

var text = dom.innerText || dom.textContent;
<p id="dom">一段文字内容<span style="position:absolute;">...</span></p>
一段文字内容…
element with position:absolute set... are closely connected to the previous text content, before and after without any spaces. However, when we obtain the <p>innerText and textContent## of the <p> element respectively with id="dom" When the # value was reached, something interesting happened. The return value of innerText actually had a space in front of the dot. 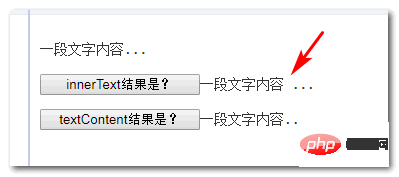 innerText<p> and
innerText<p> and textContent show differences, seeing is believing, You can click here: InnerText and textContent difference comparison demo Why is there such a difference? <p>In fact, innerText<p> will retain the line wrapping characteristics of block-level elements and present them in the form of line breaks. In HTML, if white-space is not pre or pre-wrap, it will appear as a space. That is to say, the spaces in the picture below are actually line breaks:  For example, if we set the parent element to render the result white-space:pre<p>, then The effect shown in the figure below will appear:
For example, if we set the parent element to render the result white-space:pre<p>, then The effect shown in the figure below will appear:  In this example, although the <p> element is an inline element, due to the
In this example, although the <p> element is an inline element, due to the position:absolute makes its display calculated value become block. Therefore, although there is no line break visually, when innerText is obtained Line breaks still occur, resulting in spaces. <p id="dom2">我后面有一段隐藏文字<span hidden>,就是我啦!</span></p>
dom2.textContent, as shown in the figure below:  display:none elements cannot be obtained using <p>innerText
display:none elements cannot be obtained using <p>innerText, but textContent can, regardless of whether the element is hidden or not. You can click here: InnerText and textContent difference comparison demo<p>3. Rule differences in performance and reflow<p><p>此外,由于innerText属性值的获取会考虑CSS样式,因此读取innerText的值将触发回流以确保计算出的样式是最新的,而回流在计算上很昂贵,会降低性能,因此应尽可能避免回流。而textContent只是单纯读取文本内容,因此性能更高。<p>4. IE浏览器不符合上面规则<p>但是在IE浏览器下,innerText的表现和规范是不符的,最终表现为textContent属性一样的效果,也就是没有空格,也不会不显示隐藏元素,例如下面IE11下的效果截图:<p> <p>另外,与
<p>另外,与textContent不同,在Internet Explorer(版本11及以下)中更改innerText将从元素中移除子节点,并永久销毁所有子文本节点。不可能再将节点插入任何其他元素或同一元素中。<p>三、最后的结论<p>innerText由于存在诸多特别的特性、以及兼容性差异,以及性能方面问题,以及实际开发的需求的考量,不推荐使用,推荐使用textContent获取文本内容。var text = dom.textContent;
var text = dom.textContent || dom.innerText;
innerText包含的细节这么多。innerHTML是高频使用属性,没想到原本以为相对应也会高频使用的innerText居然这么有故事,地位被textContent取代了,就像小说里的故事一样,总是出乎意料。
<p>另外,如果你要在一个DOM元素中改变文字内容,推荐使用textContent,而不是innerHTML,性能会更高一点。
<p>好了,就说这么多,一个小小的研究,希望能够对大家的学习有所帮助。
<p>原文地址:https://www.zhangxinxu.com/wordpress/?p=8941
<p>本文来自 js教程 栏目,欢迎学习!The above is the detailed content of Difference between innerText and textContent. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!