
This article mainly introduces the use of Mint UI, a mobile framework based on VUE.JS. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
Mint UI
GitHub: github.com/ElemeFE/mint
Project homepage: mint-ui.github.io/
#Demo: elemefe.github.io/mint-
Documentation: mint-ui.github.io/docs/
#Mint launched by the Eleme front-end team UI is a mobile component library based on Vue.js. Since it was open sourced in early June, some bugs have been fixed and some new components have been added based on feedback from the community and the team. Version 0.2.0 was released this week. This article describes how to build a Vue project from scratch using Mint UI.
Scaffolding
With the rapid development of Vue.js, there are currently many options for building scaffolding for a Vue project. For example, you can use the officially provided vue-cli. This article uses Ele.me’s own build tool cooking to complete this task.
First, install cooking globally:
npm i cooking -g
Create a new project folder:
mkdir mint-ui-example
Enter Project folder, use cooking to build:
cooking init vue
The last parameter vue indicates that the scaffolding based on Vue.js is being built.
During the construction process, cooking requires the following parameters:
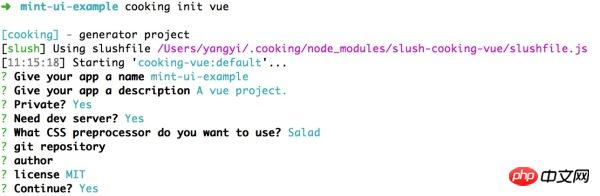
Among them, "Which CSS preprocessing to use" here is Salad, which is a A set of solutions based on PostCSS, interested students can learn about it. Of course, you can also choose other preprocessors.
The project structure after completing the build is:
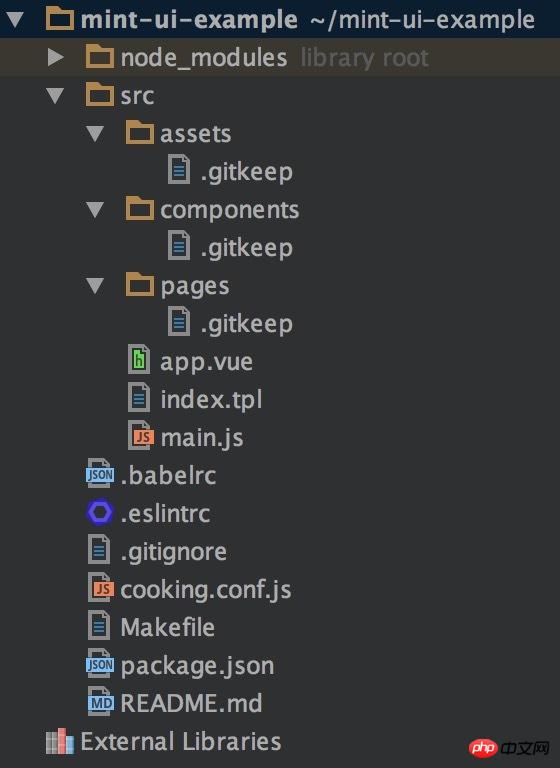
Next, install Mint UI:
npm i mint-ui --save
Introducing Mint UI
Okay, the subsequent work can be divided into two situations:
1. Introduce all components
If your project Many components in Mint UI will be used, and the easiest way is to introduce them all. At this time, it needs to be in the entry file main.js:
import MintUI from 'mint-ui'; import 'mint-ui/lib/style.css'; Vue.use(MintUI);
2. Import on demand
If you only need to use a certain component, You can only introduce this component, and Mint UI can ensure that files unrelated to this component will not appear in the final code when the code is packaged. For example, if you need to introduce the Button component, in main.js:
import Button from 'mint-ui/lib/button'; import 'mint-ui/lib/button/style.css'; Vue.component(Button.name, Button);
It can be seen that the above two introduction methods must introduce the corresponding CSS files separately. This is inconvenient, especially when you use the on-demand import method to introduce multiple components. To avoid this problem, you can use babel-plugin-component plugin. The first thing is of course to install it:
npm i babel-plugin-component -D
Then configure it in .babelrc:
##
{
"plugins": ["other-plugin", ["component", [
{ "libraryName": "mint-ui", "style": true }
]]]
}import MintUI from 'mint-ui'; Vue.use(MintUI);
##
import Button from 'mint-ui/lib/button'; Vue.component(Button.name, Button);
Please read the documentation for how to use each component. Here is just a small example. In app.vue:
<template>
<h1>mint-ui-example</h1>
<mt-button
type="primary"
@click="sheetVisible = true">
选择操作
</mt-button>
<mt-actionsheet
cancel-text=""
:actions="actions"
:visible.sync="sheetVisible">
</mt-actionsheet>
</template>
<script>
import { Toast, MessageBox } from 'mint-ui';
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
sheetVisible: false,
actions: [{
name: '展示 Toast',
method: this.showToast
}, {
name: '展示 Message Box',
method: this.showMsgbox
}]
};
},
methods: {
showToast() {
Toast('这是一个 Toast');
},
showMsgbox() {
MessageBox('提示', '这是一个 Message Box');
}
}
};
</script> ## Preview
## Preview
The above is an introduction to how to use Mint UI. If you encounter any problems during use, or want to give us some suggestions, you are welcome to file an issue in the GitHub repository.
Some students may know that in addition to this mobile component library, Ele.me also has a desktop component library vue-desktop. We are currently reconstructing it. This time with the intervention of UED, the overall vision has been greatly improved. It will also be open sourced after completion, and there will be two versions, supporting vue 1.0.x and vue 2.0 respectively. Of course, Mint UI will also consider supporting vue 2.0. Related recommendations:Detailed examples of Mint UI based on Vue.js mobile component library
VUE.JS mobile framework Mint UI Detailed introduction to the use
Introduction to the use of picker in vue mint-ui
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how to use VUE.JS mobile framework Mint UI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




