
1 protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
1. The method is modified by the native keyword
The native keyword in java indicates that this method is a local method, [java native description 】. Moreover, the execution efficiency of native modified methods is higher than that of non-native modified methods.
2. The method is modified by protected
When a class overrides the clone() method, it needs to be modified to the public access modifier to ensure that all other classes can access this class. method.
3. The method throws CloneNotSupportedException
If a class wants to override the clone() method, it must implement the java.lang.Cloneable interface itself, otherwise a CloneNotSupportedException will be thrown.
2. The role of clone()
Note: The objects here refer specifically to complex types.
1. Simple = operation
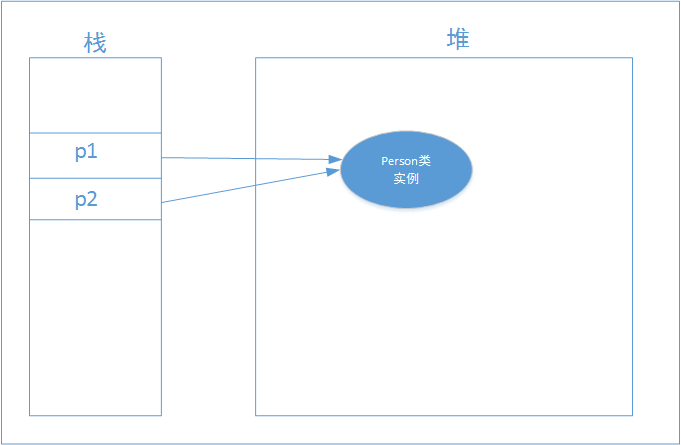
We know that complex type objects in Java are reference types, and they often store the memory address of the object. Therefore, we cannot just use simple assignment operations like the = operator. When we assign an object a to another object b, we just assign the memory address of object a to b, so that both objects point to the same memory address. The consequence of this is that modifications to one object will affect the other object. As shown in the figure below:
Person p1 = new Person(); Person p2 = p1;
2. clone()
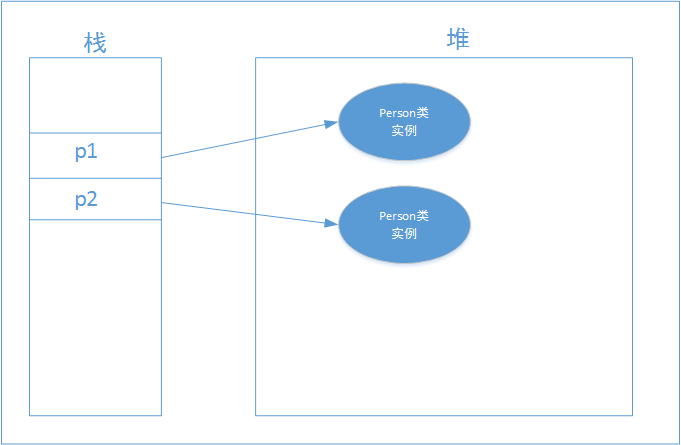
Using the clone() method, you can quickly create an object. copies, and the two objects point to different memory addresses. As shown in the figure below:
Person p1 = new Person(); Person p2 = p1.clone();
3. shallow clone and deep clone1. shallow clone (shallow copy)
shallow clone refers to Only clone the object itself, not the fields in the object. Just call super.clone(), just shallow clone. Although the copied object points to a different memory address, the fields in the object still point to the same memory address as the previous object.
public class ShallowClone implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person person;
public ShallowClone() {
}
public ShallowClone(String name, int age, Person person) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public ShallowClone clone() {
ShallowClone c = null;
try {
c = (ShallowClone) super.clone();
return c;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "p";
p.age = 10;
ShallowClone c1 = new ShallowClone("Jim", 18, p);
System.out.printf("before clone: c1 = %s, c1.person = %s\n", c1, c1.person);
ShallowClone c2 = c1.clone();
System.out.printf("after clone: c2 = %s, c2.person = %s\n", c2, c2.person);
}
}Run main() output:
before clone: c1 = cre.sample.test.object.ShallowClone@558385e3, c1.person = cre.sample.test.Person@2dcb25f1 after clone: c2 = cre.sample.test.object.ShallowClone@742808b3, c2.person = cre.sample.test.Person@2dcb25f1
Description of shallow copy, ShallowClone object memory address has changed, but the Person field memory in the object The address has not changed;
2. Deep clone (deep copy)
Deep clone refers to cloning the fields in the object while cloning the object itself.
/**
* deep clone代码示例
* Created by CreGu on 2016/6/9.
*/
public class DeepClone implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person person;
public DeepClone() {
}
public DeepClone(String name, int age, Person person) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public DeepClone clone() {
DeepClone c = null;
try {
c = (DeepClone) super.clone();
c.person = person.clone();
return c;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "p";
p.age = 10;
DeepClone c1 = new DeepClone("Jim", 18, p);
System.out.printf("before clone: c1 = %s, c1.person = %s\n", c1, c1.person);
DeepClone c2 = c1.clone();
System.out.printf("after clone: c2 = %s, c2.person = %s\n", c2, c2.person);
}
}
Run main() output:
before clone: c1 = cre.sample.test.object.DeepClone@558385e3, c1.person = cre.sample.test.Person@2dcb25f1 after clone: c2 = cre.sample.test.object.DeepClone@742808b3, c2.person = cre.sample.test.Person@70535b58
Indicates deep copy, DeepClone object memory address has changed, but The memory address of the Person field in the object has also changed.
The above comprehensive analysis of the clone method of java object is all the content shared by the editor. I hope it can give you a reference, and I also hope that everyone will support the PHP Chinese website.
For more comprehensive analysis of the clone method of java object and related articles, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!




