
Do what you need to do today, share gluten, and make progress together. I'm sweating a lot, come on.
I have forgotten some parts. I will write whatever I remember. It may be a bit confusing.
URI—Universal Resource IdentifierUniversal Resource Identifier
Web Every resource available on the Internet, such as HTML documents, images, video clips, programs, etc., is located by a URI.
URI generally consists of three parts
①The naming mechanism for accessing resources
②The storage resource Host name
③The name of the resource itself, represented by the path, with emphasis on the resource.
URL—Uniform Resource Location Uniform Resource Locator
URL is a string used to describe information resources on the Internet. It is mainly used in various WWW client programs and servers. Programmatically, especially the famous Mosaic.
URLs can be used to describe various information resources in a unified format, including files, server addresses and directories, etc.
URL generally consists of three parts
①Protocol (or service method)
②The host IP address where the resource is stored (sometimes including the port number)
③The specific address of the host resource. Such as directories and file names, etc.
Example
URI = Composition
URL = Argumentative essay, narrative, poetry...
Then
1. When describing the macro, the teacher will ask: Everyone wrote well in the "composition" of today's test, but will not say that everyone wrote well in the "argumentation", although it refers to the same thing. .
2. When describing objectively, you will say to your deskmate: What I wrote today is "poetry", instead of saying that I wrote the composition in the form of poetry today.
Similarly
When you write a technical document specification, you will say that a certain parameter should be passed a URI, instead of saying that a certain parameter should be passed a URI "URL format string".

//递归的方法
function test(n){
if(n<2){
return 1;
}
return test(n-1)+test(n-2)
}
alert(test(9))//迭代的方法
function test(n){
var num1 = 1;
var num2 = 2;
var num3 = 0;
for(var i=0;i<n-2;i++){
num3 = num1 + num2;
num1 = num2;
num2 = num3;
}
}
alert(test(9))I’m so nervous. Method 2 is written in a different way.
3. The browser sends a request to the page after the page is loaded. What happened?
was not in place. . Next
Here is another question: Will there be requests during the page rendering process? My answer: Maybe
In fact, there must be other requests for eg js, css, pictures, etc.
4. Understanding the separation of front-end and back-end
The following is the quote
Now the front-end and back-end are separated. The role of the back-end server is more like an API Server. It receives requests and only returns them in the form of data. How to render and display the data is left to the front-end presentation layer. Achieve decoupling of front-end and back-end
5. Box model
6. Understand or use the MV* framework
7. Modularization
8. Talk about the packaging tools used in your company's projects (what is the good experience for both developers and users?)
I mentioned that other projects have recently used webpack,
(1) Hot loading
(2) File compression and packaging
问了webpack的基本配置,自己回答的:entery和output,感觉好浅薄。还是用的少,了解少的缘故吧
entry:{} //加载模块的入口点
output:{}//打包文件的路径和名称
module:{}//那些加载器来处理那些文件
resolve:{}//设置模块的一些细节
plugins:[]//系统插件和扩展插件
使用了 vue-router、vue-resource,了解vuex
由此引出问题10,11,12
平时做项目能正常跳转就可以了,没有想过路由怎么路由的,没答上来。。
SPA路由实现原理不知道面试官想得到的是不是类似这样的答案。
父子组件通信的机制,传递数据使用prop属性
动态Prop
用 v-bind 动态绑定 props 的值到组件的数据中。每当父组件的数据变化时,该变化也会传导给子组件。
<p> <input v-model="parentMsg"> <br> <child v-bind:my-message="parentMsg"></child> </p> <child :my-message="parentMsg"></child>
单向数据流
prop 是单向绑定的:当父组件的属性变化时,将传导给子组件,但是不会反过来。这是为了防止子组件无意修改了父组件的状态——这会让应用的数据流难以理解。
通常有两种改变 prop 的情况:
prop 作为初始值传入,子组件之后只是将它的初始值作为本地数据的初始值使用;
prop 作为需要被转变的原始值传入。
JSONP : JSON with Padding
(1)script标签 src属性可以访问外部资源
(2)用script标签加载资源是没有跨域问题的
在资源加载进来之前定义好一个函数,函数接受一个参数,函数中包含 实现逻辑(要做什么事)
通过script标签加载远程文件资源,当远程文件被加载进来时,执行当前定义好的函数,数据就是函数传入的参数
求职定位,到底想干啥?
每一点都非常深入。
标准盒模型和怪异盒模型不再重复
box-sizing属性:content-box:标准盒模型,border-box:怪异盒模型
行内元素同样具有盒模型
<!-- 行内元素可以设置border 设置宽高无效--> <span style="border:10px solid red;width:100px;height:100px">haha</span>

<!-- 行内元素设置padding、margin--> <p style="width:90px;height:100px;background:blue;"> <span style="background:yellow;padding:5px;margin:20px;">1782</span> <p> woship </p> </p>
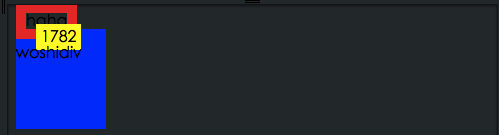
行内元素的padding-top、padding-bottom从显示的效果上是增加的,但其实设置的是无效的。并不会对他周围的元素产生任何影响。
黄色内边距5px
左边黄色距离蓝色20px
上下虽然显示padding,但是padding并没有影响其他元素
默认值:static
属性有5个分别是:relative、absolute、fixed、inherit、static
父元素p :width:500px;height:200px;position: static|absoluta|relative|fixed。 position分别取值,子元素怎么定位?
子元素p:width:200px;height:200px;position:absolute
<!-- 父元素默认static--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:50px;top:30px;"> </p> </p> <br> <!-- 父元素默认relative--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:50px;top:30px;"> </p> </p> <br/> <!-- 父元素默认fixed--> <p style="background:gray;width:500px;height:60px;position:fixed"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:50px;top:30px;"> </p> </p> <!-- 父元素默认absolute--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:absolute"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:50px;top:30px;"> </p> </p>

发现:子元素绝对定位,按照除了属性为 static以外的第一个父元素定位。所以父元素设置为:absolute、relative、fixed,子元素定位表现一致;
如果子元素设置margin、border、padding呢?子元素左上角的点以margin、border、还是padding定位
<p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:fixed;left:0px;top:30px;"> </p> </p> <br/> <!-- 最原始--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:10px;top:10px;"> </p> </p> <br/> <!-- 最原始:添加margin--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:10px;top:10px;margin:10px;"> </p> </p> <br/> <!-- 最原始:添加padding--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:10px;top:10px;padding:10px;"> </p> </p> <br/> <!-- 最原始:添加botder--> <p style="background:red;width:500px;height:60px;position:relative"> <p style="background:yellow;width:10px;height:10px;position:absolute;left:0px;top:0px;" > </p> <p style="background:blue;width:100px;height:20px;position:absolute;left:10px;top:10px;border:10px solid yellow;margin:5px;"> </p> </p>

RunJS上边分享的代码
清除遮挡
<p class="left"></p>
<p class="right"> </p>
.left {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
float: left;
}
.right {
height: 200px;
background: yellow;
overflow:hidden;//属性清楚遮挡
}关闭浮动
解决垂直双边距问题
<p style="background:gray;width:300px;height:300px;overflow:auto"> <p style="background:green;margin-top:10px;float:left;width:20px;height:20px"> </p> <p style="background:red;width:50px;height:50px;margin-top:40px;"></p> </p>
BFC的作用
//m.sbmmt.com/
<p class="container">
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
</p>
.container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row;
width:300px;
height:100px;
background:gray;
justify-content:space-around
}
.box {
width: 20px;
background:yellow;
height:20px;
}
flex参考1
flex参考2
在线例子://m.sbmmt.com/
个人觉得讲的很好的js原型、原型链
原型链
function Foo(){
}
var a = new Foo();//new的操作做了什么
var a = new Object()
a.__proto__ = Foo.prototype
Foo.call(a)闭包:当函数a的内部函数b被函数a外的一个变量引用的时候,就创建了一个闭包。
function a(){
var i=0;
function b(){
alert(i);
}
return b;
}
var c = a();
c();请求头字段和状态码
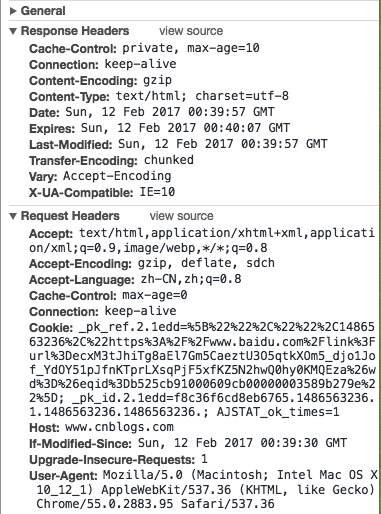
http状态码
数组去重
时间复杂度空间复杂度也不会啊。
除了技术,这个也问?感觉没啥优势,优势是移动端经验相对多一点
 Is python front-end or back-end?
Is python front-end or back-end?
 How to implement instant messaging on the front end
How to implement instant messaging on the front end
 The difference between front-end and back-end
The difference between front-end and back-end
 Introduction to the relationship between php and front-end
Introduction to the relationship between php and front-end
 Popular explanation of what Metaverse XR means
Popular explanation of what Metaverse XR means
 How to solve error1
How to solve error1
 Android voice playback function implementation method
Android voice playback function implementation method
 GAMMAINV function usage
GAMMAINV function usage




