
1. What is session
The official definition of session is: Session: In computers, especially in network applications, it is called "session control". The Session object stores the properties and configuration information required for a specific user session.
To put it bluntly, session is a data storage technology that can maintain the server side. Session mainly has the following characteristics:
1. The session is saved on the server side
2. Session is generally used with cookies. If the browser disables the cookie function , which means that you can only use URL rewriting to implement the session storage function
3. If you simply use the session to maintain the user status, then when there are a large number of users logged in at the same time, or there are many The number of sessions will lead to the problem of slow query
Essentially: session technology is a technology for temporarily storing data based on the backend that is different from the database
2. Why is there session
One of the main reasons is the statelessness of HTTP
Because of the statelessness of HTTP, we have no way to know the status of the current user when HTTP sends a request. For example, information such as which user currently belongs to, so at this time we need session to identify the current status
3. How session works
Next, let’s initially understand the principle of session through a flow chart that simulates user login. Assume that the user performs a login operation at this time. The specific session workflow is as follows:
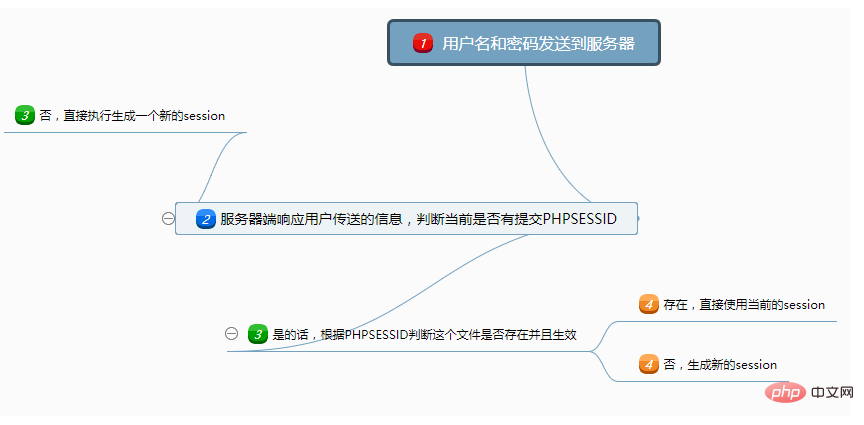
The whole process is roughly divided into the following steps:
1. The first step is to bring the session ID, user name and password in the local cookie to the background
2. The second step The background detects whether there is a corresponding session identifier. Let's take PHP as an example. Then it detects whether the corresponding PHPSESSID
3 is received. If not, a new session is directly generated. If yes, check whether the corresponding file exists and is valid
3. If it is invalid, we need to clear the session and generate a new session. It is not invalid, use the current session
Seeing here you may have a preliminary understanding of the working principle of the session
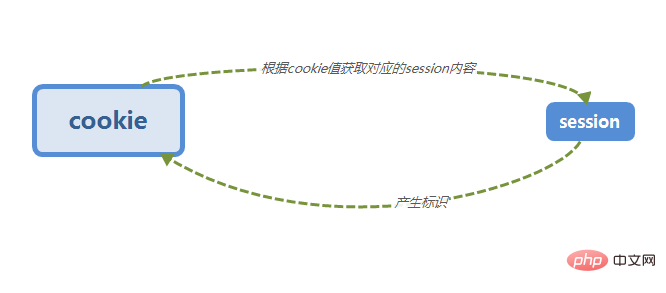
The schematic diagram of the session is as follows:
4. Common configuration of session
Let’s take PHP as an example to explain the configuration of session
First we need to configure PHP Find the php.ini file under the installation directory. The main function of this file is to configure some PHP, which will be discussed in detail later.
1. Set the field name identified in the cookie when the session is stored. The default in PHP is PHPSESSID
. The corresponding setting is: session.name = PHPSESSID
2. If the client disables cookies, you can set session.use_trans_sid to change the interaction method of the identifier from cookie to url delivery
corresponding Set to: session.use_trans_sid = 0
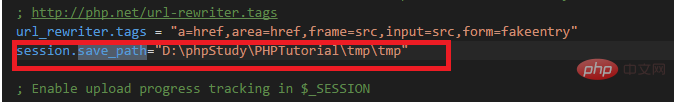
3. Set the session save location
The corresponding setting is session.save_path="D:\phpStudy\ PHPTutorial\tmp\tmp"
5. Session practice in PHP
First we need to install wamp or phpstudy, the specific method is on Baidu
In order to facilitate the observation of changes in the session file, we need to find the save path of the session (find session.save_path in php.ini), as follows:
Then find the directory pointed to. Note that generally the session is saved in the form of files, but we can also modify it according to our actual situation. We can modify and view it in the php.ini file.

The first step in using session, we need to open the session, use session_start(), and then we add a variable to the created session, we assume is demo1, the value is default, the code is as follows:
<?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * Date: 2017/12/16 */ session_start();// 打开session $_SESSION["demo1"] = "default"; ?>
The execution effect is as follows:
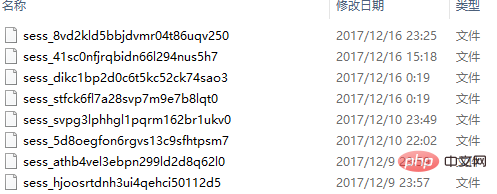
Open the corresponding file, the content inside is as follows:
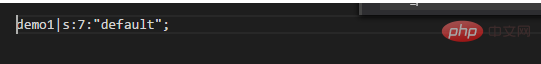
s:7 represents a string type of string type with a length of 7 characters
If we re-edit the content in the session , the effect is as follows:
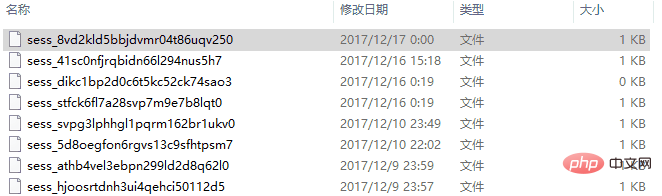
我们观察最近一条的修改日期,我们可以发现就是日期发生了变化,但是文件名没有变化,也就是说,修改session中的内容不会导致文件被新建,而是执行对文件的重新写入操作
session的销毁
销毁session一般有两种方式,unset和session_destroy,我们先来说说第一种
代码如下:
<?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * Date: 2017/12/16 */ session_start();// 打开session $_SESSION["demo1"] = "default_1"; //session的销毁 unset($_SESSION); ?>
这一个相当于没有删除session文件,但是使得即使有对应的PHPSESSID也无法获取到相应的session
session_destroy()相对来说比较彻底,直接删除对应的session文件
<?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * Date: 2017/12/16 */ session_start();// 打开session $_SESSION["demo1"] = "default_1"; var_dump(session_name()); //session的销毁 session_destroy(); ?>
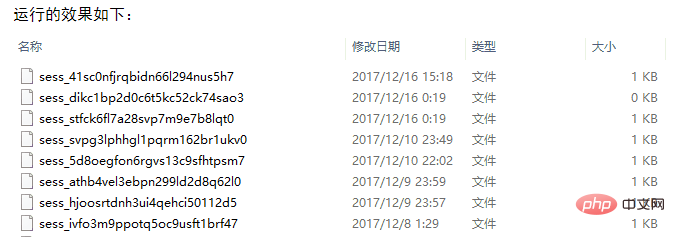
对于个人来说比较推荐使用第二种方法,因为当要销毁session的时候,那么也就意味着session已经失效了,所以这个时候我们把它给删掉才是最好的处理方式,一方面可以减少对硬盘的存储,另外一方面可以相对优化session的查询速度。
好了,这个时候我们应该要设置传递给浏览器端的cookie了,默认是自动传送,但是我们应该要学习的是怎样通过后端设置cookie过去
其中有两个方法与session有关的方法我们需要记住,第一个是session_name(),这个是获取cookie的key值得,第二个是session_id,这个是session的文件名
设置的示例代码:
<?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * Date: 2017/12/16 */ session_start();// 打开session $_SESSION["demo1"] = "default_1"; setCookie(session_name(),session_id(),time()-1000); ?>
在设置cookie的时候,我们为了程序的安全性,我们应该要禁止JS可以对cookie进行重写,所以需要设置HTTP ONLY,具体的设置方法在Php.ini中找到session.cookie_httponly
然后将其的值设置为1或者true即可
除此之外还可以通过setCookie和ini_set()来动态设置HTTPONLY属性
在使用session的时候,虽然会从浏览器把PHPSESSID传给后端,但是这个课程不需要人为的去参与。我们只需要保证HTTPONLY被设置就行了。下面是完整的代码:
<?php
/**
* Created by PhpStorm.
* Date: 2017/12/16
*/
session_start();// 打开session
if ($_SESSION) {
var_dump($_SESSION["demo1"]);
} else {
$_SESSION["demo1"] = "default_" . time();
var_dump($_SESSION["demo1"]);
setCookie(session_name(), session_id(), time(), NULL, NULL, NULL, true);
}
?>6、session的相关注意事项
1. 关闭浏览器session同样存在
如果我们没有人为的去设置cookie的生命周期的时候默认关闭浏览器session的状态是无法被保存下来的,因为没有设置cookie的生命周期,默认这个时候cookie为session cookie也就是在会话存在的时候cookie才有效,所以关闭浏览器cookie失效,导致后端拿不到对应的PHPSESSID,所以无法找到对应的session文件
2. session性能瓶颈怎样解决?
如果是后端存在大量的session的时候,那么这个时候就会出现性能的瓶颈,例如:当后端同时存在有5000个session文件的时候,假设要找的文件是在第4999个,那么也就是说前面至少需要遍历4998次,这样就会浪费过多的时间在后端的循环遍历查找文件中,所以这个时候最有效的方法是使用redis或者mongodb,原理是通过将原本保存在本地的session文件写入到内存中,通过内存换空间的形式来达到提升速度
3. 一般不使用URL重写的方法来传递PHPSESSID
其中主要有两个原因,一个是URL重写方式传递的话会导致URL混乱,影响美观。另一个是增大了用户误操作的几率
更多的session的相关配置请点击这里
7、更多的一些PHP.in中的session含义
[Session]
session.save_handler =的存储方式
session.use_cookies= 1 #使用cookies在客户端保存会话
session.use_only_cookies = 1 #去保护URL中传送session id的用户
session.name = PHPSESSID #session名称(默认PHPSESSID)
session.auto_start = 0 #不启用请求自动初始化session
session.cookie_lifetime = 0 #cookie存活时间(0为直至浏览器重启,单位秒)
session.cookie_path = / #cookie的有效路径
session.cookie_domain = #cookie的有效域名
session.cookie_httponly = #httponly标记增加到cookie上(脚本语言无法抓取)
session.serialize_handler = php #PHP标准序列化
session.gc_probability =1
session.gc_divisor =1000 #建议设置1000-5000
#概率=session.gc_probability/session.gc_divisor(1/1000)
#页面访问越频繁概率越小
session.gc_maxlifetime =1440 #过期时间(默认24分钟,单位秒)
session.bug_compat_42 = off #Global initialization session variable
session.bug_compat_warn = off
session.referer_check = #Prevent external URLs with ID
##session.entopy_length = 0 #Bytes read
session.cache_limiter = { nocache,private,pblic} #HTTP buffer type
session.cache_expire = 180 #Document expiration time (minutes)
session.use_trans_sid = 1 #trans_sid support (default 0)
session.hash_function = 0 #hash method {0:md5(128 bits),1:SHA-1(160 bits)}
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5 #When converting binary hash data into readable form, the number of bits retained per character
session.save_path = "/ var/lib/php/session" #session id storage path
The above is the detailed content of Detailed understanding of session. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!