
Inheritance and polymorphism are both characteristics of object-oriented programming. Using inheritance, you can create a subclass based on a parent class. This subclass not only has the properties and methods of the parent class, but can also create its own properties and methods. Due to the relationship between subclasses and parent classes, the problems of method rewriting and method overloading arise. There are many problems in the application of method rewriting and method overloading in inheritance and polymorphism. These concepts are easily confused. Mastering the difference between rewriting and overloading is very important for learning to use polymorphic methods to write programs and improve program reliability. Maintainability lays the foundation.
1. Method rewriting (0veriding)
How to define rewriting: In a Java program, the inheritance relationship of a class can produce a subclass. The subclass inherits the parent class. It has all the characteristics of the parent class and inherits the parent class. All methods and variables. Subclasses can define new features. When the subclass needs to modify some methods of the parent class to extend and increase its functionality, program designers often call such an operation method rewriting, also called overwriting or overwriting. Rewriting reflects the superiority of Java. Rewriting is based on inheritance relationships, which makes the language structure richer. In inheritance in Java, subclasses can both hide and access methods of the parent class, and can also override methods inherited from the parent class. Overriding the inherited parent class method in Java is achieved through method rewriting.
The so-called method rewriting means that the method in the subclass has exactly the same return value type, method name, number of parameters, and parameter type as the method inherited from the parent class. In this way, you can achieve overwriting of parent class methods. For example: The following code implements method overriding.
class Person//定义父类
fpublic void print(){//父类中的方法
System.out.println( 父类Person的print方法! );
}
}
class Student extends Person//定义子类继承Person类
{public void print(){//方法的重写
System.out.println( 子类Student的print方法! );
}
}
public class 0verrideExampleO1
{public static void main(String args[])
{Student s=new Student();
S.print();
}
}
For example:
Class Person
{public void print () {
System.out.println( 父类Person的print方法! );
}
}
class Student extends Person
{public void print () {
super.print(://访问父类中被子类覆写过的方法
System.out.println(" 子类Student的print方法!" );
}
}
public class OverrideExample02
{public static void main(String args[])
{Student s=new Student();
S.print();
}
}print method of subclass Student!
If you want to use the super keyword, it does not have to be used after method rewriting,
can also be used explicitly Indicates that a method is inherited from the parent class. Using super
When rewriting a method, you need to follow the following rules:
(1) The parameter list of the parent class method must be completely the same as the parameter list of the method overridden by the subclass, otherwise it cannot be called Rewrite but overload. ..
(2) The return type of the parent class must be the same as the return type of the method overridden by the subclass, otherwise it cannot be called rewriting but overloading. ..
(3) Java stipulates that methods overridden by subclasses cannot have more restrictive access rights than parent class methods. The relationship between access permissions is:
Anyone who has written Java programs knows that methods in the parent class cannot be rewritten under any circumstances. When the access permission modifier of the method in the parent class is private, the method It can only be accessed by its own class, not by external classes, and cannot be overridden by subclasses. If the method defined in the parent class is public and the method in the subclass is defined as private, an error will be reported when the program is run. For example:
class Person
{public void print()(//public访问权限
System.out.println( "父类Person的print方法! ");
}
}
Class Stedent extends Person
{private void print()(//重写方法降低了访问权限,错误
System.out.println( "子类Student的print方法!" );
}
}
(5) During the inheritance process, if a method in the parent class throws an exception, then when overriding the method of the parent class in the subclass, an exception must also be thrown, and the number of exceptions thrown cannot be more than in the parent class. The exception thrown (can be equal to the exception thrown in the parent class). In other words, the overridden method must not throw a new checked exception, or a checked exception that is broader than the one declared by the overridden method. For example, a method of the parent class declares a checked exception IOException. When overriding this method, you cannot throw Exception. You can only throw exceptions of subclasses of IOException, and you can throw unchecked exceptions.
Similarly, if a member variable is created in a subclass and the variable has the same name as a variable in the parent class, it is called variable overriding or attribute overriding. However, few people study this concept because it has little meaning.
三、方法重载(Overloading)
(一) 如何定义重载。方法的重写和重载只有一个字不同,很多初学者认为这两者十分相似,其实不然。方法重载是让类以统一的方式处理不同类型数据的一种手段。调用方法时通过传递给它们的不同个数和类型的参数来决定具体使用哪个方法,这就是多态性。
所谓方法重载是指在一个类中,多个方法的方法名相同,但是参数列表不同。参数列表不同指的是参数个数、参数类型或者参数的顺序不同。方法的重载在实际应用中也会经常用到。不仅是一般的方法,构造方法也可以重载。下面通过一个实例来分析。
重载的定义和使用方法。
Class Person {
{String name;
int age;
void print(){
System.out.println("姓名:" +name+"年龄:" +age);
}
void print(String a,int b){
System.out.println("姓名:" +a+"年龄:"+b);
void print(String a,int b,intC){
System.out.println("姓名:"+a+"年龄:" +b+"ID号:" +c);
}
void print(String a,int b,doubleC){
System.out.println("姓名:"+a+"年龄:" +b+"ID号:"+c);
}
}
public class OverLoadExampleOL
{publicstaticvoidmain(String args[])
{Personpl=newPerson();
p1.nanle="李明";
p1.age=22;
p1.print();
p1.print("王小早",19);
p1.print("金波",18,100325);
p1.print("婉宁",25,110903);
}
}在上面的程序中,可以看到Person类中有多个名为 void print的方法,这就是方法的重载。执行程序,运行结果如下:
姓名:李明年龄:22
姓名:王小早年龄:l9
姓名:金波年龄:18ID号:10 00325
姓名:婉宁年龄:25ID号:110903
在方法重载时,方法之间需要存在一定的联系,因为这样可以提高程序的可读性,一般只重载功能相似的方法重载规则。重载是指我们可以定义一些名称相同的方法,通过定义不同的参数来区分这些方法,然后再调用时,Java虚拟机就会根
据不同的参数列表来选择合适的方法执行。也就是说,当一个重载方法被调用时,Java用参数的类型和.. (或)个数来决定实际调用的重载方法。因此,每个重载方法的参数的类型或个数必须是不同。虽然每个重载方法可以有不同的返回类型,
但返回类型并不足以区分所使用的是哪个方法。当Java调用一个重载方法是,参数与调用参数匹配的方法被执行。在使用重载要注意以下的几点:
1.在使用重载时只能通过不同的参数列表,必须具有不同的参数列表。例如,不同的参数类型,不同的参数个数,不同的参数顺序。当然,同一方法内的几个参数类型必须不一样,例如可以是 fun(int,float),但是不能为 fun(int,int)。
2.不能通过访问权限、返回类型、抛出的异常进行重载。
3.方法的异常类型和数目不会对重载造成影响。..
4.可以有不同的返回类型,只要参数列表不同就可以了。
5.可以有不同的访问修饰符。
6.可以抛出不同的异常。
四、方法重写与方法重载的区别
通过上面例子的分析,我们可以将方法重写和重载的区别总
结成这样一个表格,如下:
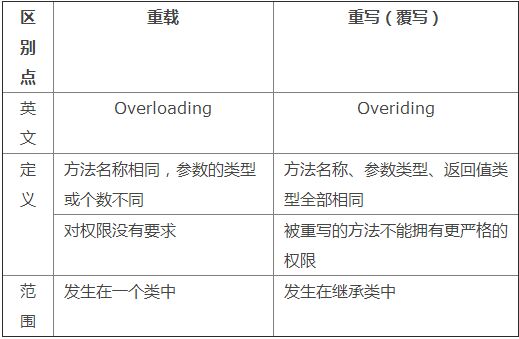
五、结束语
在面向对象程序设计的思想中,类的继承和多态性主要就是体现在子类重写父类的方法。而构造方法的重载作为方法重载的一个典型特例,可以通过重载构造方法来表达对象的多种初始化行为。灵活的运用方法重写与方法重载,不仅能减少编码的工作量,也能大大提高程序的可维护性及可扩展性。用好重写和重载
可以设计一个结构清晰而简洁的类,可以说重写和重载在编写代码过程中的作用非同一般。
 How do I set up WeChat to require my consent when people add me to a group?
How do I set up WeChat to require my consent when people add me to a group?
 Solution to Connection reset
Solution to Connection reset
 What are the servers that are exempt from registration?
What are the servers that are exempt from registration?
 Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
 What is digital currency trading
What is digital currency trading
 Usage of calendar class in java
Usage of calendar class in java
 Server rental charges
Server rental charges
 Registration-free CDN acceleration service
Registration-free CDN acceleration service




