
1. Full pagestaticificationcaching
That is, all pages are generated into html static pages. When users access Directly access the static page without going through the PHP server parsing process. This method is more common in CMS systems, such as dedecms;
A more common implementation method is to use output caching:
Ob_start()*** ***Code to run******$content = Ob_get_contents();****Write cached content to html file****Ob_end_clean ();
2. Page partial caching
This method is to statically cache the parts of a page that do not change frequently, while the frequently changing blocks are not cached, and are finally assembled together. Display; it can be implemented using a method similar to ob_get_contents, or you can use a page fragment caching strategy such as ESI to cache relatively static fragments in dynamic pages (ESI technology, please baidu, not detailed here) ).
This method can be used for product pages in shopping malls;
3. Data caching
As the name suggests, it is a way of caching data ;For example, when a certain product information in the mall is requested using the product ID, data including store information, product information and other data will be obtained. At this time, these data can be cached in a php file, and the file name contains the product id to create a unique identifier; the next time someone wants to view this product, the information in this file will be directly adjusted first, without having to go to the database to query ; in fact, what is cached in the cache file is a php array and the like;
Ecmall This method is used in the mall system;
4. Query cache
In fact, this It is the same idea as data caching, which is to cache according to the query statement; cache the data obtained by the query in a file. When the same query is encountered next time, the data will be directly retrieved from this file without checking the database. ;But the cache file name here may need to be based on the query statement to establish a unique identifier;
Caching based on time changes
Actually, this is not a real caching method; the above Caching technologies 2, 3, and 4 generally use time change judgment; that is, you need to set a valid time for the cached file. Within this valid time, the same access will first fetch the contents of the cached file, but if the cache exceeds the set cache time, you need to re-obtain the data from the database and produce the latest cache file; for example, I set the homepage of our mall to be updated once for 2 hours;
5. Caching based on content changes
This is not an independent caching technology and needs to be used in combination; that is, when the database content is modified, the cache file is immediately updated;
For example, a person In a mall with a lot of traffic and a lot of products, the product table must be relatively large, and the pressure on this table is also heavy; we can page cache the product display page;
When the merchant modifies the product information in the background , click save, and we will update the cache file at the same time; then, when the buyer accesses this product information, he actually accesses a static page without having to access the database;
Just imagine, if the product page Without caching, you will have to check the database every time you access a product. If 100,000 people browse the product online, the server will be under great pressure;
6. Memory caching
Tips At this point, the first thing you may think of is Memcached; memcached is a high-performance distributed memory cache server. The general purpose of use is to reduce the number of database accesses by caching database query results to increase the speed and scalability of dynamic web applications.
It caches the information that needs to be cached into the system memory. When the information needs to be obtained, it is retrieved directly from the memory; the more commonly used method is the key–>value method;
$memcachehost = '192.168.6.191';
$memcacheport = 11211;
$memcachelife = 60;
$memcache = new Memcache;
$memcache->connect($memcachehost,$memcacheport) or die ("Could not connect");
$memcache->set('key','cached content');
$get = $memcache->get($key); //Get information?> ;
7, apache cache module
apacheAfter installation is completed, it is not allowed to be cached. If an external cache or squid server requires web acceleration, it needs to be set in httpd.conf. Of course, the premise is that the mod_cache module must be activated when installing apache.
When installing apache: ./configure –enable-cache –enable-disk-cache –enable-mem-cache
8, php APCCache extension
Php has an APC cache extension, which is php_apc.dll under Windows. You need to load this module first, and then configure it in php.ini:
[apc]
extension=php_apc.dll
apc.rfc1867 = on
upload_max_filesize = 100M
post_max_size = 100M
apc.max_file_size = 200M
upload_max_filesize = 1000M
post_max_size = 1000M
max_execution_time = 600; Maximum time for each PHP page to run Value (seconds), default is 30 seconds
max_input_time = 600; Maximum time required for each PHP page to receive data, default is 60
memory_limit = 128M; Each PHP page consumes Maximum memory, default 8M
9, Opcode cache
We know that the execution process of php can be shown in the following figure:
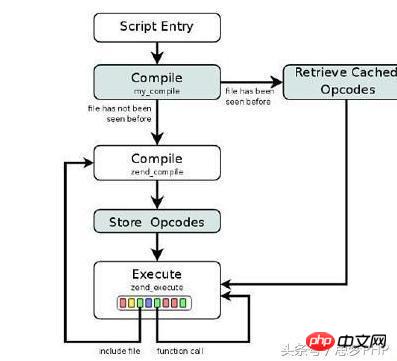
First php code is parsed into Tokens, then compiled into Opcode code, and finally the Opcode code is executed and the result is returned; therefore, for the same php file, the The Opcode code can be cached when running once. The next time you execute this page, you will directly find the cached Opcode code and execute the last step directly, without the need for intermediate steps.
The more well-known ones are XCache, Turck MM Cache, PHP Accelerator, etc.
The above is the detailed content of PHP9 large cache technology. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do I set up WeChat to require my consent when people add me to a group?
How do I set up WeChat to require my consent when people add me to a group?
 Solution to Connection reset
Solution to Connection reset
 What are the servers that are exempt from registration?
What are the servers that are exempt from registration?
 Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
 What is digital currency trading
What is digital currency trading
 Usage of calendar class in java
Usage of calendar class in java
 Server rental charges
Server rental charges
 Registration-free CDN acceleration service
Registration-free CDN acceleration service




