

How does thinkphp query the database?
Database Query
ThinkPHP has built-in very flexible query methods that can quickly perform data query operations.
Query conditions can be used for any operation such as CURD, and can be passed in as parameters of the where method.
ThinkPHP can support the direct use of strings as query conditions, but in most cases it is recommended to use index arrays or objects as query conditions, because it is safer.
Query method
1. Use strings as query conditions
This is the most traditional method, but it is safer Not high, for example:
$User = M("User"); // 实例化User对象 $User->where('type=1 AND status=1')->select();
The last generated SQL statement is
SELECT * FROM think_user WHERE type=1 AND status=1
2. Use arrays as query conditions
$User = M("User"); // 实例化User对象 $condition['name'] = 'thinkphp'; $condition['status'] = 1; // 把查询条件传入查询方法 $User->where($condition)->select();
The last generated SQL statement Yes
SELECT * FROM think_user WHERE 'name'='thinkphp' AND status=1
If you perform a multi-field query, the default logical relationship between fields is logical AND, but the default logical judgment can be changed using the following rules, by using _logic to define the query logic:
$User = M("User"); // 实例化User对象 $condition['name'] = 'thinkphp'; $condition['account'] = 'thinkphp'; $condition['_logic'] = 'OR'; //定义查询逻辑 // 把查询条件传入查询方法 $User->where($condition)->select();
The final generated SQL statement is
SELECT * FROM think_user WHERE 'name'='thinkphp' OR `account`='thinkphp'
3. Use the object method to query (here, take the stdClass built-in object as an example)
$User = M("User"); // 实例化User对象 // 定义查询条件 $condition = new stdClass(); $condition->name = 'thinkphp'; $condition->status= 1; $User->where($condition)->select();
The final generated SQL statement is the same as above
SELECT * FROM think_user WHERE `name`='thinkphp' AND status=1
The effect of using object mode query and using array query is the same, and they are interchangeable. In most cases, we recommend using array mode to be more efficient. , later we will use the array method as an example to explain the specific query language usage.
Expression query
The above query condition is just a simple equality judgment. Query expressions can be used to support more SQL query syntax and can be used Query in array or object mode (only array mode is used as an example below), the query expression format is:
$map['字段名'] = array('表达式','查询条件');
Expressions are not case-sensitive. The supported query expressions are as follows, respectively. The meaning is:
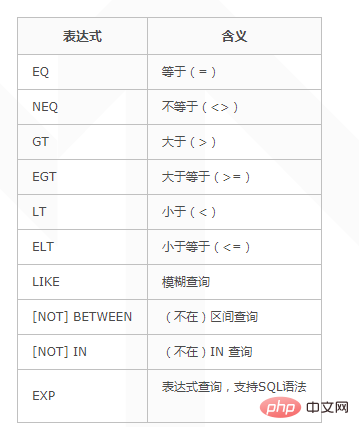 ##
##
$map['id'] = array('eq',100); id = 100; $map['id'] = array('egt',100);id >= 100 $map['name'] = array('like','thinkphp%'); name like 'thinkphp%' 模糊查询 $map['a'] =array('like',array('%thinkphp%','%tp'),'OR');$map['b'] =array('notlike',array('%thinkphp%','%tp'),'AND'); (a like '%thinkphp%' OR a like '%tp') AND (b not like '%thinkphp%' AND b not like '%tp')
//m.sbmmt.com/phpkj/thinkphp /
The above is the detailed content of How thinkphp queries the database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Which one is easier, thinkphp or laravel?
Which one is easier, thinkphp or laravel? How is the performance of thinkphp?
How is the performance of thinkphp? Solution to Connection reset
Solution to Connection reset Android voice playback function implementation method
Android voice playback function implementation method What is the reason for failure to connect to the server?
What is the reason for failure to connect to the server? Introduction to the main work content of front-end engineers
Introduction to the main work content of front-end engineers How to buy Bitcoin
How to buy Bitcoin The difference between a++ and ++a
The difference between a++ and ++a