
This article mainly introduces the method of Vue generating token and saving it in the client's localStorage. The editor thinks it is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
We have already learned that data can be saved on the client (browser) through localStorage.
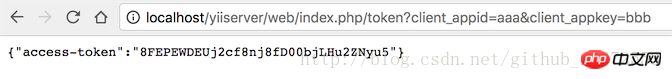
Our backend has such an interface:
http://localhost/yiiserver/web/index.php/token?client_appid=aaa&client_appkey=bbb
In fact, just Clients (understood as user table) generate a token
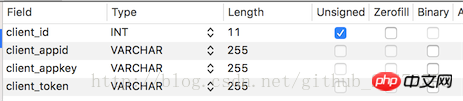
client_appid here is equivalent to the username, client_appkey is equivalent to the password.
In this way, a access-token will be generated after backend authentication. We need to save this access-token on the client.
Note: Our front-end is generally deployed on another server and will cross domains. The back-end needs to handle cross-domain issues. You can write the following code in PHP:
//指定允许其他域名访问
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET,POST");
header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-Requested-With,content-type,if-modified-since');Front-end routine
Note that since our project has already used VueX, then I will definitely use Store(Concept in vuex) to create a module.
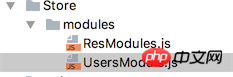
We have created a new UsersModule.js to handle the user login business. Be careful not to forget to add the entry file users-index Introduced in .js. If our "Member Backstage" also needs user-related data, it must also be introduced.
Modify in users-index.js:
//引入模块
import ResModule from './../Store/modules/ResModules';
import UsersModule from "./../Store/modules/UsersModule";
const vuex_config = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
res:ResModule,
users:UsersModule
}
});1, UsersModule.js
import Vue from "vue";
export default {
state:{
currentUser:{
get UserName(){
return localStorage.getItem("currentUser_name");
},
get UserToken(){
return localStorage.getItem("currentUser_token");
}
}
},
mutations:{
setUser(state,{user_name,user_token}){
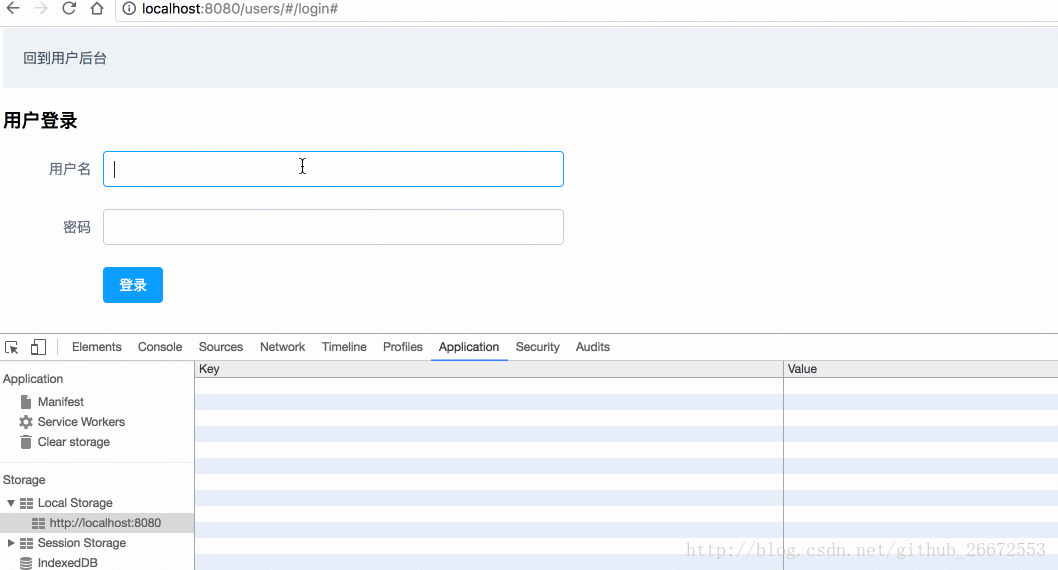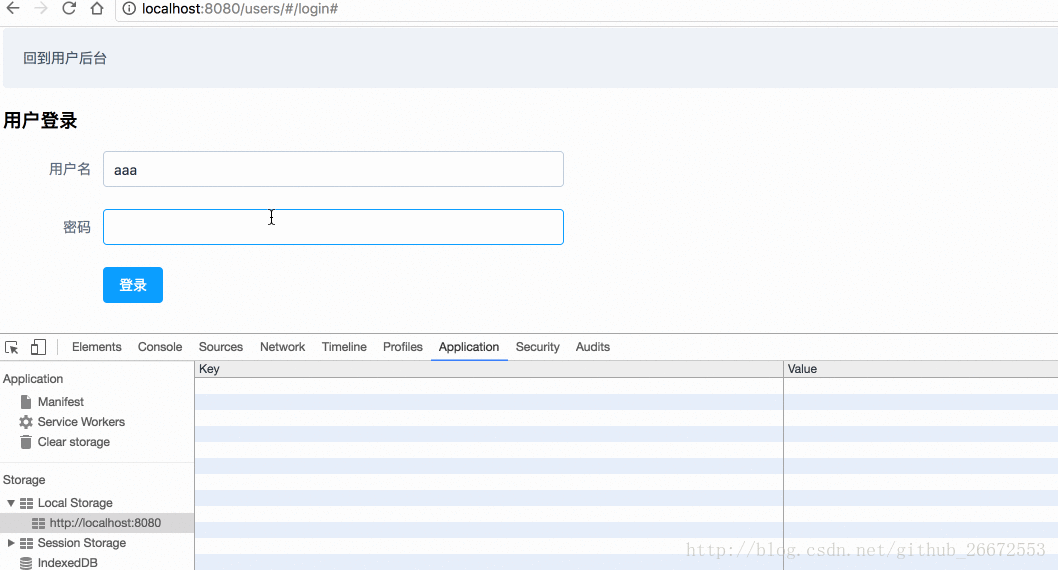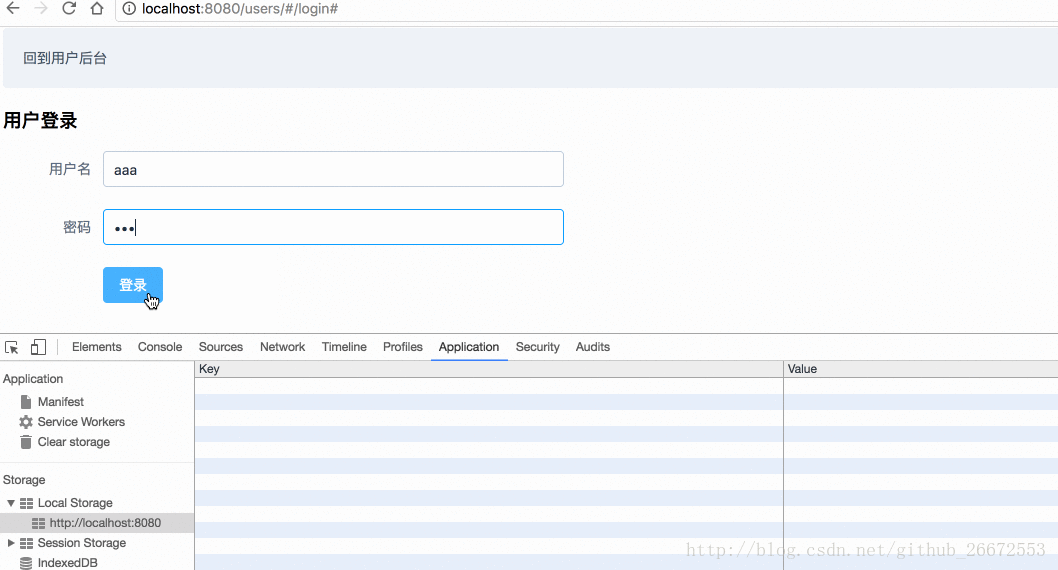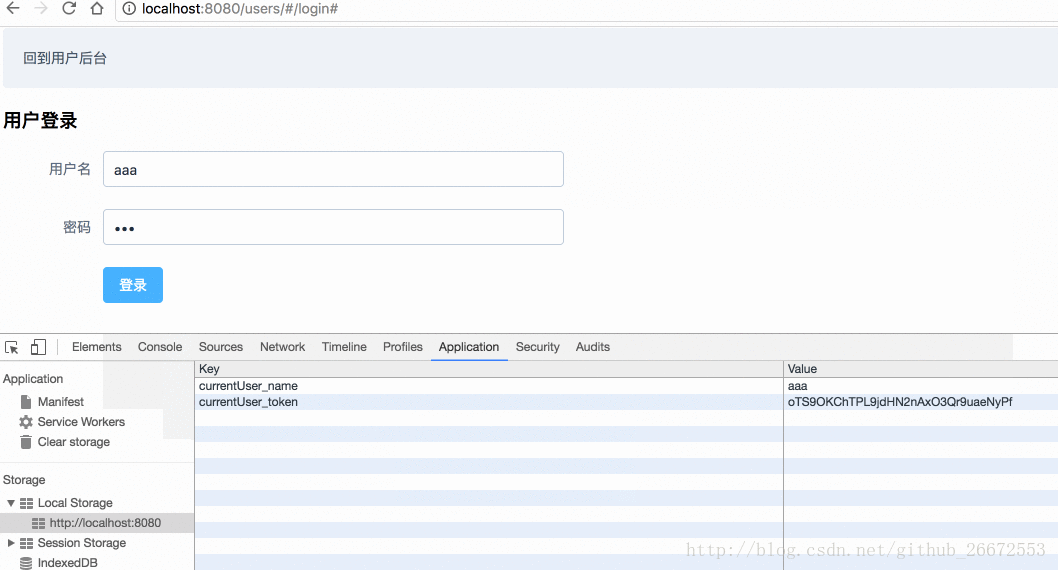
// 在这里把用户名和token保存起来
localStorage.setItem("currentUser_name",user_name);
localStorage.setItem("currentUser_token",user_token);
}
},
actions:{
userLogin(context,{user_name,user_pass}){
// 发送get请求做权限认证(真实开发建议用post的方式)
let url = "http://localhost/yiiserver/web/index.php/token?client_appid="+user_name+"&client_appkey="+user_pass;
console.log(url);
Vue.http.get(url)
.then((res)=>{
if (res!=null && res.body!=undefined && "access-token" in res.body){
var token = res.body["access-token"];
if (token != ""){
// 后端API验证通过
// 调用上面mutations里定义的方法
context.commit("setUser",{"user_name":user_name,"user_token":token});
}
}else{
alert("用户名密码错误");
}
},(res)=>{
alert("请求失败进入这里")
});
}
}
}actions part: We wrote a userLogin() method to send an http request to the backend server. The data returned successfully by the request calls the ## defined in the mutations part. #setUser() method is saved to the client.
userLogin() method in actions is for calling on the user login page, that is, in userslogin.vue.
userlogin.vue and modify the following code:
localStorage中:
methods:{
login(){
// 这个验证是element-ui框架提供的方法
this.$refs["users"].validate(function (flag) {
if(flag){
/*localStorage.setItem("currentUser",this.UserModel.user_name);
alert("用户登录成功");*/
this.$store.dispatch("userLogin",{"user_name":this.UserModel.user_name,"user_pass":this.UserModel.user_pass})
}else{
alert("用户名密码必填");
}
}.bind(this));
}
}
member-index.js of the member backend module:
//引入Module
import ResModule from './../Store/modules/ResModules';
import UsersMoule from "./../Store/modules/UsersModule";
const vuex_config = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
res:ResModule,
users:UsersMoule
}
});<a href="##" rel="external nofollow" >{{this.$store.state.users.currentUser.UserName}}</a>
Vue uses the token to jump to the login page after it expires
Vue-resource interceptor determines token failure and jumps
PHP's WeChat official account verification token, reply content, and push message method
The above is the detailed content of Vue generates a token and saves it in the client's localStorage instance.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




