What do the Three Musketeers in docker mean?
The three swordsmen in docker refer to swarm, compose and machine. Compose is a tool used to define and run one or more containers and applications; Machine is a command line tool that simplifies Docker installation; Swarm is a tool provided by the community that natively supports Docker clusters.
The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, docker-1.13.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
The three swordsmen in docker containers are swarm, compose and machine.
Compose
1. Overview
In an actual production environment, an application is often composed of many services , and the best practice of Docker is that a container only runs one process, so running multiple microservices requires running multiple containers. Multiple containers working together require an effective tool to manage them and define how these containers relate to each other. compose came into being.
compose is a tool used to define and run one or more containers (usually multiple) to run and apply. Using compose can simplify the construction of container images and the running of containers.
compose uses YAML files to define relationships between multiple containers. A docker-compose up can run the complete application. Essentially, compose parses the YAML file into the parameters of the docker command, and then calls the corresponding docker command line interface to manage the application in a containerized manner. It starts containers sequentially by resolving dependencies between containers. Dependencies between containers are specified by the links tag in the YAML file.
2. Introduction to compose configuration
Compose is an encapsulation of docker commands, and docker-compose.yml is used by default The file specifies the parameters in each command.
A simple example:
web: build: . ports: - 8080:80 volumes: - . : /code links: - redis redis: image: redis
This YAML file defines two services: Web and Redis. The name of the service is customized by the user. The image that provides the Web service is built from the Dockerfile; the Web service listens to port 80 and maps it to the host's port 8080; the current directory of the host is mounted to the /code directory in the container; the Web server accesses the backend Redis database by linking to the Redis container. . The Redis database service is provided by running the Redis image.
In the docker-compose.yml file, each defined service contains at least one of build or image, and other commands are optional. The build command specifies the directory containing the Dockerfile, which can be a relative directory or an absolute directory.
The "ports" tag in the docker-compose.yml file corresponds to the "-p" option of docker run; the "volumes" tag corresponds to the "-v" option of docker run; the "links" tag corresponds to docker run The "--links" option.
In addition, image is used to specify the image of the service.
Finally, execute the docker-compose up command in the directory where docker-compose.yml is located, and the Web and Redis services will run successfully.
Machine
1. Overview
Docker Machine is a command line tool that simplifies Docker installation. Docker can be installed on the corresponding platform through a simple command line, providing users with flexible functions so that they can run Docker containers on any host. Simply put, a Docker Machine is a combination of a Docker host and a configured Docker client.
Technically speaking, Machine is a framework and is relatively open. For any platform that provides virtual machine services, as long as a driver for the platform is developed under this framework, Docker Machine can be integrated into the platform and perform actions such as creation, deletion, startup, and stop on the platform.
The architecture of Docker Machine is shown in the figure
2. Basic concepts and processes of Machine
Docker Machine first creates a virtual machine and a Docker host on it, and then uses the Docker client to communicate with the Docker host to create an image on the Docker host and start the container.
When using Docker Machine to create a virtual machine, you need to develop the corresponding driver. Currently, the drivers that support this machine include VirtualBox driver, VMware driver and Hyper-V driver under Windows. In addition, Machine also supports the creation of cloud hosts. As long as a driver that conforms to the framework specifications is developed, Docker Machine can support the corresponding platform.
The IP address of the Docker host created by Machine is the IP address of the virtual machine created.
The running process of using Docker Machine and VirtualBox driver to create a local virtual machine and build Docker host is as follows:
Execute the
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox devcommand. This command first creates a CA certificate for communication between Docker client and Docker host. Next, create a VirtualBox virtual machine, configure TLS parameters for communication and configure the network, and finally deploy the Docker operating environment, that is, Docker host.Run the
eval "$(docker-machine env dev)"command in the Docker client to configure the environment variables used for Docker host communication.Use docker related commands to create or start the corresponding container.
Swarm
1. Overview
Swarm is the Docker community Provides tools that natively support Docker clusters. It can convert a system composed of multiple Docker hosts into a single virtual Docker host. Swarm provides two APIs to the outside world. One is the standard Docker API, such as Dokku, Compose, Krane, Flynn, Deis, Jenkins, etc.; the other is Swarm's cluster management API, which is used for cluster management.
The Swarm tool itself is not very mature and is not recommended for use in production environments.
And Google’s open source Kubernetes is currently the most popular orchestration and deployment tool in the container ecosystem.
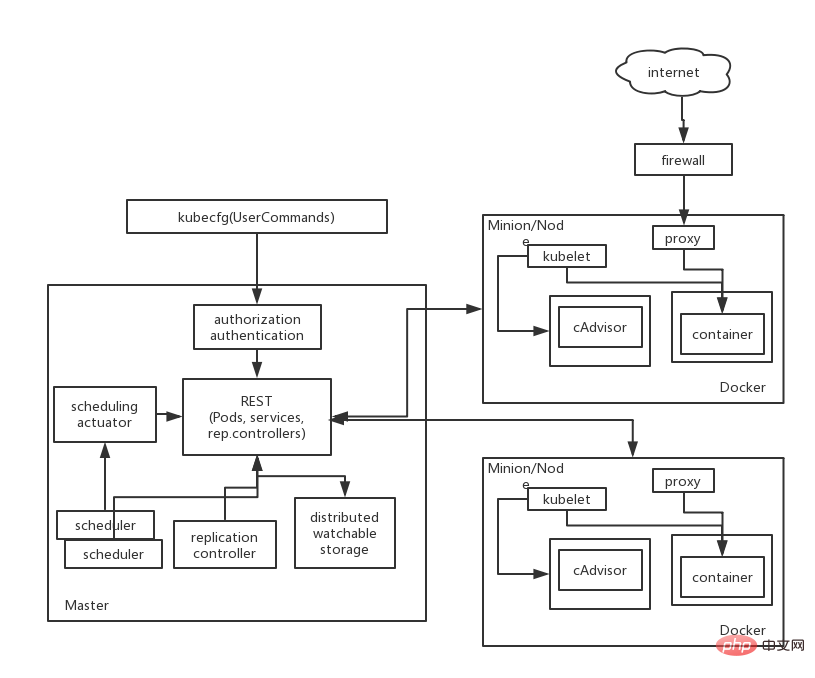
The architecture of Kubernetes is based on a Master server with multiple Minion nodes. I haven’t come into contact with K8s yet. I will summarize it here after I learn more about it.
K8s Architecture Block Diagram

Component explanation:
- Master: Master server, running the management process of kebernetes , including API services, backup controllers and schedulers, etc.
- Minion: The host of Kubelet service and Docker engine. Minion accepts instructions from Master
- Kubelet: Kubernetes node-level manager, running on Minion
- Pod: Multiple A collection of containers, and these containers run on the same Minion. Pod is the smallest management unit of K8s
- Replication Controller: manages the life cycle of Pod
- Service: defines the services and ports that allow the container to be exposed, as well as external agents for communication and interaction
- Kubecfg: Command line interface, interacts with the Master, and requests the deployment and management of application services
Recommended learning: "docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What do the Three Musketeers in docker mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

ArtGPT
AI image generator for creative art from text prompts.

Stock Market GPT
AI powered investment research for smarter decisions

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to set environment variables in PHP environment Description of adding PHP running environment variables
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
How to set environment variables in PHP environment Description of adding PHP running environment variables
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
There are three main ways to set environment variables in PHP: 1. Global configuration through php.ini; 2. Passed through a web server (such as SetEnv of Apache or fastcgi_param of Nginx); 3. Use putenv() function in PHP scripts. Among them, php.ini is suitable for global and infrequently changing configurations, web server configuration is suitable for scenarios that need to be isolated, and putenv() is suitable for temporary variables. Persistence policies include configuration files (such as php.ini or web server configuration), .env files are loaded with dotenv library, and dynamic injection of variables in CI/CD processes. Security management sensitive information should be avoided hard-coded, and it is recommended to use.en
 Creating Production-Ready Docker Environments for PHP
Jul 27, 2025 am 04:32 AM
Creating Production-Ready Docker Environments for PHP
Jul 27, 2025 am 04:32 AM
Using the correct PHP basic image and configuring a secure, performance-optimized Docker environment is the key to achieving production ready. 1. Select php:8.3-fpm-alpine as the basic image to reduce the attack surface and improve performance; 2. Disable dangerous functions through custom php.ini, turn off error display, and enable Opcache and JIT to enhance security and performance; 3. Use Nginx as the reverse proxy to restrict access to sensitive files and correctly forward PHP requests to PHP-FPM; 4. Use multi-stage optimization images to remove development dependencies, and set up non-root users to run containers; 5. Optional Supervisord to manage multiple processes such as cron; 6. Verify that no sensitive information leakage before deployment
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Building an independent PHP task container environment can be implemented through Docker. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Install Docker and DockerCompose as the basis; 2. Create an independent directory to store Dockerfile and crontab files; 3. Write Dockerfile to define the PHPCLI environment and install cron and necessary extensions; 4. Write a crontab file to define timing tasks; 5. Write a docker-compose.yml mount script directory and configure environment variables; 6. Start the container and verify the log. Compared with performing timing tasks in web containers, independent containers have the advantages of resource isolation, pure environment, strong stability, and easy expansion. To ensure logging and error capture
 How to use Kubernetes to keep PHP environment consistent Production and local container configuration standards
Jul 25, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
How to use Kubernetes to keep PHP environment consistent Production and local container configuration standards
Jul 25, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
To solve the problem of inconsistency between PHP environment and production, the core is to use Kubernetes' containerization and orchestration capabilities to achieve environmental consistency. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Build a unified Docker image, including all PHP versions, extensions, dependencies and web server configurations to ensure that the same image is used in development and production; 2. Use Kubernetes' ConfigMap and Secret to manage non-sensitive and sensitive configurations, and achieve flexible switching of different environment configurations through volume mounts or environment variable injection; 3. Ensure application behavior consistency through unified Kubernetes deployment definition files (such as Deployment and Service) and include in version control; 4.
 How to install Docker on CentOS
Sep 23, 2025 am 02:02 AM
How to install Docker on CentOS
Sep 23, 2025 am 02:02 AM
Uninstall the old version of Docker to avoid conflicts, 2. Install yum-utils and add the official Docker repository, 3. Install DockerCE, CLI and containerd, 4. Start and enable Docker services, 5. Run hello-world image to verify that the installation is successful, 6. Optionally configure non-root users to run Docker.
 How does Docker for Windows work?
Aug 29, 2025 am 09:34 AM
How does Docker for Windows work?
Aug 29, 2025 am 09:34 AM
DockerforWindowsusesaLinuxVMorWSL2toruncontainersbecauseWindowslacksnativeLinuxkernelfeatures;1)itautomaticallymanagesalightweightLinuxVM(orusesWSL2)withHyper-VtohosttheDockerdaemonandcontainers;2)theDockerCLIandDesktopinterfaceforwardcommandstotheda
 How to get started with docker
Aug 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
How to get started with docker
Aug 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
Dockerisaplatformforpackaging,shipping,andrunningapplicationsinlightweight,isolatedcontainersthatsharethehostOSkernel,unlikevirtualmachines.2.InstallDockerDesktoponWindowsormacOS,orusethecurlcommandonLinux,thentestwithdocker--versionanddockerrunhello





