
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information for getting started with Spring Batch. The introduction in the article is very detailed and has a certain reference and learning value for everyone. Friends who need it can follow the editor to learn together.
Introduction to SpringBatch:
SpringBatch is a parallel processingframeworkfor large amounts of data. It is usually used for offline migration of data and data processing. It supports transactions, concurrency, process, monitoring, vertical and horizontal expansion, and provides unified interface management and task management; SpringBatch is an effort by SpringSource and Accenture to unify industry parallel processing standards. Provide developers with a set of frameworks that facilitate development.
Official address: github.com/spring-projects/spring-batch
SpringBatch itself provides retry,Exception handling, skip , restart, task processing statistics, resource management and other features, these are the main reasons why developers value it;
SpringBatch is a lightweight batch processing framework;
SpringBatch structure is layered, business and processing strategies and structures are separated;
The running instance of the taskStatus, execution data, and parameters will all be Landing in the database;
Quick Start
pom.xml Add
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-batch
Create BatchConfig (can be another class name)
@Configuration @EnableBatchProcessing public class BatchConfig { // tag::readerwriterprocessor[] @Bean public FlatFileItemReader flatFileItemReader() { FlatFileItemReader reader = new FlatFileItemReader<>(); reader.setResource(new ClassPathResource("sample-data.csv")); FixedLengthTokenizer fixedLengthTokenizer = new FixedLengthTokenizer(); reader.setLineMapper(new DefaultLineMapper() {{ setLineTokenizer(new DelimitedLineTokenizer() {{ setNames(new String[]{"firstName", "lastName"}); }}); setFieldSetMapper(new BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper() {{ setTargetType(Person.class); }}); }}); return reader; } @Bean public JdbcPagingItemReader jdbcPagingItemReader(DataSource dataSource) { JdbcPagingItemReader reader = new JdbcPagingItemReader<>(); reader.setDataSource(dataSource); reader.setFetchSize(100); reader.setQueryProvider(new MySqlPagingQueryProvider() {{ setSelectClause("SELECT person_id,first_name,last_name"); setFromClause("from people"); setWhereClause("last_name=:lastName"); setSortKeys(new HashMap() {{ put("person_id", Order.ASCENDING); }}); }}); reader.setParameterValues(new HashMap() {{ put("lastName", "DOE"); }}); reader.setRowMapper(new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Person.class)); return reader; } @Bean public JdbcBatchItemWriter jdbcBatchItemWriter(DataSource dataSource) { JdbcBatchItemWriter writer = new JdbcBatchItemWriter<>(); writer.setItemSqlParameterSourceProvider(new BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<>()); writer.setSql("INSERT INTO people (first_name, last_name) VALUES (:firstName, :lastName)"); writer.setDataSource(dataSource); return writer; } /*@Bean public FlatFileItemWriter flatFileItemWriter(DataSource dataSource) { FlatFileItemWriter writer = new FlatFileItemWriter<>(); writer.setAppendAllowed(true); writer.setEncoding("UTF-8"); // writer.set(dataSource); return writer; }*/ // end::readerwriterprocessor[] // tag::jobstep[] @Bean public Job importUserJob(JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory, JobCompletionNotificationListener listener, Step step) { return jobBuilderFactory.get("importUserJob") .incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer()) .listener(listener) .start(step) .build(); } @Bean public Step step1(StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory, PersonItemProcessor processor, ItemWriter jdbcBatchItemWriter, ItemReader flatFileItemReader) { /*CompositeItemProcessor compositeItemProcessor = new CompositeItemProcessor(); compositeItemProcessor.setDelegates(Lists.newArrayList(processor, processor));*/ return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1") .chunk(10) .reader(flatFileItemReader) .processor(processor) .writer(jdbcBatchItemWriter) .build(); } // end::jobstep[] }
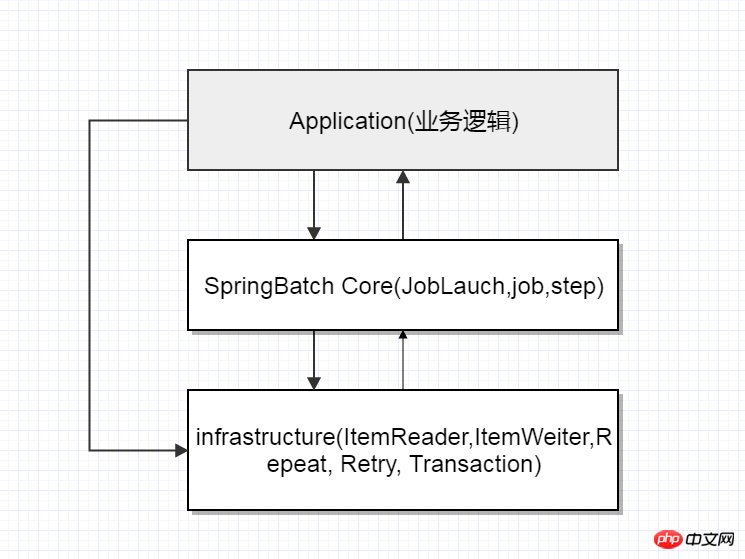
Spring Batch's layered architecture
Insfrastructure policy management: including task failure retry, exception handling, transactions, skip, and data input and output (text files, DB, Message )
Core: The core of springBatch, including JobLauch, job, step, etc.

Summarize
The above is the detailed content of Share the introduction of Spring Batch. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




