
1) Copy the jar package to the project directory
2) Add the jar package to the project's buildpath environment variable so that the classpath is also consistent with the buildpath Consistent, allowing the class loader to easily load specific subclasses
3) Reflectively load the driver class, the driver will be automatically registered4) Obtain the connection through the driver manager.
Create the jdbc.properties file under the current project, the content of which is as follows (the four parameters required to connect to Oracle and MySql databases are: loading the driver, obtaining the IP and port to connect to the database , user name, password), the purpose is to facilitate calling and modification!
#driverClass = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl #user = scott#password = tigerdriverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/companyuser = root password = 123456
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 获取连接
* 1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
* 2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
* 3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序
* 4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class DriverTest {
// 使用Properties类对象的getPropety方法与FileInputStream方法获取文件中的内容,从而创建Connection对象
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}Since every jdbc operation needs to establish a connection, we put the method of establishing the connection and the method of closing the resource as fixed methods in the JdbcUtil class for easy use:
##
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
// 获取建立连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
// 关闭资源
public static void close(Connection connection) {
close(connection, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(connection, statement, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}The connection is established successfully. Now we can communicate with the database. To communicate with the database, we need to use the Statement class. First, we need to create a User class to correspond to the user table in the company database created in the Statement class:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class User {
private String user;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String user, String password) {
super();
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [user=" + user + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}Use Statement to create the user table and insert three rows of data:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
// 使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();// 获取执行体对象
// 执行SQL
// 创建user表
String sql = "create table if not exists user(user varchar(50), password varchar(100))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行的DDL语句, 还可以执行DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('admin','admin')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user1','user1')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user2','123456')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, statement);
}
}
}Statement has drawbacks: it not only requires spelling out sql statements, but also has the problem of SQL injection. The specific problems are reflected in the following small example
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestStatement {
// 弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
String sql = "select user, password from user where user = '"
+ userName + "' and password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if(user != null){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else{
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {// (sql, Customer.class)
T t = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stam = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
stam = conn.createStatement();
rs = stam.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// //1. 获取列的名称
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 1. 获取列的别名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 注意:
// 获取结果集中(相当于数据表)列的名称(别名)
// 2. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 注意:反射根据Java中类的属性获取Field对象
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//JDBCUtils.close(rs, stam, conn);
}
return t;
}
}For this program we need to use the correct username and corresponding password to log in successfully. From the above program we can know that the username and password are:
+-------+----------+
| user | password |
+-------+----------+
| admin | admin |
| user1 | user1 |
| user2 | 123456 |
+-------+----------+
Under normal circumstances, our login situation is as follows:
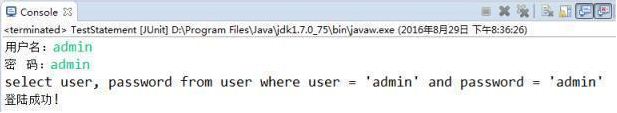
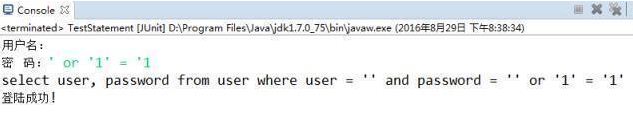
In order to prevent SQL injection problems, we need to use its subclass PreparedStatement to precompile the execution body. Let’s practice PreparedStatement below:
// Write a class Customer, including attributes name, gender, phone
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
public Customer(String name, int age, String gender, String phone,) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Customer() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}
public class PreparedStatementTest {
@Test
public void exer1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(name varchar(30), gender enum('男','女') default '男', phone varchar(20))";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement); // 在获取新的预编译对象前,一定要先关闭原来的.
String sql2 = "insert into customer(name, gender, phone) values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); // 要想重新执行新的SQL,必须再次预编译
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "13343493434");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
preparedStatement.setString(1, "李四");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1322243434");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
// 并通过客户端验证.
}
}Add attributes int age, double weight in the Customer class, add corresponding columns to the Customer table, and add records
public class PreparedStatementTest {
// 在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add age int after name";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "alter table customer add weight double";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 50);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "134234234234");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 98.5);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 添加记录
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add birthdate date";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "赵六");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 60);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "13882342323");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 40);
preparedStatement.setString(6, "1960-2-3");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 再添加记录
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "张七");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 20);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "1343434343");
preparedStatement.setObject(5, 58.8);
preparedStatement.setObject(6, "1980-3-8");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (rows == 1) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class CommonUtil {
/**
* 通用更新操作
* @param sql 一个可以包含?的SQL语句
* @param values SQL中有多少个?,可变参数就有多少个具体值
* @return 更新以后影响的记录数
*/
public static int commonUpdate(String sql, Object... values) throws FileNotFoundException,
ClassNotFoundException, IOException,
SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection(); // 获取连接
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 把带有?的SQL编译
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { // 可变参数的长度就是?的个数
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, values[i]); // 统一给所有的?替换成具体的值
}
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 替换完?或没有?, 执行更新操作
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement); // 关闭资源
}
}
}
The above is the content of Jdbc--specific code implementation, please pay attention to more related content PHP Chinese website (m.sbmmt.com)! package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.util.List;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ResultSetTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// select * from customer; 结果如下
/*
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| 张七 20 | 女 | 1343434343 | 58.8 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 40 | 男 | 1349932423 | 78.2 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 3 | 女 | 1332324234 | 70 | 1979-08-08 |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
*/
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 调用PreparedStatement对象的executeQuery方法产生ResultSet对象
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
System.out.println(resultSet);
while (resultSet.next()) { // 根据列的<span style="color:#ff0000;">序号</span>,
先检测当前游标的下一行是否有数据, 如果有数据则移动游标,并返回true, 如果没有数据,直接返回false
String name = resultSet.getString(1); // 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第1列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt(2);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第2列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString(3);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第3列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString(4);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第4列的值
double weight = resultSet.getDouble(5);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第5列的值
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate(6);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第6列的值
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t" + gender + "\t" + phone + "\t" + weight + "\t" + birthDate);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据虚表中的<span style="color:#ff0000;">列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test2() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// 基于虚表的结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询年龄大于任意数的操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表中的列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer where age > ?";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
prepareStatment.setObject(1, 20);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// <span style="color:#ff0000;">基于虚表的结果集</span>
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的
<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表</span>中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 获取查询结果,若查询结果并没有类与其对应,就需要获取虚表的表结构进行查询操作的打印输出
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
/*
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| custName | gender | age | weight | phone | birth |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| 张七 | 女 | 20 | 58.8 | 1343434343 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 男 | 40 | 78.2 | 1349932423 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 女 | 30 | 70 | 1332324234 | 1979-08-08 |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
*/
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 获取虚表的表结构对象
int cols = metaData.getColumnCount(); // 获取虚表共有多少列
//System.out.println(cols);
String colName = metaData.getColumnName(3);// 获取基表的列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
colName = metaData.getColumnName(6);// 获取基表列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
String colLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(6); // 获取虚表列名, 参数是第6列
//System.out.println(colLabel);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 列的索引总是从1开始
System.out.print(columnLabel + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 先获取列的别名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); // 根据列的别名再获取对应的值
System.out.print(value + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
}
##




