
The customization function of
XML tags is very powerful. For example, the DTD (Document Type Definition) that will be explained in this article brings people a kind of Object-oriented-like feeling, well, let’s take a look at the complete analysis of the DTD file type definition in XML
1. What is DTD
The full name of DTD is Document Type Definition is a file definition format that specifies the XML file structure and provides syntax and rules for XML files. Define the structure of the XML file in the DTD, and then write the XML file according to the declaration of the DTD. It is like the function definition in Programming Language. When using a function, it must be quoted according to the format of the function declaration. 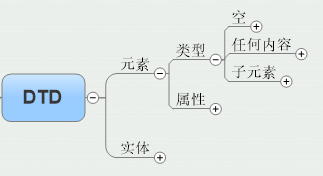
##2. Detailed explanation of DTD
1. Detailed explanation of examples
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!-- 声明内部DTD -->
<!DOCTYPE 影片目录[
<!ELEMENT 影片目录 (影片)+> <!-- 声明XML顶层元素的子元素“影片”,“+”表示有一个或多个影片子元素 -->
<!ELEMENT 影片 (片名,主演,导演,简介)> <!-- 声明“影片”元素的子元素 -->
<!ATTLIST 影片 类别 CDATA "动作" 年份 CDATA #REQUIRED> <!-- 声明“影片”元素的属性,两属性分别为“类别”和“年份”,CDATA说明属性的类型为字符型 -->
<!ENTITY 十面埋伏 "漫天大雪,三人在雪中决斗"> <!-- 实体的声明,类型为字符型,在下面使用“&实体名称;”直接引用 -->
<!ENTITY 霍元甲 "民族英雄,与西方帝国主义抗争">
<!ELEMENT 片名 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 主演 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 导演 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 简介 (#PCDATA)>
]>
<!-- 由DTD获得的XML -->
<影片目录>
<影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2008">
<片名>十面埋伏</片名>
<主演>刘德华、金城武、章子怡</主演>
<导演>张艺谋</导演>
<简介>&十面埋伏;</简介>
</影片>
<影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2006">
<片名>霍元甲</片名>
<主演>李连杰</主演>
<导演>于仁泰</导演>
<简介>&霍元甲;</简介>
</影片>
</影片目录>1.1 DTD declaration starting statement
(1) Internal declaration: (2) External declaration:
There are many forms for external declarations, mainly divided into SYSTEM and PUBLIC type files.
SYSTEM: A common DTD among many XML documents written by an author or organization;
PUBLIC: A DTD developed by an authoritative organization and provided for use by a specific industry or the public.
1.2
OthersDeclaration (1) Element:
<!ELEMENT element_name element_definition>
<!ATTLIST Element_Name Attribute_Name Type [added_declare] Attribute_Name Type [added_declare] ...... >
Internal
General:
Parameters:
External
General:
Parameters:
2. Detailed explanation of content2.1 Element declaration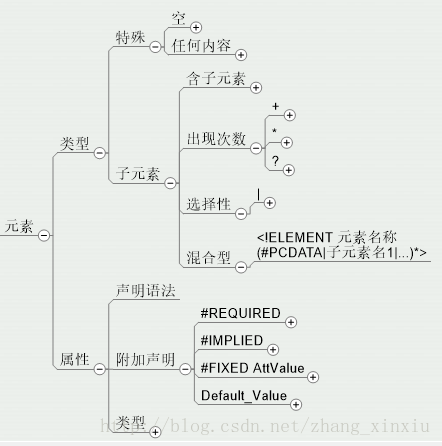 ##The main things to pay attention to in element declaration are several special The element declaration and the number of occurrences of sub-elements, selectivity, and mixed types, their functions are similar to arithmetic and
##The main things to pay attention to in element declaration are several special The element declaration and the number of occurrences of sub-elements, selectivity, and mixed types, their functions are similar to arithmetic and
in programming languages. The following is an example of a DTD with multiple elements. <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE 影片目录 [
<!ELEMENT 影片目录 (影片,其它,说明)+> <!-- 使用“+”号表明影片目录中的子元素出现至少一次 -->
<!ELEMENT 其它 EMPTY> <!-- 使用EMPTY关键字声明空元素 -->
<!ELEMENT 说明 ANY> <!-- 使用ANY关键字声明任何内容的元素 -->
<!ELEMENT 影片(片名,主演,导演,简介)> <!-- 含有子元素的元素声明格式 -->
<!ATTLIST 影片
名称 ID #FIXED "十面埋伏"
类别 CDATA "动作"
年份 CDATA #REQUIRED
票房 CDATA #IMPLIED
> <!-- 属性声明 -->
<!ENTITY introduction "漫天大雪,三人在雪中决斗">
<!ELEMENT 片名(#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 主演(#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 导演(#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 简介(#PCDATA)>
]>
2.2 Naming conflict
Sometimes elements with the same name will appear in a complex XML document. In order to avoid this phenomenon,
and Prefix identifier. 2.2.1 Namespace
Use xmlns to introduce the namespace and tell the user which part belongs to the space. In its function, it is somewhat similar to namespaces in other programming languages, ensuring the uniqueness of elements and avoiding conflicts. <?xml version="1.0" encoding='utf-8'?>
<影片 xmlns:h='http://www.abc.edu' xmlns:c='http://www.123.edu'><!-- 使用xmlns:来引用命名空间 -->
<db>
<h:table>werer</h:table> <!-- 告诉用户,此table是在http://www.abc.edu中定义的 -->
<c:table>fdfdsfsdf</c:table> <!-- 告诉用户,此table是在http://www.123.edu中定义的 -->
</db>
</影片>
2.2.2 Prefix identifier
Add an identifier before the element name and attribute name to uniquely distinguish which DTD the current element or attribute comes from. It is often used in conjunction with the namespace, as in the above example.
Why do we need to introduce entities when we have elements? To distinguish between the two, we must first look at the purpose of entity introduction. The entity mechanism is a huge time-saving tool for incorporating many different types of data into XML documents. It is like an object-oriented
abstract class, abstracting frequently used objects into an entity, which can be directly referenced wherever it is used to avoid duplication. In detail (1) Instead of characters that cannot be input, the keyboard only has 26 letters and some simple punctuation marks, and
character set
contains many N various symbols that cannot be entered Entered on the keyboard. (2) Replace some content that conflicts with XML specification reserved words, such as: < > and so on. (3) Replace large paragraphs of repeated text.
Entity references are divided into two types: internal and external according to the location of the reference, and general and parameter references according to the content of the reference. Let's look at an example of an external entity reference:
<!-- 声明外部DTD,并保存为2.dtd -->
<!ELEMENT 影片目录 (影片)+>
<!ELEMENT 影片 (片名,主演,导演,简介)>
<!ATTLIST 影片 类别 CDATA "动作" 年份 CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ENTITY 十面埋伏 "漫天大雪,三人在雪中决斗">
<!ENTITY 霍元甲 "民族英雄,与西方帝国主义抗争">
<!ELEMENT 片名 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 主演 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 导演 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 简介 (#PCDATA)>
<!ENTITY filmcomment SYSTEM "影评.xml"> <!-- 引用外部通用实体,文件名称为“影评.xml” -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding='utf-8'?>
<影评>
这些影评都是由XXX公司出品,值得观看!
</影评>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding='utf-8'?>
<影评>
这些影评都是由XXX公司出品,值得观看!
</影评>
Listing 3: Contents from xml file using dtd. <?xml version="1.0" encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE 影片目录 SYSTEM "./2.dtd" >
<影片目录>
<影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2008">
<片名>十面埋伏</片名>
<主演>刘德华、金城武、章子怡</主演>
<导演>张艺谋</导演>
<简介>&十面埋伏;</简介>
</影片>
<影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2006">
<片名>霍元甲</片名>
<主演>李连杰</主演>
<导演>于仁泰</导演>
<简介>&霍元甲;</简介>
</影片>
&filmcomment;
</影片目录>
Listing 4: Contents after opening Listing 3 using IE8 内部和外部很容易理解,主要看一般和参数两种引用的区别。 1.参数实体 清单1:test.dtd,在此该内容单独存在了一个dtd文件中是因为在内部DTD子集中。 可在XML元素中加以引用,也可以在DTD中引用,但参数实体只能在DTD中引用,并且通常情况下只能在外部DTD文档中引用。 3. 对比升华 参数实体与一般实体的区别如下: (l)在定义参数实体时,实体名前必须加一个“%”号。 (2)参数实体引用以“%”开始,而不是一般实体引用的“&”。 (3)参数实体的内容不仅可以包含文本,还可以包含标记。 (4)参数实体只能应用于DTD,而不能在文档本体中引用。即参数实体只能用来构成DTD的内容,而不能构成文档内容。 (5)参数实体只能在外部DTD文档中使用,无法应用于内部DTD。 (1)外部参数实体应用于独立的DTD文档,外部一般实体应用于XML文档。 (2)外部参数实体应用于将多个独立的DTD文档组合为一个大的DTD文档,外部一般实体用于将多个独立的XML文档组合成一个大的XML文档。 DTD定义了XML文件的使用格式,它从结构和形式上限制了XML文档,通过引用DTD可以形成统一的规范化的XML文档,另外通过使用实体简化了DTD和XML文档的内容。使用DTD验证的XML文档才能称为规范化文档,那如何验证所写的XML文档是否符合DTD的规范呢。通过如下的代码串:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE 影片目录 (View Source for full doctype...)>
- <影片目录>
- <影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2008">
<片名>十面埋伏</片名>
<主演>刘德华、金城武、章子怡</主演>
<导演>张艺谋</导演>
<简介>漫天大雪,三人在雪中决斗</简介>
</影片>
- <影片 类别="武侠" 年份="2006">
<片名>霍元甲</片名>
<主演>李连杰</主演>
<导演>于仁泰</导演>
<简介>民族英雄,与西方帝国主义抗争</简介>
</影片>
<影评>这些影评都是由XXX公司出品,值得观看!</影评>
</影片目录>
参数实体引用不能在标记声明内部出现,可以在标记声明允许出现的地方出现。然而,对于外部DTD子集,则没有这个限制。<!-- 声明外部DTD,并保存为test.dtd -->
<!-- 个人信息实体声明的是参数类型的,可以再各个元素中共同使用该参数 -->
<!ENTITY % 个人信息 "(姓名,性别,出生日期)">
<!ELEMENT 学生信息 %个人信息;>
<!ELEMENT 教师信息 %个人信息;>
<!ELEMENT 员工信息 %个人信息;>
清单2:学校信息.xml文件,引用了外部的test.dtd文件<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!-- 学校信息.xml文件 -->
<!-- 引用外部DTD -->
<!DOCTYPE 学校信息 SYSTEM './test.dtd'>
<!-- 由DTD获得的XML -->
<学校信息>
<学生信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</学生信息>
<教师信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</教师信息>
<员工信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</员工信息>
</学校信息>
清单3:使用IE8打开清单2的内容后<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
- <!--
声明内部DTD
-->
<!DOCTYPE 学校信息 (View Source for full doctype...)>
- <!--
由DTD获得的XML
-->
- <学校信息>
- <学生信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</学生信息>
- <教师信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</教师信息>
- <员工信息>
<姓名>张三</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<出生日期>2013-10-12</出生日期>
</员工信息>
</学校信息>
2. 一般实体
外部参数实体与外部一般实体的区别如下:
四、验证XML文件的合法性import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.xml.sax.InputSource;
public class ValidateDTD
{
public static void main(String[] args){
//在验证前需要把需要验证的XML和规范DTD包含在jar中
try{
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); //创建一个文档构造工厂
dbf.setValidating(true);
DocumentBuilder builder=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.parse(new InputSource("xml-2-2.xml")); //需要验证的XML名称
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
上面代码中的类和结构主要完成了XML文档的解析,并且在解析之前验证当前XML文件是否符合某个DTD的定义。在上面的代码运行前需要将需要验证的XML和提供规范化的DTD文档引入到当前ValidateDTD项目中,后运行上面的代码实例,该项目会在项目文件中自动查找规范的DTD,然后验证xml文件。
五、结语
至此,有关文件定义格式的内容已经基本上讨论了一遍,从最初的元素声明到复杂多变的实体类型,DTD的引入无疑为XML的使用指定了一个统一的标准,这种标准是由提供方规定好,使用方遵守的一种规则,并在最后讨论了如何验证引用DTD的XML合法与否。另外描述XML文档结构的不仅仅只有DTD,DTD是一种早期的定义格式,它有很多缺点,如不支持数据类型,不易于扩展等,为了避免这种缺点后来又引入了Schema,它是DTD的继任者,下篇博客将着重讨论Schema。
The above is the detailed content of Sample code for fully parsed DTD document type definition in XML (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




