
When the page where the navigation bar was hovered last time is run on IE, there will be a problem of the navigation bar shaking constantly. This article has a perfect solution. Change the positioning method of the navigation bar from the original absolute to Fixed
Last time [JS-implementing navigation bar hover] mentioned that when the page where the navigation bar is hovered is run on IE, the navigation bar will keep shaking.
The solution is as follows:
Changed the positioning method of the navigation bar from absolute to fixed. I don’t know why it was changed to fixed, so it stopped shaking. . -_-||
The code is as follows:
p.navigation{
width: 800px;
height: 40px;
background: red;
margin: 4px auto 0;
top: 400px;
left: 0px;
position: fixed;
}For this reason, JS must also be modified accordingly.
Because fixed positioning is based on the browser's visible area, the original positioning of the navigation bar must be changed.
//记录导航条原来在页面上的位置
var naviga_offsetTop = 0;
var naviga_offsetLeft = 0;
//IE7不识别getElementsByClassName,为了兼容自定义一个
function my_getElementsByClassName(class_name) {
var el = [];
//获取所有元素
_el = document.getElementsByTagName('*');
//通过className刷选
for (var i=0; i<_el.length; i++ ) {
if (_el[i].className == class_name ) {
el[el.length] = _el[i];
}
}
return el;
}
//导航条,悬停在顶部
function naviga_stay_top(){
var a_navigation_bar = [];
if(document.getElementsByClassName){//Chrome, FF
a_navigation_bar = document.getElementsByClassName("navigation");
} else {//IE
a_navigation_bar = my_getElementsByClassName("navigation");
}
var scrollTop = document.body.scrollTop || document.documentElement.scrollTop;
document.title = scrollTop;
//如果向下滚动的距离大于原来导航栏离顶部的距离
//直接将导航栏固定到可视区顶部
if( scrollTop > naviga_offsetTop ){
a_navigation_bar[0].style.top = 0 + "px";
} else {
//如果向下滚动的距离小原来导航栏离顶部的距离,则重新计算导航栏的位置
a_navigation_bar[0].style.top = (naviga_offsetTop - scrollTop) + "px";
}
}
//给导航条上四个tab,加上点击事件。
window.onload=function(){
var a_tabs = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_tabs = document.getElementsByClassName("tab");
}else{ //IE
a_tabs = my_getElementsByClassName("tab");
}
var a_contents = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_contents = document.getElementsByClassName("content");
}else{//IE
a_contents = my_getElementsByClassName("content");
}
//获取offsetLeft,即导航栏离左边框的距离
var a_main_p = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_main_p = document.getElementsByClassName("main");
}else{ //IE
a_main_p = my_getElementsByClassName("main");
}
naviga_offsetLeft = a_main_p[0].offsetLeft;
a_tabs[0].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[2].offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[1].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[3].offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[2].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[4].offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[3].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[5].offsetTop);
}
//获取页面上,导航条到顶部的位置
var a_navigation_bar = [];
if(document.getElementsByClassName){//Chrome, FF
a_navigation_bar = document.getElementsByClassName("navigation");
} else {//IE
a_navigation_bar = my_getElementsByClassName("navigation");
}
//获取offsetTop
naviga_offsetTop = a_navigation_bar[0].offsetTop;
a_navigation_bar[0].style.left = naviga_offsetLeft + "px";
//给滚动条以及鼠标加上滚动事件
if( window.attachEvent) //IE
{
window.attachEvent("onmousewheel", naviga_stay_top);
window.attachEvent("onscroll", naviga_stay_top);
document.attachEvent("onmousewheel", naviga_stay_top);
document.attachEvent("onscroll", naviga_stay_top);
} else {//Chrome ,FF
window.addEventListener("mousewheel", naviga_stay_top,false);
window.addEventListener("scroll", naviga_stay_top,false);
document.addEventListener("mousewheel", naviga_stay_top,false);
document.addEventListener("scroll", naviga_stay_top,false);
}
}
In this question, it is important to understand the difference between CSS+p positioning (relative, absolute, static, fixed).
relative,absolute,static,fixed
Let’s first look at the definition of each attribute value:
1. static: default value. Without positioning, the element appears in normal flow (ignoring top, bottom, left, right or z-index declarations).
2. Relative: Generate relatively positioned elements and position them relative to their normal positions through the settings of top, bottom, left, and right. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
3. Absolute: Generate absolutely positioned elements and position them relative to the first parent element other than static positioning. The position of the element is specified via the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
4. Fixed: Generate absolutely positioned elements and position them relative to the browser window. The position of the element is specified via the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
The positioning methods of static and fixed are easy to understand and will not be analyzed here. The following is an analysis of the commonly used relative and absolute:
1, relative. An element positioned relative is removed from the normal text flow, but its position in the text flow still exists. As shown in Figure 1: 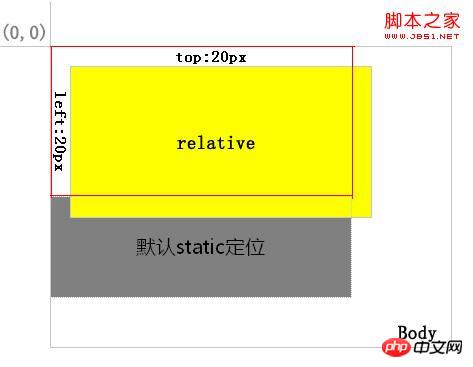
Figure 1
The layer with the yellow background is positioned relative, and the red border area is its position in the normal flow. After positioning it through top and left, you can see from the position of the gray background layer that its normal position still exists.
2. Absolute. A layer positioned as absolute is separated from the normal text flow, but the difference from relative is that its position in the normal flow no longer exists. As shown in Figure 2:  ##Figure 2
##Figure 2
As you can see, after positioning the yellow background layer as absolute, the gray background layer is automatically filled in.
3. The main difference between relative and absolute:
First of all, it is whether the position in the normal flow exists or not as mentioned above.
Secondly, the relative positioned layer is always relative to its nearest parent element, no matter how its parent element is positioned. As shown in Figure 3: 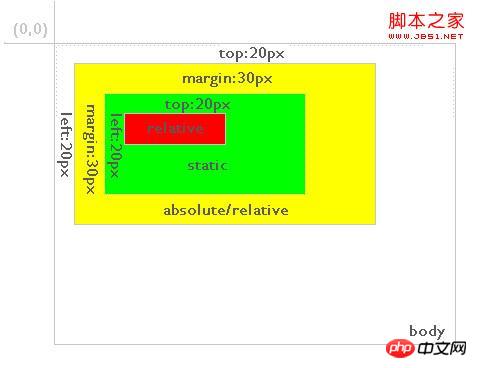 ##Figure 3 In the figure, the red background layer is relative positioned, and the green background layer of its direct parent element is static positioned by default. The position of the red background layer is the top and left 20 elements relative to the green background layer. And if the red background layer is positioned as absolute, the situation is as shown in Figure 4:
##Figure 3 In the figure, the red background layer is relative positioned, and the green background layer of its direct parent element is static positioned by default. The position of the red background layer is the top and left 20 elements relative to the green background layer. And if the red background layer is positioned as absolute, the situation is as shown in Figure 4:
 Figure 4 As you can see, the red background layer still defines top:20px; left: 20px; but its relative element becomes a yellow background layer with absolute or relative positioning mode. Therefore, a layer positioned for absolute is always relative to its nearest parent layer defined as absolute or relative, and this parent layer is not necessarily its direct parent layer. If absolute or relative is not defined in its parent layer, it will be positioned relative to the body, as shown in Figure 5:
Figure 4 As you can see, the red background layer still defines top:20px; left: 20px; but its relative element becomes a yellow background layer with absolute or relative positioning mode. Therefore, a layer positioned for absolute is always relative to its nearest parent layer defined as absolute or relative, and this parent layer is not necessarily its direct parent layer. If absolute or relative is not defined in its parent layer, it will be positioned relative to the body, as shown in Figure 5:
##Figure 5 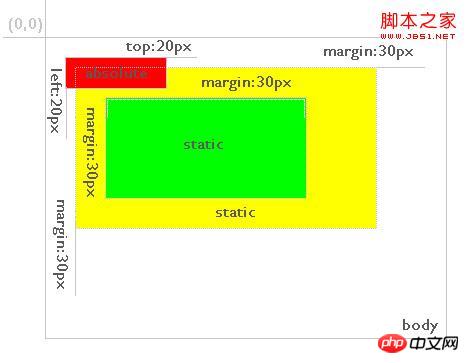 Except top, left, and right , bottom positioning, the definition of margin attribute value also conforms to the above rules.
Except top, left, and right , bottom positioning, the definition of margin attribute value also conforms to the above rules.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of graphic code on how to use JavaScript to achieve navigation bar hover effect. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




