
I recently integrated with the LinkedIn API, and it turned out to be pretty straightforward. The task was to retrieve the user's email address from LinkedIn. To achieve this, I primarily used two endpoints:
https://api.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization
https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/accessToken
Demo
Codebase
To get this working, you’ll need a LinkedIn App, which is easy to set up via the LinkedIn Developer Portal. Once created, your app will provide:
Additionally, you'll need to set up a Redirect URL. This is where LinkedIn sends the authorization code after the user approves your app

Two endpoints, right? But to make it all work, there are at least 10 steps involved. Take a look at the sequence diagram:
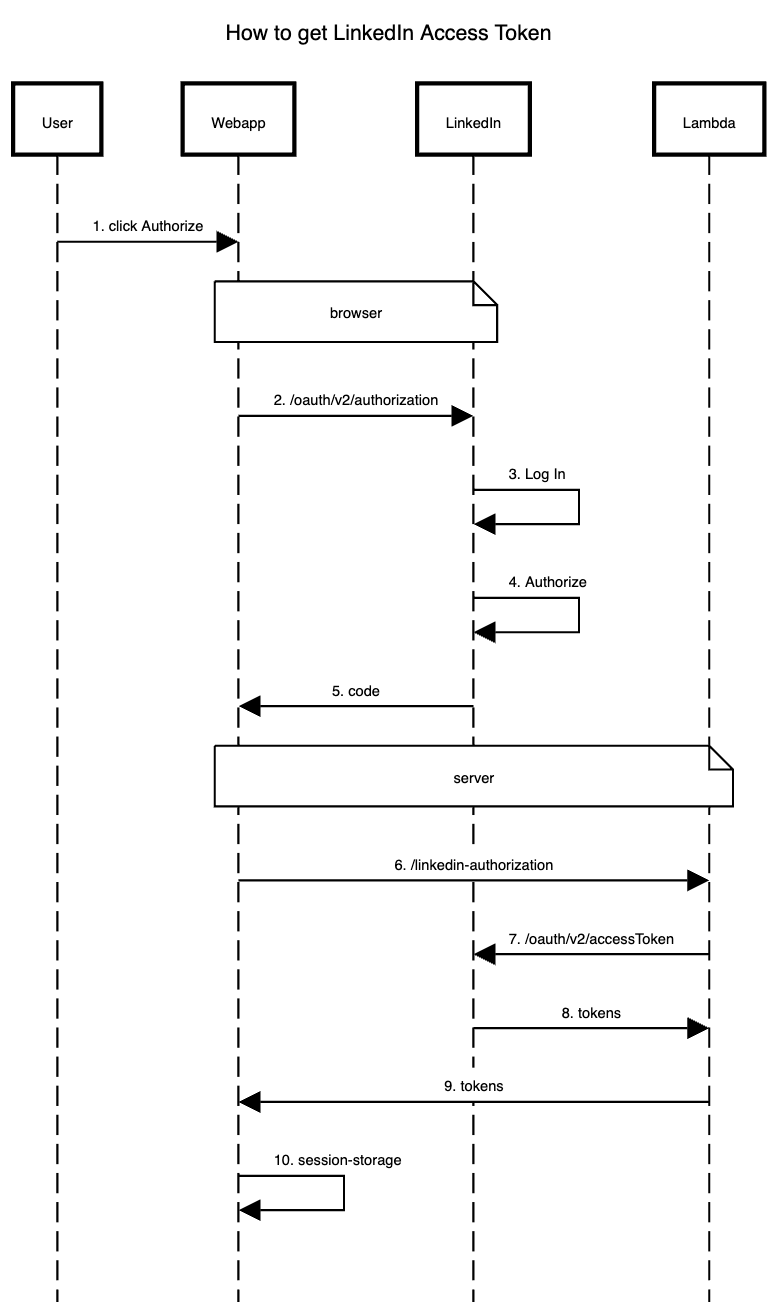

You need to redirect the user to:
https://api.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization?response_type=code&client_id=${CLIENT_ID}&redirect_uri=${REDIRECT_URI}&scope=profile%20email%20openid
Replace CLIENT_ID and REDIRECT_URI with your values defined in the developer portal.

In my case, the final redirect URL looks like this:
https://demo.garciadiazjaime.com/linkedin-api-openid-user-info?code=AQSWHfrKRe6Zvr-fSccBQl2FfpxdkPxx6penQgLAFuNWVXviCb2qmtuCdy9czV-vZIqIczV-4UQNcKuRQk1qMgA3c13CdPpGHxdItcpqMuMmJsksxXYLOohcBF7jaAAqA6nKMq6pXsLH5-itSnyGdnWVIDc1v1ynAzckv-DCOn1gP6lkQf8aWu3CM5E79Zoh8PmHS3_eWT0LymNSM7U
Notice how the code query parameter is passed. This is important because it will be used in the next step when requesting the access token.
The reason for using a Lambda function here is that the next step involves requesting an access token, which requires passing the Client ID and Client Secret. Since these credentials should remain secure, this step needs to be handled in a backend-like environment.
Take a look at the code:
https://api.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization?response_type=code&client_id=${CLIENT_ID}&redirect_uri=${REDIRECT_URI}&scope=profile%20email%20openid
The LinkedIn response for the oauth/v2/accessToken endpoint typically looks like this:
https://demo.garciadiazjaime.com/linkedin-api-openid-user-info?code=AQSWHfrKRe6Zvr-fSccBQl2FfpxdkPxx6penQgLAFuNWVXviCb2qmtuCdy9czV-vZIqIczV-4UQNcKuRQk1qMgA3c13CdPpGHxdItcpqMuMmJsksxXYLOohcBF7jaAAqA6nKMq6pXsLH5-itSnyGdnWVIDc1v1ynAzckv-DCOn1gP6lkQf8aWu3CM5E79Zoh8PmHS3_eWT0LymNSM7U
Notice how id_token is included in the response, and this is a JWT (JSON Web Token). If you decode it, you'll get something like this:
const { code } = JSON.parse(event.body);
const config = {
grant_type: "authorization_code",
code,
client_id: LINKEDIN_CLIENT_ID,
client_secret: LINKEDIN_CLIENT_SECRET,
redirect_uri: LINKEDIN_REDIRECT,
};
const response = await fetch(`https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/accessToken`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
},
body: new URLSearchParams(config),
});
which among other things it outputs:
{
access_token:"...access_token...",
expires_in: 5183999,
scope: "email,openid,profile",
token_type: "Bearer",
id_token:
"eyJ6aXAiOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImtpZCI6ImQ5Mjk2NjhhLWJhYjEtNGM2OS05NTk4LTQzNzMxNDk3MjNmZiIsImFsZyI6IlJTMjU2In0.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL3d3dy5saW5rZWRpbi5jb20vb2F1dGgiLCJhdWQiOiI4NmNtemNrN2k2dG5tOCIsImlhdCI6MTczMTg4MDM1MCwiZXhwIjoxNzMxODgzOTUwLCJzdWIiOiJlbTVqVXhDcEh4IiwibmFtZSI6IkphaW1lIEdhcmNpYSBEaWF6IiwiZ2l2ZW5fbmFtZSI6IkphaW1lIiwiZmFtaWx5X25hbWUiOiJHYXJjaWEgRGlheiIsInBpY3R1cmUiOiJodHRwczovL21lZGlhLmxpY2RuLmNvbS9kbXMvaW1hZ2UvdjIvQzU2MDNBUUhnYWc5TVNUUDNGQS9wcm9maWxlLWRpc3BsYXlwaG90by1zaHJpbmtfMTAwXzEwMC9wcm9maWxlLWRpc3BsYXlwaG90by1zaHJpbmtfMTAwXzEwMC8wLzE2NjA5MzcwNTQ2MTg_ZT0yMTQ3NDgzNjQ3JnY9YmV0YSZ0PXpuRWFMUS1vSVRYVl9LT3B5aFZGcDRfUHVLd0JabGx5VGRjNTc3ZDBoWXciLCJlbWFpbCI6ImdhcmNpYWRpYXpqYWltZUBnbWFpbC5jb20iLCJlbWFpbF92ZXJpZmllZCI6InRydWUiLCJsb2NhbGUiOiJlbl9VUyJ9...",
};
For my use case, the email field is exactly what I needed. Now that you have the access token, you can also use it to make requests to the LinkedIn REST API, like this:
import { jwtDecode } from "jwt-decode";
jwtDecode(jwt);
It'll give you basically the same info as in the JWT token, but now that you have the access token, you can use it to access any of LinkedIn's other endpoints.
Overall, integrating with LinkedIn's RESTful API was pretty straightforward. One thing to keep in mind is that the process is split between the client and server: the client handles redirecting the user to LinkedIn for authentication and authorization, while the server is responsible for interacting with LinkedIn's API and passing the ClientId and ClientSecret which should not be exposed in your client application.
The above is the detailed content of React: LinkedIn Access Token in Steps. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 OuYi exchange usdt price
OuYi exchange usdt price
 What is the difference between ibatis and mybatis
What is the difference between ibatis and mybatis
 How to convert excel to vcf
How to convert excel to vcf
 How to solve the problem of no internet access when the computer is connected to wifi
How to solve the problem of no internet access when the computer is connected to wifi
 How to activate cloud storage service
How to activate cloud storage service
 What are the network file server tools?
What are the network file server tools?
 linear-gradient property
linear-gradient property
 photoshare.db
photoshare.db




