
This article mainly introduces in detail the fourth part of the most complete Pycharm learning tutorial, Python interpreter configuration, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to
Python explanation The relevant configuration of the server is for your reference. The specific content is as follows
1. Preparation work
(1) The Pycharm version is 3.4 or higher.
(2) At least one Python interpreter has been installed on the computer.
(3) If you want to configure a remote interpreter, you need relevant support from the server.
2. Local interpreter configuration
The steps to configure the local interpreter are relatively simple and intuitive:
(1) Click the Settings button## in the toolbar #.
(2) Select the Project Interpreter page in the Settings/Preferences dialog box, select the corresponding interpreter version in thedrop-down list corresponding to Project Interpreter, or click the settings button on the right add manully.
(3) In the next case, select the Add Local option, and then select the expected interpreter (Python executable file). It is worth mentioning that some predefined virtual environments can also be added as interpreters.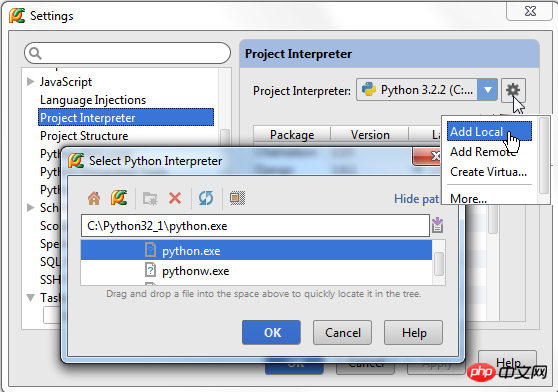
message box of Connection successful! pops up, indicating that the interpreter is connected successfully.
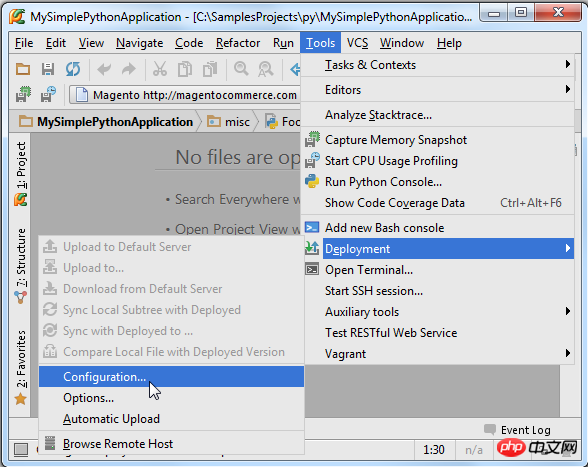
Next, click the Settings button in the main toolbar, open the Project Interpreter page in the Settings/Preferences dialog box, click the Settings icon and select Add Remote: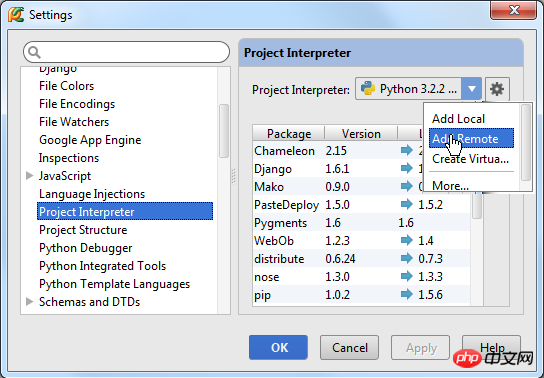
automatically completed.


variables:
The vagrant.bat file in the Vagrant installation directory. This step should be automatically completed by the installation program.
The path to the VBoxManage.exe file in Oracle's VirtualBox installation directory.
Finally, make sure that Vagrant’s related plug-ins can be used normally.
First, you need a virtual box, which requires us to configure it manually, but Pycharm provides a series of auxiliary tools so that we can complete the setup in the current IDE environment.
Click the Settings button in the main toolbar to enter the Settings/Preferences dialog box and open the Vagrant page.
Pay attention to the path to the Vagrant executable file and the folder path where the Vagrant instance is located:
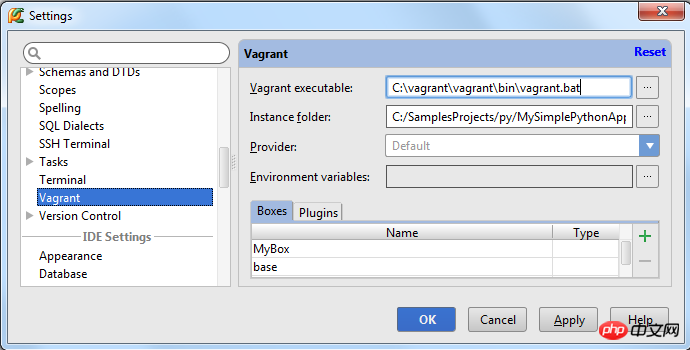
If a virtual box has been defined, it will appear in drop-down list to facilitate our selection. If there is currently no suitable virtual box available, you can create a new one by clicking the green plus sign.
Next you need to initialize the Vagrant box. Click Tools | Vagrant on the main menu, select Init in Project Root, select the vagrant up command:
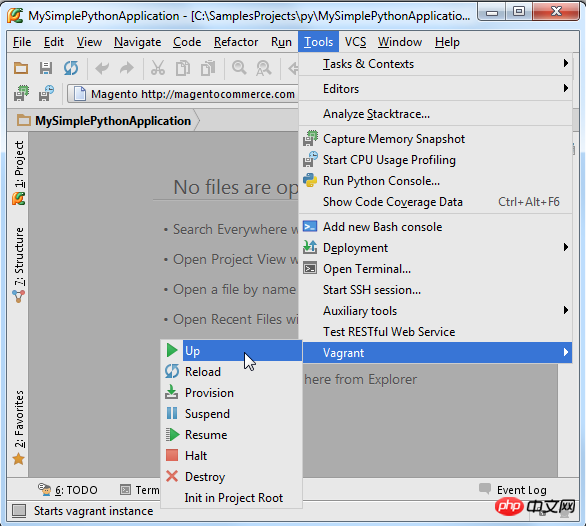
Then enter the Settings/Preferences dialog again box, open the Project Interpreter page and select Add Remote:

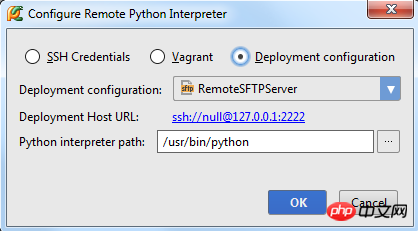
In the Configure Remote Python Interpreter dialog box, customize the server-related settings. These settings can be passed through the previously defined Configuration File to replace, so check the Vagrant option.
All server settings will be automatically filled in as follows:

At this time, this remote interpreter can be used as the interpreter of the current project. Note that everything here All remote interpreters will be named with a prefix "Remote".
See the dedicated Vagrant tutorial for more information.
7. Create a virtual environment
(1) Open the Project Interpreter page (by clicking the Settings button on the toolbar).
(2) Click the settings icon and select Create Virtual Environment.
(3) In the Create Virtual Environment dialog box, enter the name and location of the new virtual environment, and specify the Python interpreter that the virtual environment depends on:

It may take some time to create a virtual environment. Pycharm will give a progress bar to indicate the current creation process:

8 , third-party library and path configuration
After configuring the virtual environment, you will see all the currently installed third-party libraries. Pycharm will list the version and response of each currently installed third-party library. The latest version, you can decide whether to upgrade it:

# In order to view the installation path, you can click the Settings button in the dialog box and select More. View all available Python interpreters:
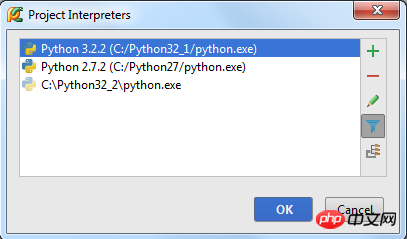
Select an interpreter and click the  button in the right toolbar to view its corresponding path structure:
button in the right toolbar to view its corresponding path structure:
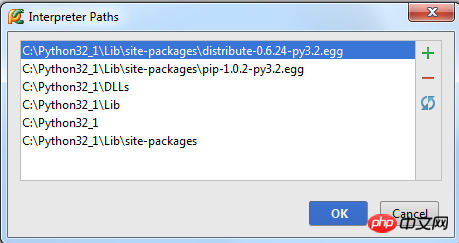
If an interpreter has been updated, it is best to update its path by clicking  .
.
【Related recommendations】
3. Python object-oriented video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Basic introduction to Pycharm configuration interpreter. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




