
The IP address consists of two parts: a network address and a host address. The network address identifies a network. An IP address refers to an Internet Protocol address, also known as an Internet Protocol address. All hosts on the same physical network use the same network ID, and a host on the network has a corresponding host ID.

The IP address actually consists of two parts: a network address and a host address, where the network address identifies a network.
Related introduction:
IP address (Internet Protocol Address) refers to the Internet Protocol address, also translated as Internet Protocol address.
The IP address is a unified address format provided by the IP protocol. It assigns a logical address to each network and each host on the Internet to shield the differences in physical addresses.
Each IP address includes two identification codes (ID), namely network ID and host ID. All hosts on the same physical network use the same network ID. A host on the network (including workstations, servers, routers, etc.) on the network has a host ID corresponding to it.
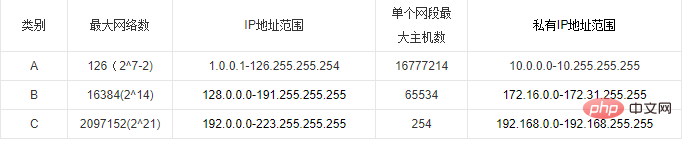
The Internet Committee has defined 5 IP address types to suit networks of different capacities, namely Class A ~ Class E.
Among them, classes A, B, and C3 (as shown in the figure below) are uniformly allocated globally by InternetNIC, and classes D and E are special addresses.
The above is the detailed content of What two parts does an IP address consist of?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




