
The following editor will bring you an articlemysql How to convert columns to rows and merge fields (must read). The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference for everyone. Let’s follow the editor to take a look.
Data table:
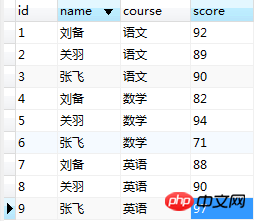
##Column switching: use max( case when then)
max---AggregationFunction Take the maximum value
(case course when '中文' then score else 0 end) ---JudgmentSELECT `name`, MAX( CASE WHEN course='语文' THEN score END ) AS 语文, MAX( CASE WHEN course='数学' THEN score END ) AS 数学, MAX( CASE WHEN course='英语' THEN score END ) AS 英语 FROM student GROUP BY `name` ;
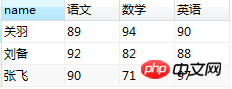
SELECT `name`, GROUP_CONCAT(course, ":", score) AS 成绩 FROM student GROUP BY `name`;
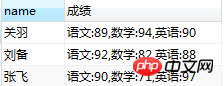
with a connection from a group The string result of a NULL value. is relatively abstract and difficult to understand.
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(`name`)
FROM
student
GROUP BY
`name`;
group_concat('name')
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(`name`)
FROM
student
;
group_concat('name')
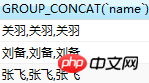
Can the above prove that group_concat can only have an effect when used together with the group by statement? The following is an actual test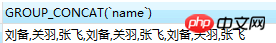
ConstantConfiguration impact on group_concat(): SET @@GROUP_CONCAT_MAX_LEN=4
SET [SESSION | GLOBAL] group_concat_max_len = val;
SET @@global.GROUP_CONCAT_MAX_LEN=4;
global可以省略,那么就变成了:SET @@GROUP_CONCAT_MAX_LEN=4;
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(`name`)
FROM
student;
group_concat('name')
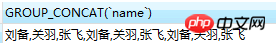
group_concat() function needs to be used together with the group by statement to get the required effect. The reason can be understood like this: group_concat() gets all members belonging to group x (the column parameters in the function specify which fields need to be displayed). Where did group x come from?
If there is no group by specified, then there is no way to know which group group_concat() will display the members according to. Therefore, when there is no group by clause like the above, Liu Bei, Guan Yu, Zhang Fei, Liu Bei, Guan Yu, Zhang Fei, Liu Bei, Guan Yu, Zhang Fei are displayed.
If you needquery
SELECT
`name`,
GROUP_CONCAT(course, ":", score) AS 成绩
FROM
student
;
group_concat() Specifying a column is the best case. If multiple columns are specified.
SELECT `name`, GROUP_CONCAT(course, ":", score) AS 成绩 FROM student GROUP BY `name`;
group_concat(course,":",score)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the method of converting MySQL columns to rows and merging fields (pictures and texts). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




