

Suppose there is a student class (Student)
{ { name =
Age { ;
Address { ;If you need to determine whether some fields (attributes) are empty, Whether it is greater than 0, there will be the following code:
public static string ValidateStudent(Student student)
{
StringBuilder validateMessage = new StringBuilder();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(student.Name))
{
validateMessage.Append("名字不能为空");
} if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(student.Sex))
{
validateMessage.Append("性别不能为空");
} if (student.Age <= 0)
{
validateMessage.Append("年龄必填大于0");
}
//...... 几百行
// 写到这里发现不对啊,如果必填项有20多个,难道我要一直这样写吗!
return validateMessage.ToString();
}Such code has low reusability and low efficiency.
We can use attributes, reflection, and then iterate over the properties and check the attributes.
First customize a [required] attribute class, inherited from Attribute
/// <summary>
/// 【必填】特性,继承自Attribute /// </summary>
public sealed class RequireAttribute : Attribute
{ private bool isRequire; public bool IsRequire
{ get { return isRequire; }
} /// <summary>
/// 构造函数 /// </summary>
/// <param name="isRequire"></param>
public RequireAttribute(bool isRequire)
{ this.isRequire = isRequire;
}
}Then use this customized attribute to mark the member attributes of the student class:
/// <summary>
/// 学生类 /// </summary>
public class Student
{
/// <summary>
/// 名字 /// </summary>
private string name;
[Require(true)] public string Name
{ get { return name; } set { name = value; }
} /// <summary>
/// 年龄 /// </summary>
[Require(true)] public int Age { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 地址 /// </summary>
[Require(false)] public string Address { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 性别 /// </summary>
[Require(true)]
public string Sex;
}Check the properties of the class by attributes:
/// <summary>
/// 检查方法,支持泛型 /// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="instance"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string CheckRequire<T>(T instance)
{
var validateMsg = new StringBuilder();
//获取T类的属性
Type t = typeof (T);
var propertyInfos = t.GetProperties();
//遍历属性
foreach (var propertyInfo in propertyInfos)
{
//检查属性是否标记了特性
RequireAttribute attribute = (RequireAttribute) Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(propertyInfo, typeof (RequireAttribute));
//没标记,直接跳过
if (attribute == null)
{
continue;
}
//获取属性的数据类型
var type = propertyInfo.PropertyType.ToString().ToLower();
//获取该属性的值
var value = propertyInfo.GetValue(instance);
if (type.Contains("system.string"))
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty((string) value) && attribute.IsRequire)
validateMsg.Append(propertyInfo.Name).Append("不能为空").Append(",");
}
else if (type.Contains("system.int"))
{
if ((int) value == 0 && attribute.IsRequire)
validateMsg.Append(propertyInfo.Name).Append("必须大于0").Append(",");
}
} return validateMsg.ToString();
}Perform validation:
static void Main(string[] args)
{ var obj = new Student()
{
Name = ""
};
Console.WriteLine(CheckRequire(obj));
Console.Read();
}Result output:
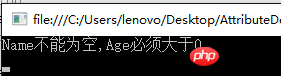
#Some people will find that Sex is also marked [Require(true)], why there is no verification information, this is because, Sex does not implement the properties {get; set; }, and GetProperties cannot be obtained
The above is the detailed content of Simplified example code using reflection and features in C#. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




