
Construction method and Destruction method are two special methods in object, they are both related to the life cycle of the object . The constructor method is The first method that is automatically called by the object after the object is created. This is the reason why we use the constructor method in the object. The destructor method is the last method that is automatically called by the object before it is destroyed. This is why we use the destructor method in the object. Therefore, the construction method is usually used to complete the initialization work of some objects, and the destructor method is used to complete the cleaning work of some objects before destruction. 1. Constructor method
function construct( [参数列表] ){ //构造方法名称是以两个下划线开始的
//方法体,通常用来对成员属性进行初始化赋值}programming languages. In this way, when creating an object, if no parameters are passed in the constructor, default parameters are used to initialize member properties. The constructor can accept parameters and can assign values to object properties when creating an object
The constructor can call class methods or other functions
The constructor can call the constructor of other classes
<?phpclass Person{
private $name;
private $age;
private $gender;
public function construct($name,$age,$gender){
$this->setName($name); //调用类方法
$this->age = $age;
$this->setGender($gender);
} public function setName($name){
$this->name = $name;
} // ... setter 方法}$person = new Person("yeoman",23,'男');?>function construct(){
parent::construct(); // 调用父类的构造函数必须显示的使用parent调用父类构造函数
classname::construct(); // 调用其他类的构造函数,classname是类名
//其他操作}Inheritance
and constructors The constructor of a subclass in PHP will not actively call the constructor of the parent class. To be displayed, use parent::construct() call: <?php
class Animal{
private $name;
function construct($name){
$this->setName($name)
echo "动物类被创建!";
} // ... 其他方法}class Birds extends Animal{
private $name;
private $leg;
function construct($name,$leg){
parent::construct($name); // 显示调用
$this->setLeg($leg);
echo "鸟类被创建!";
} // ... 其他方法}?>
// 接上例class Parrot extends Birds{
private $name;
private $leg;
private $wing;
function construct($name){
parent::construct($name);
// 此时没有找到父类(Birds类)合适的构造函数,只能向上搜索,搜索到Animal类时,才找到合适的构造函数
echo "鹦鹉类被创建!";
$this->smackTalk();
/*
输出结果:
"动物类被创建!"
"鹦鹉说话!"
*/
} function smackTalk(){
echo "鹦鹉说话!";
}
}function construct($name,$leg){
Animal::construct($name); // 调用Animal构造函数
Birds::construct($name,$leg); // 调用Birds构造函数}2.
Destructor The declaration format of the destructor method is as follows:
function deconstruct(){
//方法体,通常用来完成一些在对象销毁前的清理任务}After the PHP page is loaded;
unset() class;
PHP's memory recycling mechanism is very similar to JAVA's. Objects without any references are destroyed and recycled using reference counter technology.
example:
<?php
class test{
function destruct(){
echo "当对象销毁时会调用!!!";
}
}$a = $b = $c = new test();$a = null;unset($b);echo "<hr />";?> 此例子,如下图,有三个变量引用$a,$b,$c指向test对象,test对象就有3个引用计数,当$a = null时,$a对test对象的引用丢失,计数-1,变为2,当$b被unset()时,$b对test对象的引用也丢失了,计数再-1,变为1,最后页面加载完毕,$c指向test对象的引用自动被释放,此时计数再-1,变为0,test对象已没有变量引用,就会被销毁,此时就会调用析构函数。 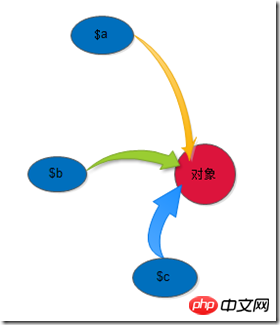
在PHP中析构方法并不是很常用,它属于类中可选的一部分,只有需要时才在类中声明。
<?phpclass Person{
var $name;
var $sex;
var $age;
function construct($name, $sex, $age){
$this->name = $name;
$this->sex = $sex;
$this->age = $age;
}
function destruct(){
echo "再见" . $this->name . "<br />";
}
}
$person1 = new Person("张三三", "男", 23);
$person1 = null; //第一个对象将失去引用
$person2 = new Person("李四四", "女", 17);
$person3 = new Person("王五五", "男", 43);
?>运行结果:
再见张三三 再见王五五 再见李四四
第一个对象在声明完成以后,它的引用就被赋予了空值,所以第一个对象最先失去的引用,不能再被访问了,人后自动调用第一个对象中的析构方法输出“再见张三三”。后面声明的两个对象都是在页面执行结束时失去的引用,也都自动调用了析构方法。但因为对象的引用都是放在栈内存中的,由于栈的后进先出特点,最后创建的对象会被最先释放,多以先自动调用第三个对象的析构方法,最后才调用第二个对象的析构方法。
The above is the detailed content of PHP object-oriented-code case sharing of constructor and destructor methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




