
ActiveMQ supports persistent messages and non-persistent messages in the JMS specification
Persistent messages Usually used to ensure that messages will be consumed by the consumer regardless of whether the consumer is online or not. When the message is confirmed to be consumed, it will be deleted from the storage
Non-persistent messages are usually used to send notifications and real-time data. Performance is usually required first, and message reliability is not a must.
MQ supports pluggable message storage, such as memory, file and relational database
Queue message model Storage in ActiveMQ
adopts first-in-first-out (FIFO) storage. A message can only be consumed by one consumer, and will be deleted only after the message is confirmed to be consumed.
Topic message model (for durable subscription)
The message obtained by each subscriber is actually a copy of the message. Only one copy of the message will be stored. MQ provides a pointer To point to the message store and distribute a copy of the message to subscribers, the message cannot be deleted until all persistent subscribers have received it.
Persistent storage method:
KahaDB message storage
AMQ message storage
JDBC message storage
Memory message storage
KahaDB is the default persistence plug-in starting from ActiveMQ 5.4. KahaDb's recovery time is much shorter than its predecessor AMQ and uses fewer data files, so it can completely replace AMQ. KahaDB's persistence mechanism is also based on log files, indexes and caches.
(1) Main features of KahaDB:
Store messages in log form;
The message index is stored in a B-Tree structure and can be updated quickly;
Fully supports JMS transactions;
Supports a variety of Recovery mechanism;
(2) Applicable scenarios:
High throughput Application
Storing messages with large amounts of data
(3) Configuration method conf/activemq.xml:
<persistenceAdapter><kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/></persistenceAdapter>
(四)、KahaDB存储原理:
当有活动消费者时,用于临时存储,消息会被发送给消费着,同时被安排将被存储,如果消息及时被确认,就不需要写入到磁盘。写入到磁盘中的数据消息,在后续的消息活动中,如果消息发送成功,变标记为可删除的。系统会周期性的清除或者归档日志文件。
1、KahaDB内部结构

Data logs:消息日志包含了消息日志和一些命令
Cache:当有活动消费者时,用于临时存储,消息会被发送给消费着,同时被安排将被存储,如果消息及时被确认,这不需要写入到磁盘
Btree indexes(消息索引):用于引用消息日志(message id),它存储在内存中,这样能快速定位到。MQ会定期将内存中的消息索引保存到metadata store中,避免大量消息未发送时,消息索引占用过多内存空间。
Redo log用于在非正常关机情况下维护索引完整性。
2、目录结构:
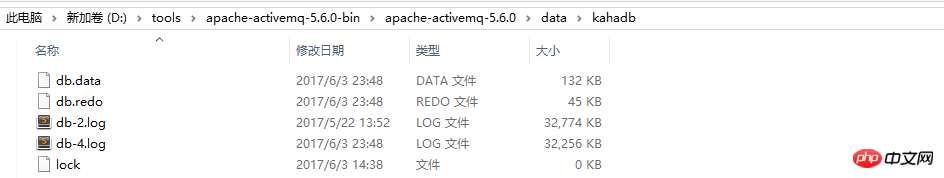
Db log files:用于存储消息(默认大小32M),当log日志满了,会创建一个新的,当log日志中的消息都被删除,该日志文件会被删除或者归档。
Archive directory:当datalog不在被kahadb需要会被归档(通过archiveDataLogs属性控制)。
Db.data:存放Btree indexs。
Db.redo:存放redo file,用于恢复Btree indexs。
写入消息时,会将消息写入日志文件,由于是顺序追加写,性能很高。为了提升性能,创建消息主键索引,并且提供缓存机制,进一步提升性能。每个日志文件的大小都是有限制的(默认32m,可自行配置)。当超过这个大小,系统会重新建立一个文件。当所有的消息都消费完成,系统会删除这个文件或者归档(取决于配置)。主要的缺点是AMQ Message会为每一个Destination创建一个索引,如果使用了大量的Queue,索引文件的大小会占用很多磁盘空间。而且由于索引巨大,一旦Broker崩溃,重建索引的速度会非常慢。
特点:类似KahaDB,也包含了事务日志,每个destination都包含一个index文件,AMQ适用于高吞吐量的应用场景,但是不适合多个队列的场景。
配置方式conf/activemq.xml:
<!--AMQ directory:数据存储路径 syncOnWrite:是否同步写入 maxFileLength:日志文件大小 --><persistenceAdapter><amqPersistenceAdapterdirectory="${activemq.data}/AMQdb"syncOnWrite="true"maxFileLength="10mb" /></persistenceAdapter>1、AMQ内部结构:
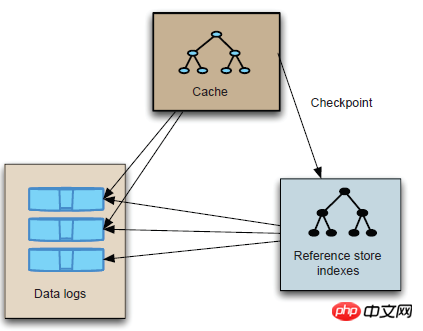
Data logs:消息日志包含了消息日志
Cache:用于消息的快速检索
Reference store indexes:用于引用datalogs中的消息,通过message ID 关联
2、目录结构:
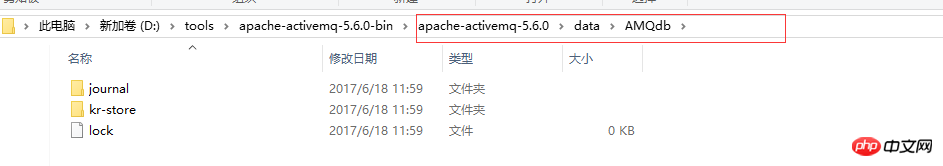
Lock:保证同一时间只有一个borker访问文件目录
temp-storag:用于存储非持久化消息(当不在被存储在内存中),如等待慢消费者处理消息
Kr-store:用于存储引用消息日志数据
journal directory:包含了消息文件、消息日志和消息控制信息
Archive:归档的数据日志
支持通过JDBC将消息存储到关系数据库,性能上不如文件存储,能通过关系型数据库查询到消息的信息。
MQ支持的数据库:Apache Derby、MYsql、PostgreSQL、Oracle、SQLServer、Sybase、Informix、MaxDB。
存储表结构:
A、ACTIVEMQ_MSGS:用于存储消息,Queue和Topic都存储在这个表中:
ID:自增的数据库主键
CONTAINER:消息的Destination
MSGID_PROD:消息发送者客户端的主键
MSG_SEQ:是发送消息的顺序,MSGID_PROD+MSG_SEQ可以组成JMS的MessageID
EXPIRATION:消息的过期时间,存储的是从1970-01-01到现在的毫秒数
MSG:消息本体的Java序列化对象的二进制数据
PRIORITY:优先级,从0-9,数值越大优先级越高
B、ACTIVEMQ_ACKS:用于存储订阅关系。如果是持久化Topic,订阅者和服务器的订阅关系在这个表保存:
主要的数据库字段如下:
CONTAINER:消息的Destination
SUB_DEST:如果是使用Static集群,这个字段会有集群其他系统的信息
CLIENT_ID:每个订阅者都必须有一个唯一的客户端ID用以区分
SUB_NAME:订阅者名称
SELECTOR:选择器,可以选择只消费满足条件的消息。条件可以用自定义属性实现,可支持多属性AND和OR操作
LAST_ACKED_ID:记录消费过的消息的ID。
C、ACTIVEMQ_LOCK(消息锁,保证同一时间只能有一个broker访问这些表结构):
表activemq_lock在集群环境中才有用,只有一个Broker可以获得消息,称为Master Broker,其他的只能作为备份等待Master Broker不可用,才可能成为下一个Master Broker。这个表用于记录哪个Broker是当前的Master Broker。
配置方式:
1、配置数据源 conf/acticvemq.xml文件:
<!-- 配置数据源--> <bean id="mysql-ds" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"><property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activemq?relaxAutoCommit=true"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="111111"/><property name="maxActive" value="200"/><property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true"/> </bean>
2、配置broke中的persistenceAdapter :
dataSource指定持久化数据库的bean,createTablesOnStartup是否在启动的时候创建数据表,默认值是true,这样每次启动都会去创建数据表了,一般是第一次启动的时候设置为true,之后改成false。
<!-- JDBC配置 --><persistenceAdapter><jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds" createTablesOnStartup="false"/></persistenceAdapter>
ps:数据库activemq 需要手动创建。
内存消息存储,会将所有的持久化消息存储在内存中,必须注意JVM使用情况以及内存限制,适用于一些能快速消费的数据量不大的小消息,当MQ关闭或者宕机,未被消费的内存消息会被清空。
配置方式 设置 broker属性值 persistent="false":
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="localhost" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}" persistent="false">
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of JMS Active MQ message storage instance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Data encryption storage measures
Data encryption storage measures
 What does it mean when a message has been sent but rejected by the other party?
What does it mean when a message has been sent but rejected by the other party?
 How to solve dns_probe_possible
How to solve dns_probe_possible
 css set text color
css set text color
 Is the success rate of railway 12306 standby ticket high?
Is the success rate of railway 12306 standby ticket high?
 Reasons why computers often have blue screens
Reasons why computers often have blue screens
 ASUS f83se
ASUS f83se
 Domestic free ChatGPT encyclopedia
Domestic free ChatGPT encyclopedia




