
This article brings you an introduction to the scope chain and execution environment in JavaScript (pictures and text). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope It will help you.
Each function has a [[Scope]] internal property, which contains a collection of objects in the scope in which the function was created. This collection is the scope chain of the function. For example, the following global function:
fucntion add(num1, num2){
var sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}When the function add is created, an object variable is inserted into its scope chain, which contains all variables defined in the global scope.
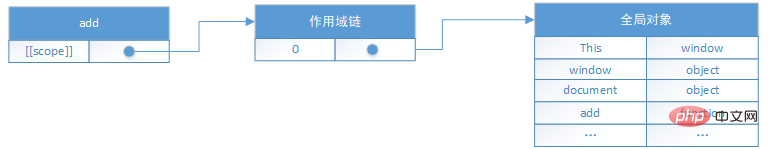
The scope of function add will be used when the function is executed. Each time the function is executed, an internal object of the execution environment will be created. Each execution environment has own scope chain. When the function runs, a new object called the active object is created for the execution environment, which contains all the local variables of the function, named parameters, parameter collections, and this. Assume that var total = add(5,10) is executed, and the corresponding scope chain is as follows:
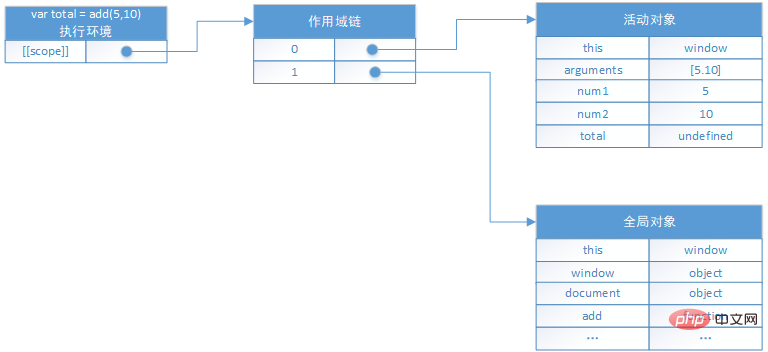
During function execution, the search for variables starts from the scope head Search, and if found use the value of the mutator. If it is not found, continue searching from the next object in the scope until the change is found. If no match is found, it is undefined. When global variables are used frequently, you can first use a local variable to save them, and then directly access the local variables to reduce the number of searches and improve efficiency. For example:
function initUI(){
var doc = document,
bd = doc.body,
links = doc.getElementsByTagName("a");
....
}When the function execution is completed, the active object will also be destroyed. But when closed, the active object will not be destroyed. This is also why closures take up a lot of memory.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to scope chain and execution environment in JavaScript (picture and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!