
This article brings you what is the os module in Python? This introduction to the common methods of the os module has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
os module: It can process files and directories. It is an interface for the Python system and the operating system to interact.
Common methods of the os module:
os.getcwd( ): Get the current working directory (that is, the directory path where the current Python script works)
os.chdir('dirname'): Change the working directory of the current script, equivalent to cd under the shell
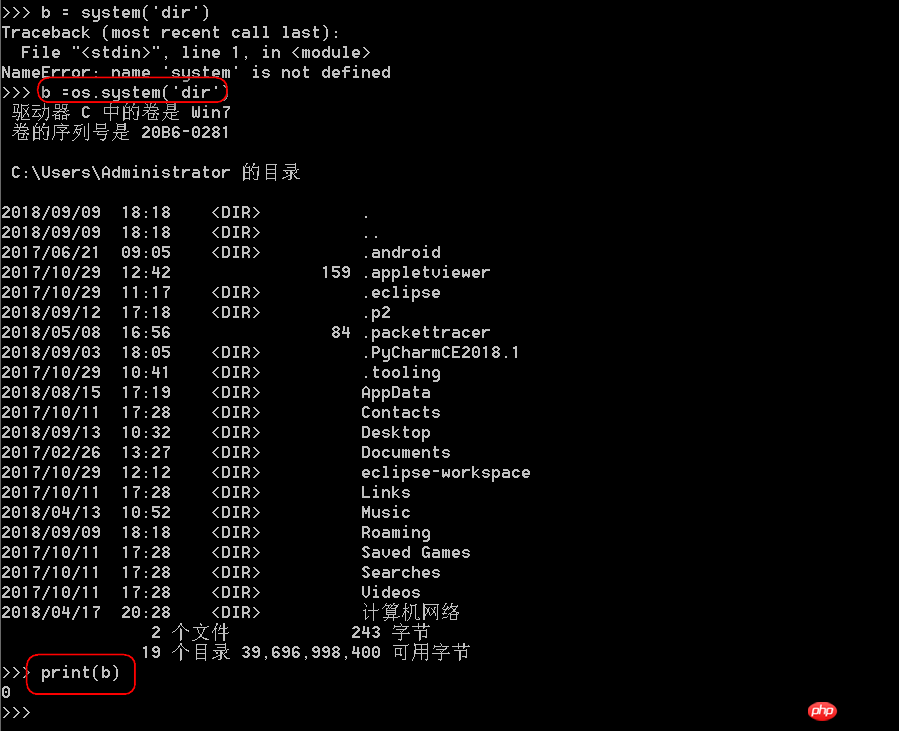
os.system('bash command'): Run the shell command and display it directly (equivalent to starting a new shell and then executing that command. After the command execution is completed, the shell exits directly)
os. curdir: Returns the string name of the current directory
os.pardir: Returns the string name of the parent directory of the current directory
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2'): Can generate a multi-layer Recursive directory
os.removedirs('dirname1'): If the directory is empty, delete it and recurse to the upper-level directory. If it is also empty, delete it, and so on
os .mkdir('dirname'): Create a directory
os.rmdir('dirname'): Delete a directory. If the directory is not empty, it cannot be deleted and an error will be reported
os.listdir( 'dirname'): Display all files and subdirectories in the specified directory, including hidden files
os.remove(): Delete files
os.rename('oldname', 'newname'): Rename the file/directory. If the new file name/directory name already exists, an error will be reported
os.stat(' path/filename'): Get the file/directory information and can Get the size of the file
os.sep: Output the operating system-specific path separator, such as: win is '\\', Linux is '/'
os.liesep: Output the current The line terminator used by the platform, such as '\t\n' for win and '\n' for Linux
os.pathsep: Outputs the string used to split the file path
os. name: The output string indicates the current platform, such as win ->'nt'; Linux ->'posix'
os.environ: Get the environment variable of the operating system
os. path.abspath(path): Returns the normalized absolute path of path
os.path.split(path): Splits the path into a directory and file name tuple and returns
os.path. dirname(path): Returns the directory of path
os.path.basename(path): Returns the last file name of path (an absolute path only returns the last file name)
os.path .exists(path): Determine whether the path exists. If the path exists, return True; if it does not exist, return False
os.path.isabs(path): Determine whether it is an absolute path. If so, return True
os.path.isfile(path): Determine whether it is a file
os.path.isdir(path): Determine whether it is an existing directory
os .path.join(path1[,path2[,.....]]): Divide the path and file name into two elements in a list and put them together
os.path .getatime(path): Returns the last access time of the file or directory pointed to by path
os.path.getmtime(path): Returns the last modification time of the file or directory pointed by path
os.popen('dir'): Equivalent to opening a temporary file to store the opened directory (can be assigned to a variable, in the form of a string)
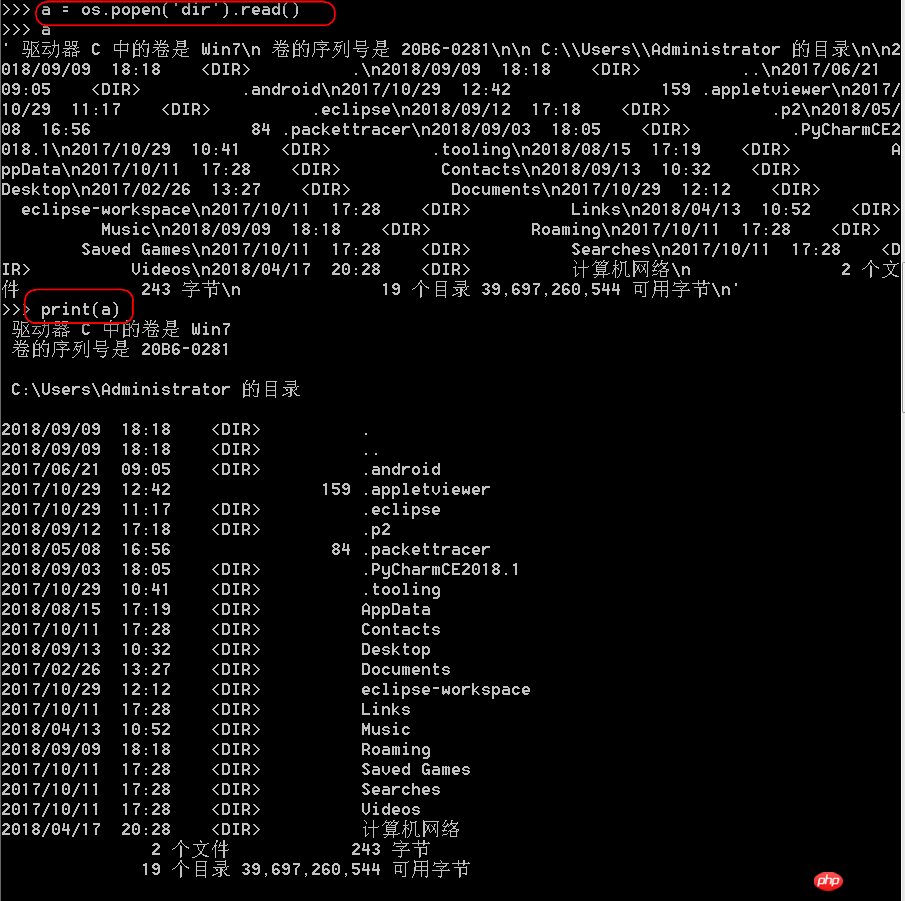
##The difference between system() and popen():
The above is the detailed content of What is the os module in Python? Introduction to common methods of os module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!