How to check phpmyadmin database password

You cannot see the original password, you can only see the encrypted password of the database user. If it is md5 encryption, you can try to use the online md5 cracking tool to crack it.
1. Open phpmyadmin;
2. Select the mysql library from the main menu on the left, and then select the user table;
You can see the encrypted user information in the user table Password, see attached picture:
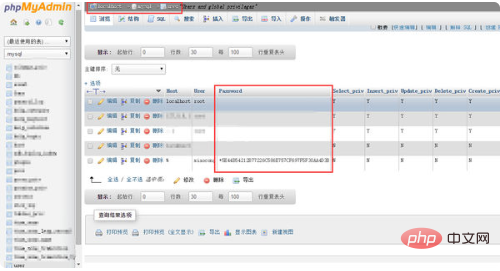
PHP Chinese website has a large number of free phpmyadmin introductory tutorials, everyone is welcome to learn!
The above is the detailed content of How to check phpmyadmin database password. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to install MySQL 8.0 on Windows/Linux?
Jun 11, 2025 pm 03:25 PM
How to install MySQL 8.0 on Windows/Linux?
Jun 11, 2025 pm 03:25 PM
The key to installing MySQL 8.0 is to follow the steps and pay attention to common problems. It is recommended to use the MSI installation package on Windows. The steps include downloading the installation package, running the installer, selecting the installation type, setting the root password, enabling service startup, and paying attention to port conflicts or manually configuring the ZIP version; Linux (such as Ubuntu) is installed through apt, and the steps are to update the source, installing the server, running security scripts, checking service status, and modifying the root authentication method; no matter which platform, you should modify the default password, create ordinary users, set up firewalls, adjust configuration files to optimize character sets and other parameters to ensure security and normal use.
 How to view all databases in MongoDB
Jun 04, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
How to view all databases in MongoDB
Jun 04, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
The way to view all databases in MongoDB is to enter the command "showdbs". 1. This command only displays non-empty databases. 2. You can switch the database through the "use" command and insert data to make it display. 3. Pay attention to internal databases such as "local" and "config". 4. When using the driver, you need to use the "listDatabases()" method to obtain detailed information. 5. The "db.stats()" command can view detailed database statistics.
 How to export data in phpMyAdmin? Supports multiple format selection
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to export data in phpMyAdmin? Supports multiple format selection
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
When using phpMyAdmin to export MySQL database, you should choose the appropriate format according to your purpose. 1. The correct way to enter the export page is to click on the database or table name and select the "Export" tab in the top menu bar. If you need to export multiple tables, you can check it first before operating; 2. Common export formats include SQL (for backup or migration), CSV (for table tool opening), Excel (for non-technical personnel viewing), JSON (for interface debugging), and XML (for structured data exchange); 3. Select the format according to the purpose: SQL is suitable for migrating databases, CSV or Excel is suitable for business personnel viewing, JSON is suitable for front-end and back-end interaction, XML is suitable for specific system imports, and some formats support setting separators
 sql database statements summary of common statements for sql database
May 28, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
sql database statements summary of common statements for sql database
May 28, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
Common SQL statements include: 1. CREATETABLE creates tables, such as CREATETABLEemployees(idINTPRIMARYKEY, nameVARCHAR(100), salaryDECIMAL(10,2)); 2. CREATEINDEX creates indexes, such as CREATEINDEXidx_nameONemployees(name); 3. INSERTINTO inserts data, such as INSERTINTO employeees(id, name, salary)VALUES(1,'JohnDoe',75000.00); 4. SELECT check
 How to generate a relationship diagram in phpMyAdmin? Visualize the database structure
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
How to generate a relationship diagram in phpMyAdmin? Visualize the database structure
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
To enable the "Relational View" function of phpMyAdmin, you must first make sure that there is a configuration table in the database. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Log in to phpMyAdmin and select the target database; 2. Click "Settings" at the top to enter the configuration interface; 3. Click "Create the required relationship table" in the "Affiliation/Relation View" section, and the system will automatically generate necessary tables such as pma__relation; 4. After completion, you can generate a chart by clicking "Relation View". Note when generating a relationship diagram: Foreign key constraints must be defined, otherwise the association cannot be automatically recognized. If there are many tables that cause confusion, you can choose to manage multiple pages in key tables or group them. Without foreign keys, the graph cannot be generated automatically. It is recommended to use foreign keys in a standardized manner or use other tools. Remember after adjusting the layout
 Solve the encoding problem that occurs when PHPMyAdmin imports data
May 19, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
Solve the encoding problem that occurs when PHPMyAdmin imports data
May 19, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
To solve the encoding problem when importing data by PHPMyAdmin, you need to ensure that the import file and database encoding are consistent. The specific steps include: 1. Use the set_charset method to set the connection character set to utf8mb4; 2. Ensure that the SQL file is encoded in UTF-8 without BOM format; 3. Add SETNAMESutf8mb4 and other statements to set the session character set; 4. Handle the settings of special characters in the SQL file and database default character sets.
 How to modify table structure in phpMyAdmin? Adjust fields and types
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
How to modify table structure in phpMyAdmin? Adjust fields and types
Jun 04, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
The operation of modifying the table structure in phpMyAdmin mainly includes the following steps: 1. Enter the "Structure" page of the target database and table; 2. Click the "Change" button of the field to edit; 3. Modify the field name, type, length, whether it is allowed to be empty; 4. Adjust the field order or add new fields; 5. Confirm data compatibility and application layer logic before saving. When modifying, special attention should be paid to the compatibility of primary keys, index fields and existing data to avoid index failure or data loss. It is recommended to back up data before operation.
 How to manage user permissions with phpMyAdmin? Ensure database security
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
How to manage user permissions with phpMyAdmin? Ensure database security
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
The key to managing user permissions with phpMyAdmin is to assign on demand and review regularly. 1. Enter the "User Account" interface of the top menu to view or manage the user list; 2. After filling in the user name and password when creating a user, check global, database or table-level permissions according to your needs in the permission settings to avoid giving "all permissions"; 3. Click "Edit Permissions" when modifying existing user permissions, cancel unnecessary operations such as DROP or DELETE, and be sure to click "Execute" to save; 4. Regularly check whether there are redundant accounts, excessive permissions or simple passwords for user accounts, and clean and adjust them in time to ensure security. Rationally configuring permissions can effectively improve database security.







