
This article introduces about saving sessions in PHP database. Now I share it with everyone. It can also be a reference for friends in need. Let’s take a look together
By default, PHP will save all session data in text files on the server. These files are usually saved on the server. Inside the temporary directory on.
Then why do we need to save the session in the database?
The main reason: to improve the security of the system. On a shared server, without special settings, all websites will use the same temporary directory, which means that dozens of programs are reading and writing files in the same location. Not only was the speed slowed down, but it was also possible for someone else to steal my site's user data.
Saving session data to the database can also make it easier to search for more information about web site sessions. We can query the number of active sessions (the number of users online at the same time), and we can also query Session data is backed up.
If my site runs on multiple servers at the same time, then a user may send multiple requests to different servers during a session, but if the session data is saved in On a certain server, other servers cannot use these session data. If one of my servers only plays the role of a database, wouldn't it be very convenient for you to save all session data in the database?
For more understanding of PHP session, please refer to this blog. Thoroughly understand PHP’s SESSION mechanism
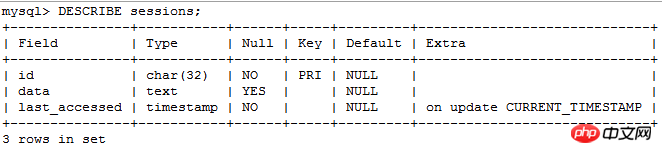
Since the session data is stored on the server, and an index (sessionID) is stored on the client, this index corresponds to a certain piece of session data on the server. Therefore, the two fields that the table must contain are id and data, and the session will have expiration time, so there is another field here which is last_accessed. Here I build the table under the test database:
CREATE TABLE sessions( id CHAR(32) NOT NULL, data TEXT, last_accessed TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id) );
PS: If the program needs to save a large amount of data in the session, the data field may need to be defined as MEDIUMTEXT or LONGTEXT type.
这里我们主要有两个步骤:
定义与数据库交互的函数
使PHP能使用这些自定义函数
在第二步中,是通过调用函数 session_set_save_handler()来完成的,调用它需要6个参数,分别是 open(启动会话)、close(关闭会话)、read(读取会话)、write(写入会话)、destroy(销毁会话)、clean(垃圾回收)。
我们新建php文件 sessions.inc.php ,代码如下:
Copy after login
PS:
处理“读取”函数外,其他函数必须返回一个布尔值,“读取”函数必须返回一个字符串。
.每次会话启动时,“打开”和“读取”函数将会立即被调用。当“读取”函数被调用的时候,可能会发生垃圾回收过程。
当脚本结束时,“写入”函数就会被调用,然后就是“关闭”函数,除非会话被销毁了,而这种情况下,“写入”函数不会被调用。但是,在“关闭”函数之后,“销毁”函数将会被调用。
.session_set_save_handler()函数参数顺序不能更改,因为它们一一对应 open 、close、read、、、、
会话数据最后将会以数据序列化的方式保存在数据库中。
使用新会话处理程序只是调用session_set_save_handler()函数,使我们的自定义函数能够被自动调用而已。其他关于会话的操作都没有发生变化(以前怎么用现在怎么用,我们的函数会在后台自动被调用),包括在会话中存储数据,访问保存的会话数据以及销毁数据。
在这里,我们新建 sessions.php 文件,该脚本将在没有会话信息时创建一些会话数据,并显示所有的会话数据,在用户点击 ‘log out’(注销)时销毁会话数据。
代码:
DB session test Session data stored"; }else{ echo "Session data exists:
".print_r($_SESSION,1)."Copy after loginCopy after login
session destroyed
"; }else{ echo " log out"; }echo "session data :
".print_r($_SESSION,1)."
解析 session_write_close():
顾名思义,该函数就是先写入会话数据,然后关闭session会话,按道理这两步在脚本执行完后会自动执行,为什么我们还要显式调用它呢?因为这里涉及到了数据库的连接!
由于我们知道,PHP会在脚本执行完后自动关闭数据库的所有连接,而同时会话函数会尝试向数据库写入数据并关闭连接。这样一来就会导致会话数据没法写入数据库,并且出现一大堆错误,例如write_session()、close_session()函数中都有用到数据库的连接。
为了避免以上说的问题,我们在脚本执行完之前调用 session_write_close()函数,他就会调用“写入”函数和“关闭”函数,而此时数据库连接还是存在的!
PS:在使用header()函数重定向浏览器之前也应该调用session_write_close()函数,假如有数据库的操作时!
在浏览器中打开 sessions.php,刷新页面,然后再看看数据库有没有添加数据。在另一个浏览器打开 sessions.php ,看看数据库中有没有添加另一条数据。。。。。
本博客主要是参考自《深入理解PHP高级技巧、面向对象与核心技术》,希望能帮到大家。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of PHP database save session session. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




