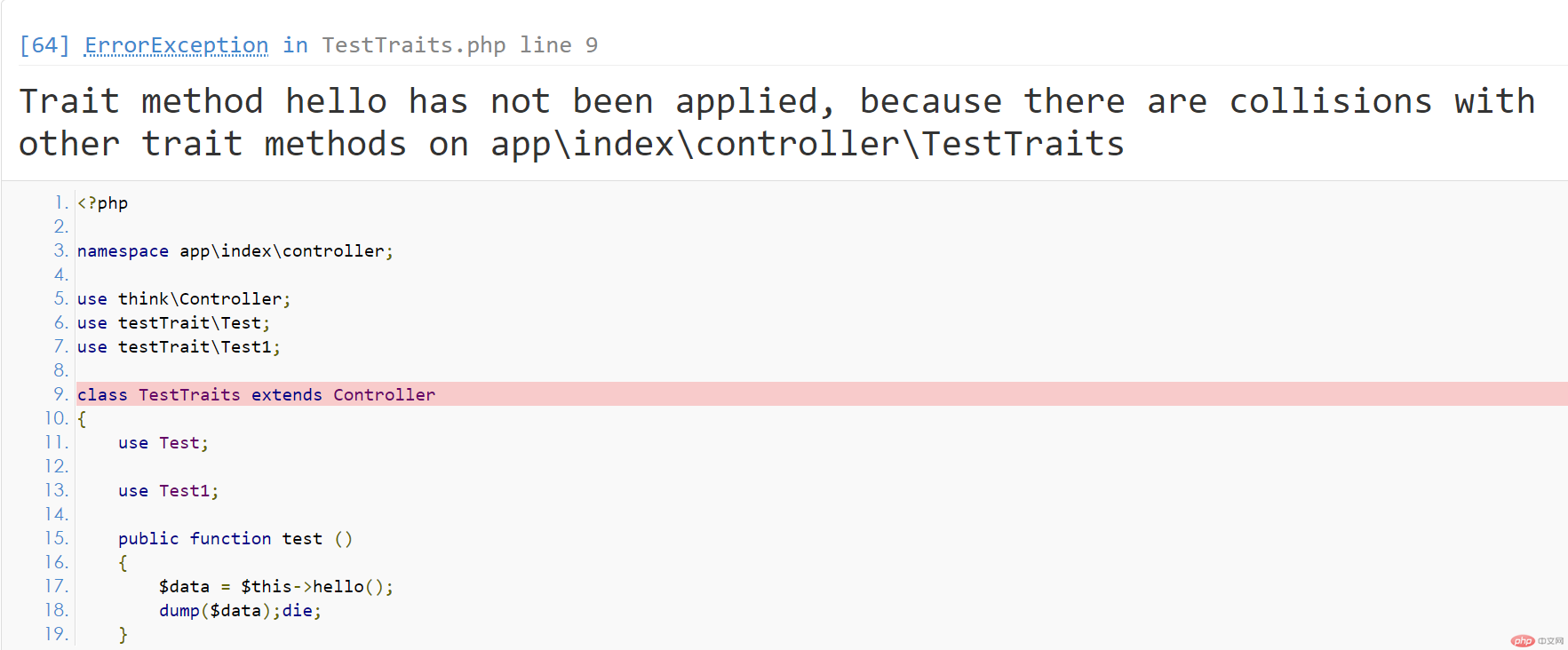
The error message in the above picture is caused by using two superclasses in the controller. This is how to use it in the picture below.
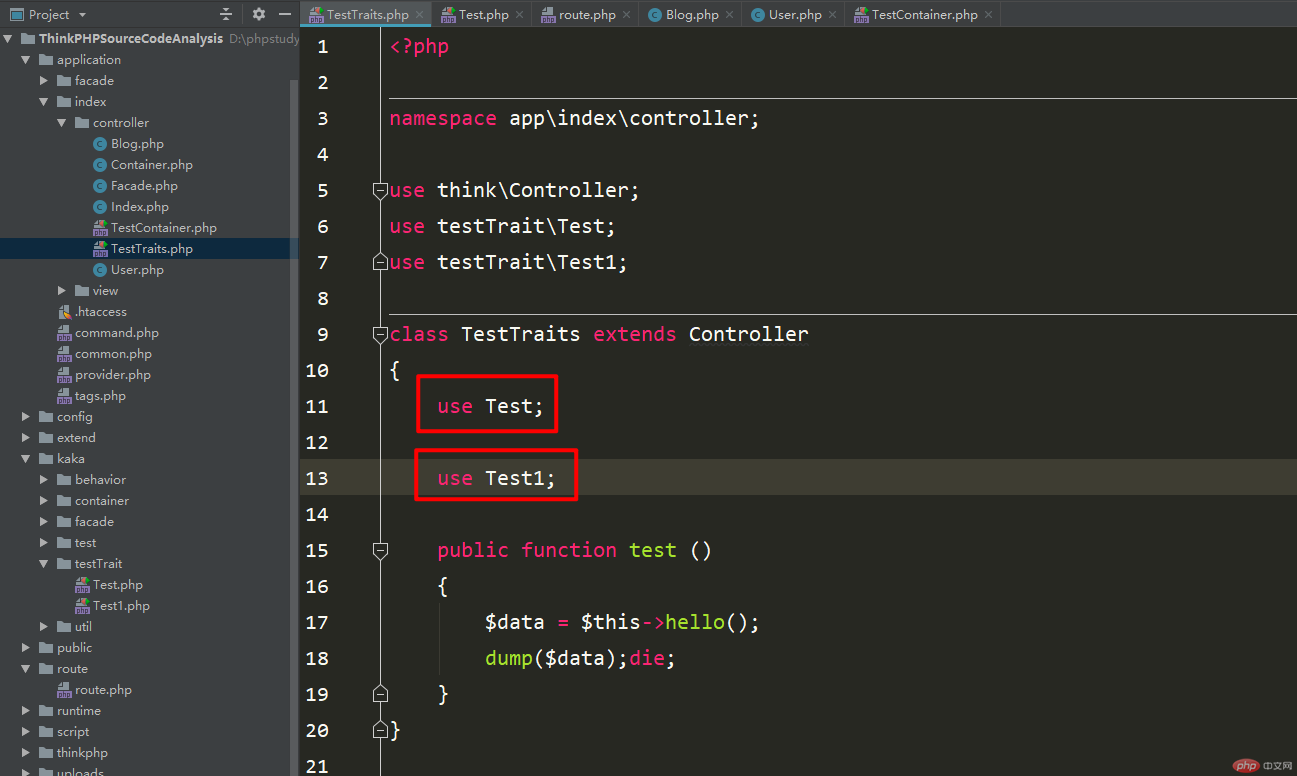
So how to solve this error message! Next, follow the rhythm of this click.
Resolving error messages
Before solving the previous problem, you must first understand what caused this problem.
The reason for this error is that the two traits referenced have hello functions with the same name, and there is a conflict.
But this situation can be avoided in daily development, because it is still very convenient to change the method name manually, but here Kaka teaches you how to solve this problem.
The first is to use the hello method in one trait to overwrite the method of the same name in another trait. Because the contents of the two methods are consistent, I directly choose insteadof to overwrite it here;
The second is to They use as aliases so there won't be conflicts. The as keyword has another use, which is to modify the access control of a method.
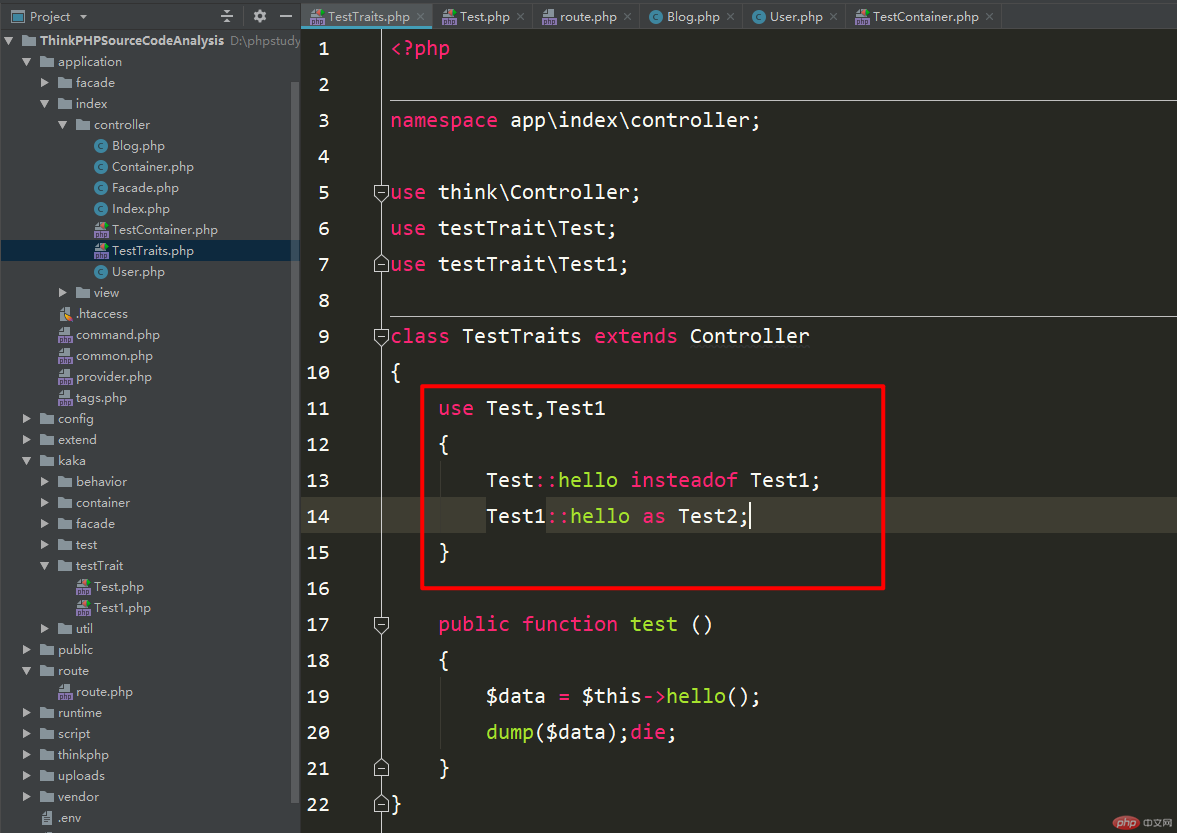
After the changes in the above picture, visit again and take a look at the return results.

Then some partners will have questions at this time, that is, the case printing result has always been the method of the Test class, and the method of the Test1 class has not been printed.
How to access it! Let’s take a look.
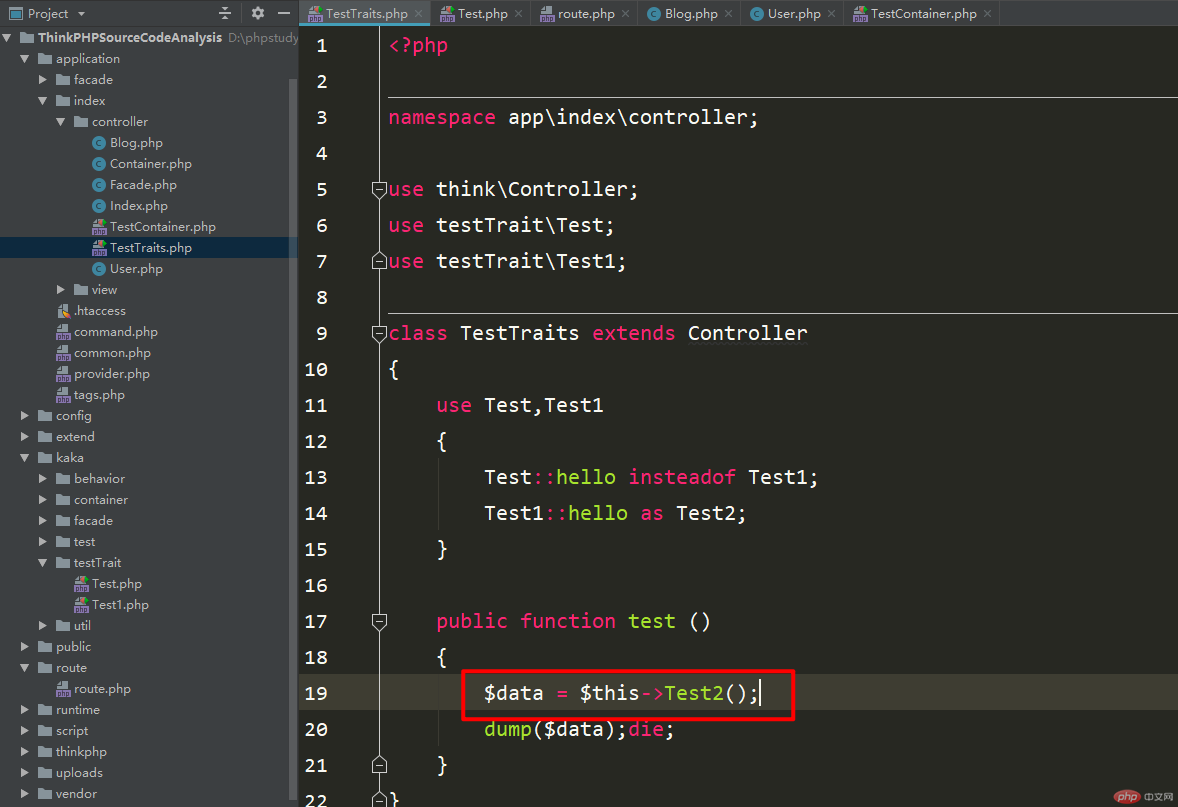
As you can see from the above figure, the access method is changed to alias to control access, and then come Take a look at the visit results.

As you can see from the above figure, the return result is the return result of the super class Test1 class .
So regarding the use of as, you need to search for how to use it. Sometimes you can learn a lot of knowledge by paying attention to the details.
This is it for the source code analysis of the controller. Kaka will analyze how to instantiate the controller through the source code. of.
The calling relationship between ArrayAccess and magic methods is also discussed again. You must have your own thinking to think about the problem.
This is how to respond to data after accessing the controller, etc.
I also learned about the clever use of fastcgi_finish_request method in the source code, but when using this function, you must pay attention to the two points mentioned about Kaka.
Finally, there is a simple case description of the super class.
“Persistence in learning, persistence in blogging, and persistence in sharing are the beliefs that Kaka has always upheld since his career. I hope that Kaka’s articles in the huge Internet can bring you a little Please help me. I’m Kaka, see you next time.
”
The above is the detailed content of Features fastcgi_finish_request and trait used by ThinkPHP framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!