
Related learning recommendations: javascript
Speaking of JavaScript, everyone knows that it is A scripting language. So what the hell is ES? ES stands for ECMAScript, which is the international standard for JavaScript language.
Recently summarized some knowledge points related to the basic features of js, let’s take a look at it together

function funValue(value) {
value="dada";
alert(value); // dada
alert(argument[0]); // 非严格模式:dada
// 严格模式模式 dadaqianduan}
funValue('dadaqianduan');复制代码How to declare a class in JavaScript? How to define methods in a class? How to instantiate an object?
Let’s take a look at the following code example:
// es5let dada = function(type) { this.type = type
}
dada.prototype.study = function() { console.log('魔王哪吒');
}let da1 = new dada('程序员')let da2 = new dada('It')
da1.constructor.prototype.study = function() { console.log('dadaqianduan');
}
da1.study()复制代码
JavaScript constructorProperties
Definition and usage
constructor Property returns a reference to the array function that created this object.
Syntax
object.constructor
constructor is a method used to create and initialize class Special methods of the created object.
// es6class Da { constructor(name) { // 构造函数内写属性
this.name = name;
}
eat() { // 构造函数外写方法
console.log('i eat')
}
}const da1 = new Da('da1');console.log(da1.name); // da1console.log(da1);复制代码var daObj = {
get val() {
return ;
},
set val(value) {
}
}复制代码get:
var da = { a: 1,
get val(){ return this.a + 1;
}
}console.log(da.val);//2da.val = 100;console.log(da.val);//2class Da { constructor(type) { this.type = type
}
get age() { return 1
}
set age(val) { this.realAge = val
}
eat() { console.log('i am eat')
}
}let da1 = new Da('da1')console.log(da1.age)
da1.age = 1console.log(da1.realAge)复制代码class Da {
constructor(type, age) {
this.type = type
this.age1 = age
}
get age() {
return this._age
}
set age(val) {
this._age = val
}
}复制代码Use set/get to encapsulate element.innerHTML
class myHTMLElement {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element
}
get html() {
return this.element.innerHTML
}
set html(value) {
this.element.innerHTML = value
}
}复制代码Set a closure and use certain rules to Limit modifications to it:
let myName = 'dada'
class Da {
constructor(type) {
this.type = type
}
get name() {
return myName
}
set name(val) {
myName = val
}
}复制代码Static method implemented in es5:
let Da = function (type) { this.type = type this.eat = function() { console.log('i eat')
}
}
Da.study = function(book) { console.log('i book');
}复制代码let Da = function(type) { this.type = type
}
Da.prototype.eat = function() {
Da.walk() console.log('i am')
}
Da.walk = function(){ console.log('walk')
}let da1 = new Da('da1')
da1.eat()// walk// i am复制代码The static method cannot be found in your instantiated object The
static method in es6, marked static
class Da {
constructor(type) {
this.type = type
}
eat() {
console.log('i eat')
}
static study() {
console.log('i study')
}
}复制代码Inheritance in es5:
// 定义一个父类
let Da = function(type) {
this.type = type
}
// 定义方法
Da.prototype.eat = function() {
console.log('i am')
}
// 定义静态方法
Da.study = function(book) {
console.log('i study')
}
// 定义子类
let Da1 = function() {
// 初始化父类
Da.call(this, 'da1');
this.run = function() {
console.log('i run')
}
}
// 继承
Da1.prototype = Da.prototype复制代码in es6 Inheritance in
class Da { constructor(type) { this.type = type
}
eat() { // Da.walk();
console.log('i eat')
} static walk(){ console.log('i walk')
}
}class da extends Da { // 构造函数
//constructor (type) {
//super(type)
//}
run() { console.log('i run')
}
}let da1 = new da('da1')复制代码Class declaration, properties, methods, static methods, inheritance, polymorphism, private properties
// 类的声明
let Da = function(type) {
this.type = type
this.eat = function() {
console.log('i eat');
}
}
let da = new Da('da');复制代码// prototype
let Da = function(type) {
this.type = type
}
Da.prototype.eat = function() {
console.log('i eat')
}
let da1 = new Da('da1')复制代码Class
class Da {
// 构造函数
constructor(type) {
this.type = type
}
// 方法
walk() {
console.log('i walk')
}
}
let da = new Da('da');
// console.log(typeof Da); function复制代码Function parameters are parsed from left to right. If there is no default value, it will be parsed into
undefined
// 参数默认值
function da (x,y,z) {
}
function sum() {
let num = 0
Array.prototype.forEach.call(arguments, function(item){
num += item * 1
})
Array.from(arguments).forEach(function(item){
num += item * 1
})
return num
}复制代码// 不确定
function sum(...nums) {
let num = 0
nums.forEach(function(item){
num += item * 1
})
return num
}
console.log(sum(1,2,3,4,5))复制代码function sum () {
let num = 0
Array.prototype.forEach.call(arguments, function (item) {
num += item * 1
})
return num
}
function sum (...nums) {
let num = 0
nums.forEach(function (item) {
num += item * 1
})
return num
}复制代码Arrow function expressions have a more concise syntax than function expressions and do not have their own this, arguments, super or new. target. Arrow function expressions are more suitable where an anonymous function would otherwise be required, and it cannot be used as a constructor.
() => {}
// function Da() {}
// let da = function() {}
let da = () => {
console.log('hello')
}
da()
let da = name => {}复制代码const materials = [ 'Hydrogen', 'Helium', 'Lithium', 'Beryllium'];console.log(materials.map(material => material.length));// expected output: Array [8, 6, 7, 9]复制代码
Extension
The judgment function has several parameters
console.log(sum(...[4])) console.log(sum.apply(null, [4]))复制代码
In JavaScript, there are three dots in front of the parameters of the function, What does it represent? Let’s take a look at the code example:
function myFunc(a, b, ...args) {
console.log(a); // 22
console.log(b); // 98
console.log(args); // [43, 3, 26]
};
myFunc(22, 98, 43, 3, 26);复制代码function myFunc(x, y, ...params) { // used rest operator here
console.log(x); console.log(y); console.log(params);
}var inputs = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
myFunc(...inputs); // used spread operator here// "a"// "b"// ["c", "d", "e", "f"]复制代码var obj1 = { foo: 'bar', x: 42 };var obj2 = { foo: 'baz', y: 13 };var clonedObj = { ...obj1 };// Object { foo: "bar", x: 42 }var mergedObj = { ...obj1, ...obj2 };// Object { foo: "baz", x: 42, y: 13 }复制代码The property definition of the object in JS, the code example is as follows:
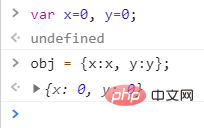
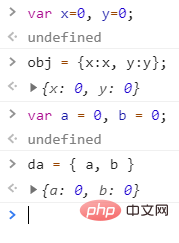
let x = 'da1';
let y = 'da2';
let obj = {
x,
y
}
console.log(obj);
// 结果
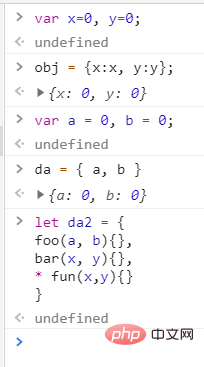
{x:'da1',y:'da2'}复制代码let x=1; let y=2; let z=3
let obj = {
'x': x,
y,
[z+y]: 4,
* hello() { // 异步
console.log('dada')
}
}
// function* functionName() {}
obj.hello()复制代码The members stored in Set are not allowed to be repeated (it is similar to an array)
Set itself is a constructor used to generate the Set data structure.
const s = new Set(); [2, 3, 5].forEach(x => s.add(x)); Set 函数可以接受一个数组(或类似数组的对象)作为参数,用来初始化 const set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 4]);复制代码
Implementing array deduplication
var arr = [1,1,2,2,3,3]; // step1:数组转集合
var s = new Set(arr); // 已经去掉重复值,当前不是数组,而集合
s.size; // 3
// step2:集合转数组
console.log([...s]); // 1,2,3;
// Array.form 方法可以将 Set 结构转为数组
const items = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
const arr = Array.from(items);
function dada(array) {
return Array.from(new Set(array));
}
dada([1, 1, 2])复制代码Set traversal
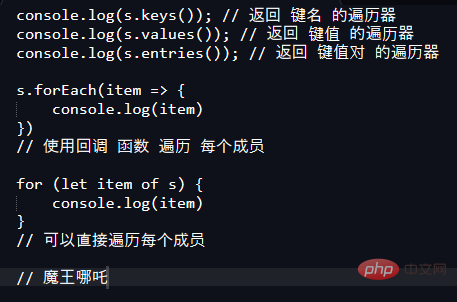
keys():返回键名的遍历器values():返回键值的遍历器entries():返回键值对的遍历器forEach():使用回调函数遍历每个成员操作方法
add(value):添加某个值,返回Set结构本身。delete(value):删除某个值,返回一个布尔值,表示删除是否成功。has(value):返回一个布尔值,表示该值是否为Set的成员。clear():清除所有成员,没有返回值。let set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 4]);
// 添加数据
let addSet = set.add(5);
console.log(addSet); // Set(5) {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
// 删除数据
let delSet = set.delete(4);
console.log(delSet); // true
// 查看是否存在数据 4
let hasSet = set.has(4);
console.log(hasSet); // false
// 清除所有数据
set.clear();
console.log(set); // Set(0) {}复制代码实现并集(Union)、交集(Intersect)和差集(Difference)
let a = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
let b = new Set([4, 3, 2, 1]);
// 并集
let union = new Set([...a, ...b]);
// Set {1, 2, 3, 4}
// 交集
let intersect = new Set([...a].filter(x => b.has(x)));
// set {1, 2, 3}
// 差集
let difference = new Set([...b].filter(x => !a.has(x)));
// Set {4}复制代码JS当中的哈希表,使用方法如下:
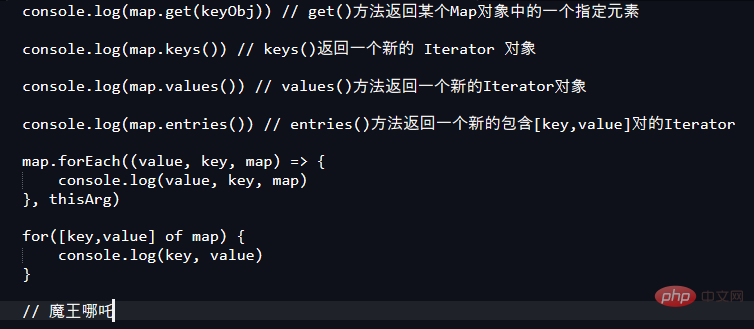
let map = new Map()
map.set(1, 2)
map.set(3, 4)
map.set(1, 3)
console.log(map)
创建
var da = new Map();
var jeskson = {};
遍历
da.forEach(function(value,key,map){}
长度
da.size
删除
//da.delete() 删除key,全部清楚da.clear()
新增
da.set(key,value)
da.has(查索引值)
da.forEach((value,key) =>{
})
for( let [key, value] of map){}
// let map = new Map( [[1,2], [3,4]] )
map的key任意都可以
let o = function() {
console.log('o')
}
map.set(o, 3)
console.log(map.get(o)); // 3复制代码// map.js
var Dictionary = function() {
var items = {};
// 检查键
this.has = function(key) {
return key in items;
}
// 添加键值对
this.set = function(key, value){
items[key] = value;
}
// 通过键移除元素
this.delete = function(key) {
if(this.has(key)){
delete items[key]
return true
}
return false
}
// 键获取值
this.get = function(key){
return this.has(key) ? items[key] : undefined;
}
// 列表返回字典值
this.values = function() {
var values = [];
for(var k in items) {
if(this.has(k)) {
values.push(items[k])
}
}
return values;
}
// 获取全部键名
this.keys = function() {
return Object.keys(items);
}
// 获取私有变量items
this.getItems = function() {
return items;
}
}复制代码Map数据结构,它类似于对象,也是键值对的集合,但是“键”的范围不限于字符串,各种类型的值(包括对象)都可以当作键。
Object.assign() 方法用于将所有可枚举属性的值从一个或多个源对象复制到目标对象。它将返回目标对象。
const target = { a: 1, b: 2 };
const source = { b: 4, c: 5 };
const returnedTarget = Object.assign(target, source);
console.log(target);
// expected output: Object { a: 1, b: 4, c: 5 }
console.log(returnedTarget);
// expected output: Object { a: 1, b: 4, c: 5 }
> Object { a: 1, b: 4, c: 5 }
> Object { a: 1, b: 4, c: 5 }复制代码语法
Object.assign(target, ...sources)复制代码
参数
target复制代码
目标对象
sources复制代码
源对象
返回值
目标对象。
const obj = { a: 1 };
const copy = Object.assign({}, obj);
console.log(copy); // { a: 1 }复制代码Object.assign(undefined) // 报错
Object.assign(null) // 报错
let obj = {a: 1};
Object.assign(obj, undefined) === obj // true
Object.assign(obj, null) === obj // true
const obj1 = {a: {b: 1}};
const obj2 = Object.assign({}, obj1);
obj1.a.b = 2;
obj2.a.b // 2
const target = { a: { b: 'c', d: 'e' } }
const source = { a: { b: 'hello' } }
Object.assign(target, source)
// { a: { b: 'hello' } }
const source = {
get foo() { return 1 }
};
const target = {};
Object.assign(target, source)
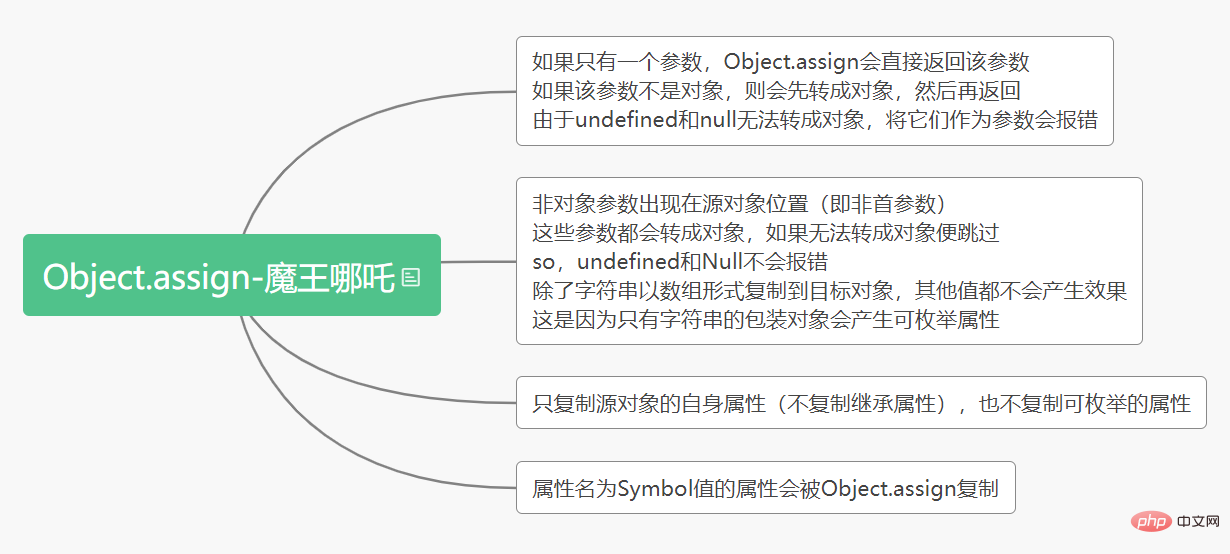
// { foo: 1 }复制代码Object.assign复制的是属性值value,如果属性值是一个引用类型,那么复制的其实是引用地址,就会存在引用共享的问题(Object.assign(target,source1,...,sourceN)浅拷贝的过程)
要点:
function ObjectAssign(target, ...sources) {
// 对第一个参数的判断,不能为undefined和null
if(target === undefined || target === null) {
throw my TypeError('error');
}
// 将第一个参数转为对象(不是对象转换为对象)
const targetObj = Object(target);
// 将源对象自身的所有可枚举属性复制到目标对象
for(let i = 0; i<sources.length; i++){
let source = sources[i];
// 对于undefined和null在源中不会报错,会直接跳过
if(source !== undefined && source !== null) {
// 将源象转换成对象
// 需要将源自身的可枚举数据进行复制
// Reflect.ownKeys(obj)
const keysArray = Reflect.ownKeys(Object(source));
for (let nextIndex = 0; nextIndex < keysArray.length; nextIndex++) {
const nextKey = keysArray[nextIndex];
// 去除不可枚举属性
const desc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(source,nextKey);
if(desc!==undefined&&desc.enumerable){
targetObj[nextKey] = source[nextKey];
}
}
}
}
return targetObj;
}
if(typeof Object.myAssign !== 'function'){
Object.defineProperty(Object, 'myAssign', {
value: ObjectAssign,
writable: true,
enumerable: false,
configurable: true
});
}复制代码浅拷贝 Object.assign 的实现原理
拷贝第一层的基本类似值和第一层的引用类型地址:
let da1 = { name: 'da1', age: 1}let da2 = { name: 'da2', study: { title: 'web'
}
}let da3 = Object.assign(da1,da2);console.log(da3);// {// name: 'da2',// age: 1,// study: { title: 'web' }// }console.log( da1 === da3); // trueda2.name = 'da22';
da2.study.title = 'web2';console.log(da2);// {// name: 'da22',// study: { title: 'web2' }// }console.log(da1);// {// age: 1,// name: 'da2',// study: { title: 'web2' }// }复制代码如果源对象的属性值是一个指向对象的引用,它也只拷贝这个引用地址哦!
let da1 = { name: 'da1', age: 1}let da2 = { a: Symbol('dadaqianduan'), b: null, c: undefined}let da3 = Object.assign(da1, da2);console.log(da3);// {// name: 'da1',// age: 1,// a: Symbol('dadaqianduan'),// b: null,// c: undefined// }console.log(da1 === da3); // true复制代码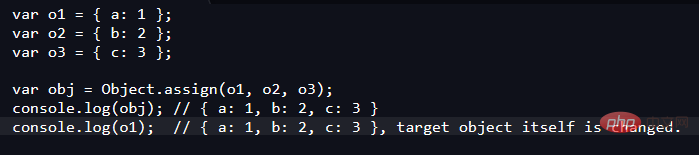
let map = new Map([iterable]) // Map是用来实现字典的功能-Object键值对复制代码
动态属性键
// ES5 code
var
key1 = 'one',
obj = {
two: 2,
three: 3
};
obj[key1] = 1;
// obj.one = 1, obj.two = 2, obj.three = 3
// ES6 code
const
key1 = 'one',
obj = {
[key1]: 1,
two: 2,
three: 3
};
// obj.one = 1, obj.two = 2, obj.three = 3
// ES6 code
const
i = 1,
obj = {
['i' + i]: i
};
console.log(obj.i1); // 1复制代码补充:前端面试考点,HTML和CSS,性能优化,原型,作用域,异步,各种手写代码,DOM事件和Ajax,HTTP协议。
模板文字是es2015/es6的新功能,与es5及以下版本相比,可以通过新颖的方式使用字符串,先只需要反引号代替单引号或双引号即可:
const module_string = `dadaqianduan`复制代码
它们之所以独特是因为它们提供了很多用引号构建的普通字符串不具备的功能:
使用多行字符串
在es6之前的版本:
// 要创建跨越两行的字符串,必须\在行尾使用字符const dada = 'dada \ dadaqianduan' // 呈现效果:在两行上创建一个字符串,但是仅在一行上呈现复制代码
要在多行上呈现,则需要使用\n在每行的末尾添加
const string = 'dada 魔王哪吒\n \ dadaqianduan'复制代码
使用反引号打开模板文字后,只需要按enter键就行:
const dada = `dadaqianduan 魔王哪吒`复制代码
在这里请记住空间是有意义的:
const da = `First
Second`复制代码
使用trim()方法,可以消除第一个字符之前的任何空格
插补:模板文字提供了一种将变量和表达式插入字符串的简便的方法
const da = `dadaqianduan ${mydada}`
${}里面可以添加任何东西
const da1 = `dada ${1+2+3}`
const da2 = `dada ${dafun() ? 'x' : 'y'}`复制代码let da = ['hello', 'world'] let [firstName, surName] = da cosole.log(firstName, surName);复制代码
解构赋值在于赋值,拷贝出来赋值给变量,而赋值的元素本身不会发生改变
默认值
let [da1, da2] = [];console.log(da1); // undefinedconsole.log(da2); // undefined复制代码
给变量赋值(默认值),防止出现undefined的情况:
let [da1= 'da1', da2 = 'da2']=['dadaqianduan] console.log(da1); // dadaqianduan console.log(da2); // da2复制代码
解构分配
ES5中的索引提取这些值:
var myArray = ['a', 'b', 'c'];var one = myArray[0], two = myArray[1], three = myArray[2];// one = 'a', two = 'b', three = 'c'复制代码
ES6解构允许使用更简单方法:
const [one, , three] = myArray;// one = 'a', three = 'c'复制代码
使用rest运算符(...)提取剩余元素:
const [one, ...two] = myArray;// one = 'a', two = ['b, 'c']复制代码
const myObject = { one: 'a', two: 'b', three: 'c'};// ES6 destructuring exampleconst {one: first, two: second, three: third} = myObject;// first = 'a', second = 'b', third = 'c'复制代码可变值交换
var a = 1, b = 2;// ES5 swapvar temp = a; a = b; b = temp;// a = 2, b = 1// ES6 swap back[a, b] = [b, a];// a = 1, b = 2[b, c, d, e, a] = [a, b, c, d, e];复制代码
在ES6中,我们可以为任何参数分配默认值
function dada(param = {}) {复制代码函数返回多个值(函数只能返回一个值,但可以是一个复杂的对象或多维数组)
function f() { return [1, 2, 3];
}const [a, b, c] = f();// a = 1, b = 2, c = 3复制代码ES6 JavaScript深度解构
默认情况下,找不到的属性为undefined
var {da} = {bar: 'dada'}console.log(da)// undefined复制代码如果访问不存在的父级的深层嵌套属性,则将获得异常。
var {da:{bar}} = {dada: 'dadaqianduan'}// Exception复制代码var key = 'dadaqianduan'var { [key]: foo } = { dadaqianduan: 'bar' }console.log(foo)// 'bar'复制代码var {da=3} = { da: 2 }console.log(da)// 2var {da=3} = { da: undefined }console.log(da)// 3var {da=3} = { bar: 2 }console.log(da)// 3var [a] = []console.log(a)// undefinedvar [b=10] = [undefined]console.log(b)// 10var [c=10] = []console.log(c)// 10function da () { return { x: 1, y: 2
}
}var {x, y} = da()console.log(x)// 1console.log(y)// 2复制代码Callback
Promise
function loadScript(src) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { let script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = src
script.onload = () => resolve(src)
script.onerror = (err) => reject(err) document.head.append(script)
})
}复制代码function loadScript(src) { let script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = src; document.head.append(script)
}复制代码var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
resolve('传递给then的值')
})
promise.then(function(value){
console.log(value)
},function(error){
console.error(error)
})复制代码Promise对象是用于表示一个异步操作的最终完成(或失败),以及其结果值。
示例:
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('da');
}, 200);
});
promise.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
});
console.log(promise);复制代码语法:
new Promise(function (resolve,reject){...});复制代码描述:Promise对象是一个代理对象,被代理的值在Promise对象创建时可能是未知的,它允许你为异步操作的成功和失败分别绑定相应的处理方法,这让异步方法可以像同步方法那样返回值,但并不是立即返回最终执行结果,而是一个能代表未来出现的结果的promise对象。
一个Promise有以下几种状态:
pending状态的Promise对象可能会变为fulfilled状态并传递一个值给相应的状态处理方法。
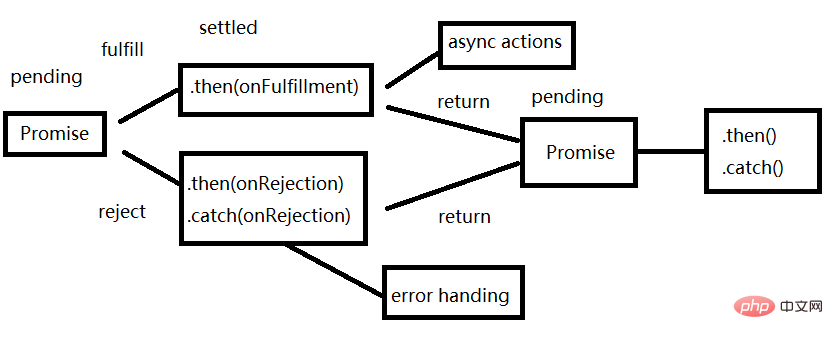
Promise.prototype.then和Promise.prototype.catch方法返回promise对象,所以它们可以被链式调用。
方法:
Promise.all(iterable)
Promise.any(iterable)
Promise.reject(reason)
Promise.resolve(value)
Promise原型
属性:Promise.prototype.constructor返回被创建的实例函数,默认为Promise函数。
方法:
function myAsyncFunction(url) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET',url);
xhr.onload = () => resolve(xhr.responseText);
xhr.onerror = () => reject(xhr.statusText);
xhr.send();
});
}复制代码示例:
var target = {}var handler = {}var proxy = new Proxy(target, handler)
proxy.a = 'b'console.log(target.a)// 'b'console.log(proxy.c === undefined)// true复制代码为了更好地了解代理的有用性,让我们做一些小练习。
示例:
想象一下,您已经17岁了,即将满18岁。并且您希望您的程序在打开时自动向您祝贺。为此,您可以使用代理。
var person = { name: "dada", age: 17};
person = new Proxy(person, {
set(target, property, value) { if (value === 18) { console.log("Congratulations! You are of legal age"); Reflect.set(target, property, value); return true;
}
}
});
person.age = 18;if (value < 13 && value > 99) { throw new Error('The age should be between 13 and 99')
} else { Reflect.set(target, property, value)
}复制代码语法:
let p = new Proxy(target, handler)复制代码
如果不想再调用key的时候,返回undefined:
console.log(o.dada || '')复制代码
使用Proxy
let o = {
name: 'dada', age: 1}let handler = {
get(obj, key) { return Reflect.has(obj, key)?obj[key]:''
}
}let p = new Proxy(o, handler)console.log(p.from)复制代码希望从服务器获取的数据只读,不允许修改:
for (let [key] of Object.entries(response.data)) {
Object.defineProperty(response.data, key, {
writable: false
})
}复制代码使用Proxy:
let data = new Proxy(response.data, {
set(obj, key, value) { return false
}
})复制代码检验逻辑代码:
// Validator.jsexport default(obj, key, vlaue) => { if(Reflect.has(key) && value > 20) {
obj[key] = value
}
}import Validator from './Validator'let data = new Proxy(response.data, { set: Validator
})复制代码使用Proxy,对读写进行监控:
let validator = {
set(target, key, value) { if(key === 'age') { if(typeof value !== 'number' || Number.isNaN(value)) { throw new TypeError('Age must be a number')
} if(value<=0){ throw new TypeError('Age must be a positive number')
}
} return true
}
}const person = { age: 12 }const proxy = new Proxy(person,validator)
proxy.age = 'dada' // TypeError numberproxy.age = NaNproxy.age = 0 // positive numberproxy.age = 3复制代码示例:每个对象都有一个自己的id
class Component { constructor() { this.proxy = new Proxy({ id: Math.random().toString(36).slice(-8)
})
}
get id() { return this.proxy.id
}
}复制代码
function * dada() {
for(let i=0; i<2; i++ {
yield console.log(i);
}
}
const da = dada()
da.next()
da.next()复制代码Generator函数与普通函数的区别在于定义的时候有一个*,执行下面函数:
function* dada() {
console.log('dadaqianduan');
}
dada(); // 没有执行函数
如需要输出,改为:
var da = dada();
da.next();复制代码要生成一个自增的id:
var count_id = 0;
function dada_id() {
count_id ++;
return count_id;
}复制代码方法
Generator.prototype.next() 返回一个由 yield表达式生成的值。 Generator.prototype.return() 返回给定的值并结束生成器。 Generator.prototype.throw() 向生成器抛出一个错误。复制代码
书写风格:
function *da() {
}
function* da(){
}复制代码方法
Generator对象方法:next,return,throw
通过Next方法来获取每一次遍历的结果,这个方法返回一个对象,这个对象包含两个value和done。
value:当前程序的运行结果 done:遍历是否结束
next是可以接收参数的,这个参数可以让你在generator外部给内部传递数据,这个参数就是作为yield的返回值。
return()方法可以让generator遍历终止
function * da() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
var d = da()
console.log(d.next()) // {value:1,done:false}
console.log(d.return()) // {value:undefined,done:true}
console.log(d.next()) // {value:undefined,done:true}复制代码return可以传入参数,作为返回的value的值
function * da() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
var d = da()
console.log(d.nex()) // {value:1,done:false}
console.log(d.return(100)) // {value:100,done:true}
console.log(d.next()) // {value:undefined,done:true}复制代码throw()方法在generator外部控制内部执行的“终断”
generator函数声明:
function* genFunc(){...}
const genObj = genFunc();复制代码generator表达式:
const genFunc = function* () {...}
const genObj = genFunc();复制代码对象中定义:
const obj = {
* generatorMethod(){
...
}
}
const genObj = obj.generatorMethod();复制代码类定义(类声明或类表达式):
class MyClass{
* generatorMethod(){
...
}
}
const myInst = new MyClass();
const genObj = myInst.generatorMethod();复制代码最简单的iterator遍历规范:
authors[Symbol.iterator] = function(){
// this
return {
next(){
return{
done:false,
value:1
}
}
}
}复制代码在es6前,js文件之间的导入,导出是借助require.js,sea.js,如现在使用import,export,来实现原生javascript的导入,导出。
export:
导出变量或者常量
export const da = 'dadaqianduan'
export let da1 = 'da1'
export var da2 = 'da1'
const name = 'dada'
let name1 = 'dada1'
export {
name,
name1
}
导出函数
export function da(value){
console.log(value)
}
const da = (value) => {
console.log(value);
}
export {
da
}
导出Object
export({
name: 'da1',
message: 'dadaqianduan'
})
let da = {
name: 'name1'
}
export {
da
}
导出Class
class Da {
constructor(){
this.id = 1
}
}
export {
Da
}
export class Da {
constructor() {
this.id = 1
}
}
修改导出名称
const name = 'da1'
export {
name as cname
}
export default name复制代码import
// 直接导入
const name = 'dada'
let name1 = 'dada1'
var name2 = 'dada2'
export {
name as cname
}
export default name2
import name2, {name1, name} from A复制代码export const sqrt = Math.sqrt;
export function square(x) {
return x * x;
}
export function dada(x,y) {
return sqrt(square(x) + square(y));
}
import {square,da} from 'da';
console.log(square(11)); // 121
console.log();复制代码export default function() {...}
import myFunc from 'myFunc';
export default class{...}
import MyClass from 'MyClass';
const inst = new MyClass();复制代码require
--lib.js--
function add(x,y){
return x + y
}
module.exports = {
add: add,
};
--main.js--
var add = require('lib').addd;
console.log(add(1,2));复制代码import
--lib.js--
export function add(x,y) {
return x + y
}
--main.js--
import {add} from 'lib';
console.log(add(1,2));复制代码--lib.js--
export const sqrt = Math.sqrt;
export function square(x) {
return x * x;
}
export function da(x,y) {
return sqrt(square(x)+square(y));
}
--main.js--
import {square, da} from 'lib'
--myFunc.js--
export default function() {...};
--main.js--
import myFunc from 'myFunc';
myFunc();复制代码该方法判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,返回布尔值
let da1 = [1,2,3]; console.log(da1.includes(2));复制代码
arr.find(function(item){
return item === 1;
})
arr.filter(function(item){
return item === 2;
})
Math.pow(2,3)->2**3复制代码async function firstAsync(){
let promise = new Promise ((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(function(){
resolve('dadaqianduan')
},1000)
})
console.log(await promise)
console.log(await Promise.resolve(1))
console.log(2)
return Promise.resolve(3)
}
firstAsync().then(val => {
console.log(val)
})复制代码await后面是Promise对象
Object.values()返回一个数组,其元素是再对象上找到的可枚举属性值。
let da = {
'da': 1,
'da2': 2
}
console.log(Object.value(da)) // [1,2]
Object.values是在对象上找到可枚举的属性的值,所以只要这个对象是可枚举的就可以复制代码Object.entries()方法返回一个给定对象自身可枚举属性的键值对数组
题目一:
Promise.resolve().then(()=>{
console.log(1)
}).catch(()=>{
console.log(2)
}).then(()=>{
console.log(3)
})复制代码题目二:
Promise.resolve().then(()=>{
console.log(1)
throw new Error('da')
}).catch(()=>{
console.log(2)
}).then(()=>{
console.log(3)
})复制代码题目三:
Promise.resolve().then(()=>{
console.log(1)
throw new Error('da')
}).catch(()=>{
console.log(2)
}).catch(()=>{
console.log(3)
})复制代码题目四:
async function fn() {
return 1
}
(async function() {
const a = fn() // ??
const b = await fn() // ??
})()复制代码题目五:
console.log(100)
setTimeout( () => {
console.log(200)
})
Promise.resolve().then( ()=> {
console.log(300)
})
console.log(400)复制代码题目六:
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2 () {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('setTimeout')
},0)
async1()
new Promise(function (resolve){
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
}).then(function(){
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')复制代码加载图片:
// 加载
function loadImg(src) {
const p = new Promise(
(resolve,reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img')
img.onload = () =>{
resolve(img)
}
img.onerror = () =>{
const err = new Error('图片加载失败')
reject(err)
}
img.src = src
}
)
return p
}
const url = 'https'
const p = loadImg(url)
p.then(img =>{
console.log(img.width)
return img
}).then(img =>{
console.log(img.height)
}).catch(ex => {
console.error(ex)
})复制代码async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start') // 2
await async2() // undefined
console.log('async1 end') // 5
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2') // 3
}
console.log('script start') // 1
async1()
console.log('script end') // 4复制代码for...of常用于异步的遍历
function add(num) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(num*num)
},1000)
})
}
const nums = [1,2,3]
nums.forEach(async(i)=>{
const res = await add(i)
})复制代码宏任务:setTimeout,setInterval,ajax等 微任务:Promise async/await
微任务执行时比宏任务要早:
宏任务:DOM渲染后触发,如setTimeout
微任务:DOM渲染前触发,如Promise
function da(time) {
return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
setTimeout(function(){
resolve(time)
},time)
})
}
async function test() {
let arr = [da(2000),da(1000),da(3000)]
for await (let item of arr) {
console.log(Date.now(), item)
}
}复制代码const input = {
a: 1,
b: 2
}
const output = {
...input,
c: 3
}
console.log(output)
const input = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
}
let {a, ...rest } = input复制代码该方法会按照一个可指定的深度递归遍历数组,并将所有元素与遍历到的子数组中的元素合为一个新数组。
Array.prototype.flat()建议将数组递归展平至指定范围depth并返回新数组。
depth(指定要提取嵌套数组的结构深度)
语法:Array.prototype.flat(depth)
depth —默认值1,Infinity用于展平所有嵌套数组。
const numbers = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]; // Considers default depth of 1 numbers.flat(); > [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]] // With depth of 2 numbers.flat(2); > [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] // Executes two flat operations numbers.flat().flat(); > [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] // Flattens recursively until the array contains no nested arrays numbers.flat(Infinity) > [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]复制代码
语法:Array.prototype.flatMap(callback)
callback:function产生新Array的元素。
const numbers = [1, 2, 3]; numbers.map(x => [x * 2]); > [[2], [4], [6]] numbers.flatMap(x => [x * 2]); > [2, 4, 6]复制代码
Object.fromEntries
Object.fromEntries执行与的相反操作Object.entries。它将一组键值对转换为一个对象。
const records = [['name','da'], ['age', 32]];
const obj = Object.fromEntries(records);
> { name: 'da', age: 32}
Object.entries(obj);
> [['name','Mathew'], ['age', 32]];复制代码Symbol.prototype.description
只读属性,返回Symbol对象的可选描述:
Symbol('desc').toString(); > "Symbol(desc)" Symbol('desc').description; > "desc" Symbol('').description; > "" Symbol().description; > undefined复制代码
完结,笑纳。
想了解更多编程学习,敬请关注php培训栏目!
The above is the detailed content of After fighting with wolfberry for many nights, I summarized 25 important knowledge points about JavaScript and ES.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!