
Thinking: Each variable has attributes. Are there some properties that are owned by all objects?
1. Static member variables
1) Define static member variables
Ø The keyword static can be used to describe members of a class,
static members Provides a sharing mechanism for similar objects
Ø When a member of a class is specified as static, no matter how many objects of this class are created, these objects share this static member
Ø Static members Belongs to a class, it is not an object member

2. Static member function
1) Concept
Ø The number of static member functions is preceded by key Word static
Ø Static member function provides common operations that do not depend on the class data structure. It does not have this pointer
Ø When calling a static member function outside the class, use "class name::" as a qualification word, or calling through an object

# Difficult question: Ordinary variables cannot be used in static member functions.
//Static member variables belong to the entire class. It is not clear whether they are attributes of that specific object.
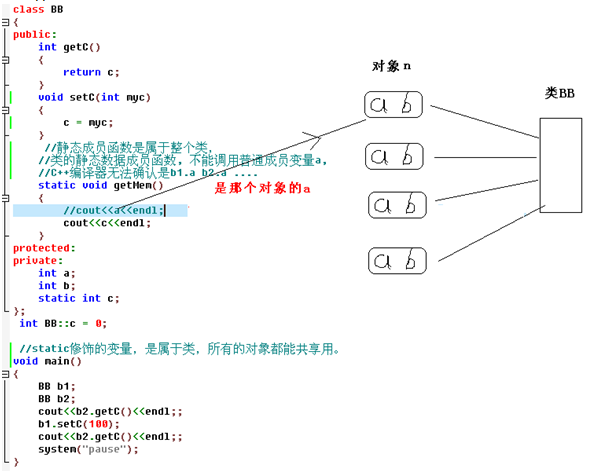
Summary: static modified member variables belong to the class itself, ordinary member variables belong to objects, and there will be as many corresponding member variables as there are objects; static members Variables are shared.
The function modified by static belongs to the class itself, and static functions cannot access non-static variables! Static functions can be accessed through objects or through class names.
The above is the content of static member variables and member functions in the fifth summary of C++ review points. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (m.sbmmt.com)!
 What are the differences between c++ and c language
What are the differences between c++ and c language
 Recommended learning order for c++ and python
Recommended learning order for c++ and python
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
 Is c language the same as c++?
Is c language the same as c++?
 Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
 The difference and connection between c language and c++
The difference and connection between c language and c++
 C++ software Chinese change tutorial
C++ software Chinese change tutorial
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++




