
This article mainly introduces PHP to operate the MySQL database based on the ORM method, and analyzes PHP's encapsulation and usage skills for common operations of the MySQL database based on specific examples. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope to be helpful.
The example in this article describes how PHP operates the MySQL database based on the ORM method. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
ORM----Oriented Relationship Mapper, which uses an object-oriented approach to operate the database. In the final analysis, it is still about the encapsulation of SQL statements.
First of all, our database has the following table:
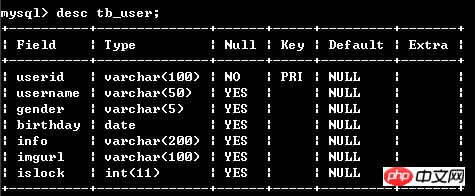
We hope to use setUserid("11111") on this table, that is, Set userid; getUserid() can get the userid of the object. Therefore, we need to create a model object corresponding to the table in the database.
Since the model corresponding to each table should have set/get operations, we use a parent class BasicModel to define it. Other models inherit from this model.
The code of BasicModel is as follows:
map = array(); } function __set($key,$value){ $this->map[$key] = $value; } function __get($key){ return $this->map[$key]; } function __call($name,$arguments) { if(substr($name,0,3)=='set'){ $this->__set(strtolower(substr($name,3)),$arguments[0]); }else{ return $this->__get(strtolower(substr($name,3))); } } } ?>
Then, the model class TbUser corresponding to the tb_user table inherits it.
In this way, we can perform set/get operations on the instance of TbUser.
To use ORM to operate the database, you must be able to query with findByWhere($where), and the returned object array; save($tbUser) to save; delete($obj) to delete; update($obj) ) to perform the update operation.
Essentially, the user passes in an object, and we use code to convert the object into a SQL statement. In essence, SQL statements are still executed.
So, we use interfaces to represent a series of operations. The code of IBasicDAO is as follows:
The most important thing for us is to implement this interface. Complete the conversion of objects and SQL.
BasicDAO code is as follows:
h,$this->user,$this->pass,$this->db); return $conn; } //初始化 public function init() { //根据model的名字得到表的名字 $this->tableName = strtolower(substr($this->modelName,0,2))."_".strtolower(substr($this->modelName,2)); } //获得一个表的列名 public function getColumn($tableName) { $sql = "show columns from ".$tableName; $conn = $this->getConnection(); $columns = array(); if($conn!=null){ $rtn = mysqli_query($conn,$sql); while($rtn!==false&&($row=mysqli_fetch_array($rtn))!=null){ $columns[] = $row[0]; } mysqli_close($conn); } return $columns; } //条件查询 public function findByWhere($where){ //获得数据表的列名 $columns = $this->getColumn($this->tableName); //拼接sql语句 $sql = "select * from ".$this->tableName." where ".$where; $conn = $this->getConnection(); $arr = array(); if($conn!=null){ $rtn = mysqli_query($conn,$sql); while($rtn!==false&&($row=mysqli_fetch_array($rtn))!=null){ $index = -1; $obj = new $this->modelName(); foreach($columns as $column){ $obj->{"set".ucfirst($column)}($row[++$index]); } $arr[] = $obj; } mysqli_close($conn); } return $arr; } //分页查询;支持排序 public function findWhereOrderBy($where,$order,$start=null,$limit=null){ //获得数据表的列名 $columns = $this->getColumn($this->tableName); //拼接sql语句 $sql = "select * from ".$this->tableName." where ".$where." order by ".$order; if($start!=null&&$limit!=null){ $sql .= "limit ".$start.",".$limit; } $conn = $this->getConnection(); $arr = array(); if($conn!=null){ $rtn = mysqli_query($conn,$sql); while($rtn!==false&&($row=mysqli_fetch_array($rtn))!=null){ $index = -1; $obj = new $this->modelName(); foreach($columns as $column){ $obj->{"set".ucfirst($column)}($row[++$index]); } $arr[] = $obj; } mysqli_close($conn); } return $arr; } //保存操作 public function save($obj){ $columns = $this->getColumn($this->tableName); $conn = $this->getConnection(); $tag = false; if($conn!=null){ $sql = "insert into ".$this->tableName."("; foreach($columns as $column){ $sql .= $column.","; } $sql = substr($sql,0,strlen($sql)-1).") values("; foreach($columns as $column){ $value = $obj->{"get".ucfirst($column)}(); //判断$value的类型 if($value==null){ $sql .= "null,"; }else if(preg_match("/^[0-9]*$/", $value)){ //是数字 $sql .= $value.","; }else{ $sql .= "'".$value."',"; } } $sql = substr($sql,0,strlen($sql)-1); $sql .= ")"; //执行sql语句 mysqli_query($conn,$sql); $tag = true; mysqli_close($conn); } return $tag; } //删除操作 public function delete($obj){ $conn = $this->getConnection(); $tag = false; if($conn!=null){ $sql = "delete from ".$this->tableName." where "; $columns = $this->getColumn($this->tableName); $value = $obj->{"get".ucfirst($columns[0])}(); if($value!=null){ //是数字 if(preg_match("/^[0-9]*$/", $value)){ $sql .= $columns[0]."=".$value; }else{ $sql .= $columns[0]."='".$value."'"; } //执行 mysqli_query($conn,$sql); $tag = true; } mysqli_close($conn); } return $tag; } //更新操作 public function update($obj){ $conn = $this->getConnection(); $columns = $this->getColumn($this->tableName); $tag = false; if($conn!=null){ $sql = "update ".$this->tableName." set "; for($i=1;$i{"get".ucfirst($columns[$i])}(); if($value==null){ $sql .= $column."=null,"; }else if(preg_match("/^[0-9]*$/",$value)){ $sql .= $column."=".$value.","; }else{ $sql .= $column."='".$value."',"; } } $sql = substr($sql,0,strlen($sql)-1); $sql .= " where "; $tempColumn = $columns[0]; $tempValue = $obj->{"get".ucfirst($columns[0])}(); if(preg_match("/^[0-9]*$/", $tempValue)){ $sql .= $tempColumn."=".$tempValue; }else{ $sql .= $tempColumn."='".$tempValue."'"; } //执行操作 mysqli_query($conn,$sql); $tag = true; mysqli_close($conn); } return $tag; } } ?>
So, when operating the tb_user table, TbUserDAO is mainly used. It sets the modelName to "TbUser", and the code knows that the table being operated is tb_user, and then You can perform a series of operations.
modelName = 'TbUser'; parent::init(); } } ?>
Then, you can operate the database in an object-oriented manner.
For example:
$tbUserDAO = new TbUserDAO(); $tbUser = new TbUser(); $tbUser->setUserid("fetchingsoft@163.com"); $tbUser->setUsername("fetching"); $tbUserDAO->update($tbUser); echo "执行成功!"; print_r($list);
Update the records in the database.
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of how to batch modify the table structure in PHP
Detailed explanation of PHP's addition, deletion and modification of xml files
Detailed explanation of how PHP implements csv file import into the database
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of PHP operating database based on ORM. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




