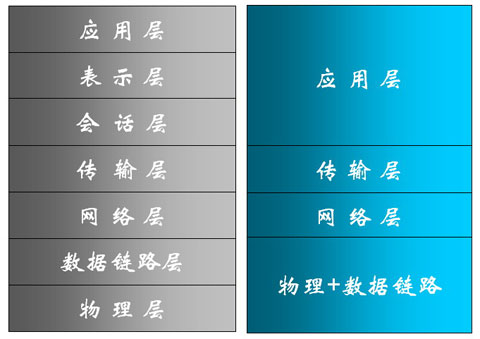
OSI model and TCP/IP protocol cluster
1. First of all, TCP/IP is a protocol cluster; OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) is a model, and TCP/IP was developed before OSI.
2. TCP/IP is a hierarchical protocol made of some interactive modules, where each module provides specific functions; OSI specifies which function belongs to which layer.
3. TCP/IP is a five-layer structure, while OSI is a seven-layer structure.
4.TCP/IP is the currently used protocol, while OSI is used for learning
When computers transmit data, they need to use MAC addresses and IP network addresses for transmission. The IP address is only used to identify the network, and the MAC address is still used for actual transmission.
IP address:
IPv4: 32bits binary number.
8bits.8bits.8bits.8bits
Range: 0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255
Network ID:
0 000 0000 - 0 111 1111: 1-127
Number of networks: 126, 127
Number of hosts in each network: 2^24-2
Default subnet mask: 255.0.0.0,/8
Class B :
The first two The segment is the network number, and the last two segments are the host number
Network number:
10 00 0000 - 10 11 1111: 128-191
Number of networks: 2^14
Number of hosts in each network: 2^16-2
Default Subnet mask: 255.255.0.0,/16 1:192-223
Number of networks: 2 ^21
Number of hosts in each network: 2^8-2
Default subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, /24
Class D: Multicast
1110 0000 - 1110 1111: 224-239
Class E: Scientific research
240-255
Class A: 1.0.0.0~126.255.255.255, default subnet mask/8, which is 255.0.0.0
(where 127.0.0.0~127.255.255.255 is the loopback address, used for local loopback testing etc.);
Private network address: 10.0.0.0~10.255.255.255;
Class B: 128.0.0.0~191.255.255.255, default subnet mask/16, which is 255.255.0.0;
Private network address: 172.16. 0.0~172.31.0.0;
Category C: 192.0.0.0~223.255.255.255, default subnet mask/24, which is 255.255.255.0;
Private network address 192.168.0.0~192.168.255.255
Class E: 240.0.0.0~255.255.255.255 (255.255.255.255 is the whole network broadcast address)
Class E addresses are generally used for scientific research
Place L inux Host access to the network
IP/NETMASK: local communication
Routing (gateway): cross-network communication
DNS server address: host name-based communication
Configuration methods:
Static assignment
Dynamic allocation (DHCP)
Modify the configuration file (will not take effect immediately, can be permanent)
Static allocation:
netstat: status and statistics view
iproute2 family:
ip OBJECT:
Use the ifconfig command to view the network card information
[root@bogon ~]# ifconfig [eth0] #可省略
Configure the ip address information of the network card
[root@bogon ~]# ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.1.199/24
Then use the ifconifg command to view it, and you can see the information of the two network cards, respectively: eth0 and eth0:0. If you want to add more IPs, then the network card names will be: eth0:1, eth0:2...fill in as many as you want. OK!
Modify the network card MAC address
[root@bogon ~]# ifconfig eth0 hw ether 00:11:22:33:44:55
At this time, the hardware address of the network card has been changed. At this time, you can deceive the IP address bonding in the LAN.
Disable the network card
[root@bogon ~]# ifconfig eth0 down
Enable the network card
[root@bogon ~]# ifconfig eth0 up
route command
Function
route The command is used to view and configure the linux kernel routing table, which is used to View and configure Linux static routing tables.
Description
route command operation is based on the Linux kernel routing table. Its main function is to create a static route to allow a specified host or network to pass through a network interface, such as eth0. When the "add" or "del" parameter is used, the routing table is modified. If there are no parameters, the current contents of the routing table are displayed.
Command format
route command format is as follows:
route [-nee] route add [-net|-host] [网络或主机] netmask [mask] [gw|dev] route del [-net|-host] [网络或主机] netmask [mask] [gw|dev]
Parameter description
-n: #In the output routing information, directly display the IP address without displaying the host name, like the netstat command also has this parameter ;
-ee: #Display more detailed static routing information;
Add a new route (add) and delete a route (del) Related parameters of the route:
-net: #Destination address Is a network;
-host: #The target address is a host;
netmask: #When adding a network route, you need to use a network mask to determine the size of the network domain;
gw: #Abbreviation of gateway, route The gateway through which the data packet passes is followed by the IP address, which is different from dev;
dev: # If you just want to specify which network card goes out, use this setting, followed by the name of the network card device such as eth0;
Route viewing and management
[root@bogon ~]# route -n #查看 Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
Meaning of routing table fields Destination network or destination host. time, only Shows the IP address, otherwise the hostname).
Gateway Gateway
The gateway address or ‘*’ if none set. Gateway address, if not, an asterisk will be displayed (0.0.0.0 when adding the -n option).
Genmask Netmask
Flags Possible flags include flags, commonly used ones are U and G.
U (route is up) route enabled
Ref Don’t worry, it will always be 0. Number of references to this route. (Not used in the Linux ker-nel.)
Use The number of times this route has been used can provide a rough estimate of the network traffic leading to the specified network address.
Count of lookups for the route. Depending on the use of -F and-C this will be either route cache misses (-F) or hits (-C).
Iface interface, i.e. eth0, eth0, etc. Network interface name Interface to which packets for this route will be sent.
Add route
[root@bogon ~]# route add -net 192.168.3.0/24 gw 192.168.1.1 dev eth0
Add default route
[root@bogon ~]# route add default gw 192.168.1.1
[root@bogon ~]# route add -net 192.168.3.0/24 gw 192.168.1.1 dev eth0
Usage
netstat [-veenNcCF] [
netstat {-V|--version|-h|--help}
netstat [-vnNcaeol] [Common parameters
-a (all)显示所有选项,默认不显示LISTEN相关
-t (tcp)仅显示tcp相关选项
-u (udp)仅显示udp相关选项
-n 拒绝显示别名,能显示数字的全部转化成数字。
-l 仅列出有在 Listen (监听) 的服务状态
-p 显示建立相关链接的程序名
-r 显示路由信息,路由表
-e 显示扩展信息,例如uid等
-s 按各个协议进行统计
-c 每隔一个固定时间,执行该netstat命令。
提示:LISTEN和LISTENING的状态只有用-a或者-l才能看到
常用组合
-tan, -uan, -tnl, -unl, -tunlp ...
列出处于监听状态的socket
[root@bogon ~]# netstat -l
显示所有被监听的tcp连接
[root@bogon ~]# netstat -tal Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:smtp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 52 bogon:ssh bogon:6170 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:smtp *:* LISTEN
显示所有接口的统计数据
[root@bogon ~]# netstat -i Kernel Interface table Iface MTU Met RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg eth0 1500 0 3898 0 0 0 1828 0 0 0 BMRU eth0:0 1500 0 - no statistics available - BMRU lo 65536 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 LRU
-I
更多网络基础与Linux网络配置之一 ifconfig、route、netstat命令详解相关文章请关注PHP中文网!
 How to be invisible online on TikTok
How to be invisible online on TikTok
 Kernelutil.dll error repair method
Kernelutil.dll error repair method
 The difference between injective and surjective
The difference between injective and surjective
 What software is dreamweaver?
What software is dreamweaver?
 How to set cad point style
How to set cad point style
 How to buy and sell Bitcoin on Huobi.com
How to buy and sell Bitcoin on Huobi.com
 How to speed up web pages
How to speed up web pages
 The difference between static web pages and dynamic web pages
The difference between static web pages and dynamic web pages




