 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 Introduction to Mysql transaction isolation level content (read commit)
Introduction to Mysql transaction isolation level content (read commit)
Introduction to Mysql transaction isolation level content (read commit)
The content of this article is an introduction to the content of Mysql transaction isolation level (read commit). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Mysql transaction isolation level read commit
View mysql transaction isolation levelmysql> show variables like '%isolation%'; +---------------+----------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+----------------+ | tx_isolation | READ-COMMITTED | +---------------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
You can see that the current transaction isolation level is READ-COMMITTED read commit
Let’s look at the transaction isolation details under the current isolation level and open two query terminals A and B.
There is a order table below, the initial data is as follows
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The first step is to open the transaction in both A and B
mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
The second step Query the number value in both terminals
A
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
B
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The third step changes the number in B to 2, but does not commit the transaction
mysql> update `order` set number=2; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
The fourth step queries the value in A
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
It is found that the value in A has not been modified.
The fifth step is to submit transaction B and query the value in A again
B
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
A
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
It is found that the value in A has changed
The sixth step is to submit the transaction in A and query the values of A and B again.
A
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
B
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Found A and B The values have been changed to 2.
The following is a simple diagram
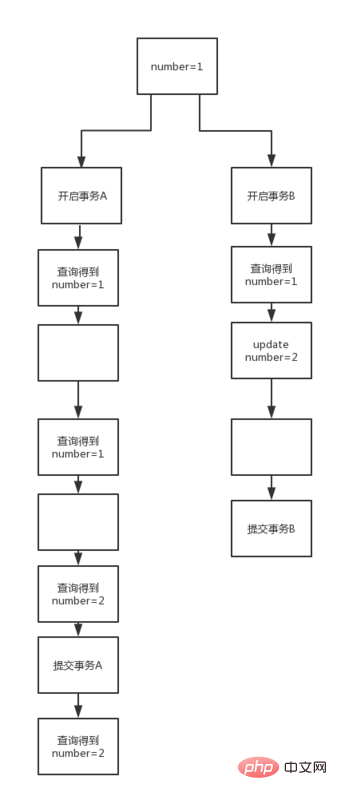
We can see that the transaction isolation level is Read Committed In the case of B, after the transaction in B is submitted, the result of B transaction submission can be read even if A has not submitted. This solves the problem of dirty reading.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Mysql transaction isolation level content (read commit). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 How to build a log management system with PHP PHP log collection and analysis tool
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
How to build a log management system with PHP PHP log collection and analysis tool
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Select logging method: In the early stage, you can use the built-in error_log() for PHP. After the project is expanded, be sure to switch to mature libraries such as Monolog, support multiple handlers and log levels, and ensure that the log contains timestamps, levels, file line numbers and error details; 2. Design storage structure: A small amount of logs can be stored in files, and if there is a large number of logs, select a database if there is a large number of analysis. Use MySQL/PostgreSQL to structured data. Elasticsearch Kibana is recommended for semi-structured/unstructured. At the same time, it is formulated for backup and regular cleaning strategies; 3. Development and analysis interface: It should have search, filtering, aggregation, and visualization functions. It can be directly integrated into Kibana, or use the PHP framework chart library to develop self-development, focusing on the simplicity and ease of interface.
 What are transactions in MongoDB, and how do they provide ACID properties for multi-document operations?
Jul 31, 2025 am 06:25 AM
What are transactions in MongoDB, and how do they provide ACID properties for multi-document operations?
Jul 31, 2025 am 06:25 AM
MongoDBintroducedmulti-documenttransactionsinversion4.0,enablingatomicoperationsacrosscollectionsforstrongconsistency.Transactionsallowmultipleread/writeoperationstobegroupedasasingleunit,eitherallsucceedingorfailingtogether.Theyaresupportedinreplica
 Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
MySQL needs to be optimized for financial systems: 1. Financial data must be used to ensure accuracy using DECIMAL type, and DATETIME is used in time fields to avoid time zone problems; 2. Index design should be reasonable, avoid frequent updates of fields to build indexes, combine indexes in query order and clean useless indexes regularly; 3. Use transactions to ensure consistency, control transaction granularity, avoid long transactions and non-core operations embedded in it, and select appropriate isolation levels based on business; 4. Partition historical data by time, archive cold data and use compressed tables to improve query efficiency and optimize storage.
 Advanced conditional query and filtering of relational data in MySQL/Laravel
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Advanced conditional query and filtering of relational data in MySQL/Laravel
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
This article aims to explore how to use EloquentORM to perform advanced conditional query and filtering of associated data in the Laravel framework to solve the need to implement "conditional connection" in database relationships. The article will clarify the actual role of foreign keys in MySQL, and explain in detail how to apply specific WHERE clauses to the preloaded association model through Eloquent's with method combined with closure functions, so as to flexibly filter out relevant data that meets the conditions and improve the accuracy of data retrieval.
 Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
TooptimizeMySQLforreal-timedatafeeds,firstchoosetheInnoDBstorageenginefortransactionsandrow-levellocking,useMEMORYorROCKSDBfortemporarydata,andpartitiontime-seriesdatabytime.Second,indexstrategicallybyonlyapplyingindexestoWHERE,JOIN,orORDERBYcolumns,
 MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
Whether MySQL is worth moving to the cloud depends on the specific usage scenario. If your business needs to be launched quickly, expand elastically and simplify operations and maintenance, and can accept a pay-as-you-go model, then moving to the cloud is worth it; but if your database is stable for a long time, latency sensitive or compliance restrictions, it may not be cost-effective. The keys to controlling costs include selecting the right vendor and package, configuring resources reasonably, utilizing reserved instances, managing backup logs and optimizing query performance.
 Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
TosecureMySQLeffectively,useobject-levelprivilegestolimituseraccessbasedontheirspecificneeds.Beginbyunderstandingthatobject-levelprivilegesapplytodatabases,tables,orcolumns,offeringfinercontrolthanglobalprivileges.Next,applytheprincipleofleastprivile






