
Generative AI (Gen AI) is reshaping industries with its potential for creativity, problem-solving, and automation. However, developers often face significant challenges when integrating large language models (LLMs) from different providers due to fragmented APIs and configurations. This lack of interoperability complicates workflows, extends development timelines, and hampers the creation of effective Gen AI applications.
To address this, Andrew Ng’s team has introduced AISuite, an open-source Python library that streamlines the integration of LLMs across providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Ollama. AISuite enables developers to switch between models with a simple “provider:model” string (e.g., openai:gpt-4o or anthropic:claude-3-5), eliminating the need for extensive code rewrites. By providing a unified interface, AISuite significantly reduces complexity, accelerates development, and opens new possibilities for building versatile Gen AI applications.
In this article, we will explore how AISuite works, its practical applications, and its effectiveness in addressing the challenges of working with diverse LLMs.
AISuite is an open-source Python library developed by Andrew Ng’s team to simplify the integration and management of large language models (LLMs) from multiple providers. It abstracts the complexities of working with diverse APIs, configurations, and data formats, providing developers with a unified framework to streamline their workflows.
AISuite addresses a critical pain point in the Gen AI ecosystem: the lack of interoperability between LLMs from different providers. By providing a unified interface, it simplifies the development process, saving time and reducing costs. This flexibility allows teams to optimize performance by selecting the best model for specific tasks.
Early benchmarks and community feedback highlight AISuite’s ability to reduce integration time for multi-model applications, improving developer efficiency and productivity. As the Gen AI ecosystem grows, AISuite lowers barriers for experimenting, building, and scaling AI-powered solutions.
Lets get started exploring AISuite by installing necessary dependencies.
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate #for ubuntu venv/Scripts/activate #for windows
pip install aisuite[all] openai python-dotenv
Create a file named .env. This file will store your environment variables, including the OpenAI key.
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-proj-7XyPjkdaG_gDl0_... GROQ_API_KEY=gsk_8NIgj24k2P0J5RwrwoOBW...
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
os.environ['ANTHROPIC_API_KEY'] = getpass('Enter your ANTHROPIC API key: ')
Create an instance of the AISuite client, enabling standardized interaction with multiple LLMs.
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate #for ubuntu venv/Scripts/activate #for windows
User can query the model using AISuite as follows.
pip install aisuite[all] openai python-dotenv
Lets create a chat completion code using OpenAI model.
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-proj-7XyPjkdaG_gDl0_... GROQ_API_KEY=gsk_8NIgj24k2P0J5RwrwoOBW...
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
os.environ['ANTHROPIC_API_KEY'] = getpass('Enter your ANTHROPIC API key: ')
You will get output as follows,
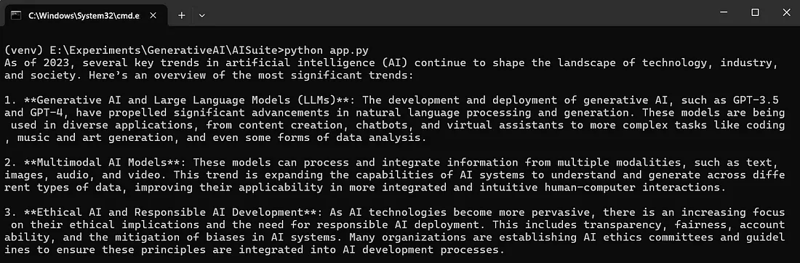
Instead of writing separate code for calling different models, let’s create a generic function to eliminate code repetition and improve efficiency.
client = ai.Client()
Defining the prompt
The prompt syntax closely resembles OpenAI’s structure, incorporating roles and content.
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell a joke in 1 line."}
]
The ask function is a reusable utility designed for sending queries to an AI model. It accepts the following parameters:
Below is the complete code for interacting with the OpenAI model using the generic ask function.
# openai model response = client.chat.completions.create(model="openai:gpt-4o", messages=messages, temperature=0.75) # ollama model response = client.chat.completions.create(model="ollama:llama3.1:8b", messages=messages, temperature=0.75) # anthropic model response = client.chat.completions.create(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022", messages=messages, temperature=0.75) # groq model response = client.chat.completions.create(model="groq:llama-3.2-3b-preview", messages=messages, temperature=0.75) print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Running the code will produce the following output.
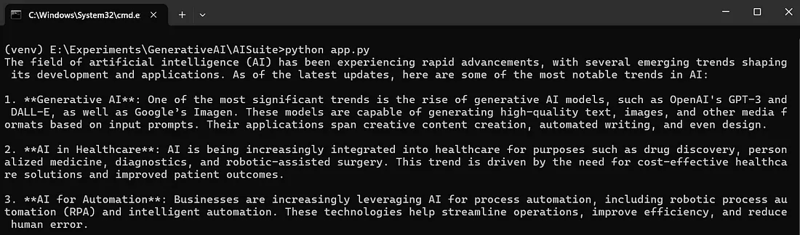
Let’s explore interacting with multiple models using AISuite through the following code.
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
import aisuite as ai
client = ai.Client()
provider = "openai"
model_id = "gpt-4o"
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant"},
{"role": "user", "content": "Provide an overview of the latest trends in AI"},
]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = f"{provider}:{model_id}",
messages = messages,
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
There may be challenges when interacting with providers like Anthropic or Groq. Hopefully, the AISuite team is actively addressing these issues to ensure seamless integration and functionality.
AISuite is a powerful tool for navigating the landscape of large language models. It enables users to leverage the strengths of multiple AI providers while streamlining development and encouraging innovation. With its open-source foundation and intuitive design, AISuite stands out as a cornerstone for modern AI application development.
Thanks for reading this article !!
Thanks Gowri M Bhatt for reviewing the content.
If you enjoyed this article, please click on the heart button ♥ and share to help others find it!
The full source code for this tutorial can be found here,
GitHub - codemaker2015/aisuite-examples : github.com
GitHub - andrewyng/aisuite: Simple, unified interface to multiple Generative AI providers : github.com
The above is the detailed content of AISuite: Simplifying GenAI integration across multiple LLM providers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Today's Toutiao gold coin is equal to 1 yuan
Today's Toutiao gold coin is equal to 1 yuan
 How to configure the path environment variable in java
How to configure the path environment variable in java
 What are the microcontroller programming software?
What are the microcontroller programming software?
 Tutorial on making word document tables
Tutorial on making word document tables
 Cancel WeChat campaign
Cancel WeChat campaign
 How to export excel files from Kingsoft Documents
How to export excel files from Kingsoft Documents
 How to use php web page source code
How to use php web page source code
 How to set path environment variable
How to set path environment variable




